Leaf Structure and Function
advertisement

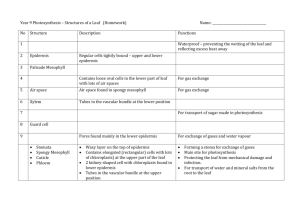
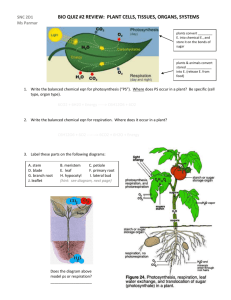
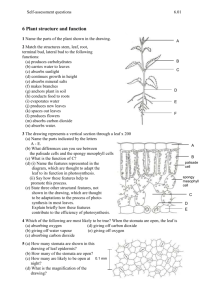
Leaf Structure Function of Leaves To carry out photosynthesis How? They need to absorb carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight; and dispose of the products (glucose and oxygen) once they are made Leaf Structure Blade: Fleshy part of the leaf Petiole: Stem of the leaf Vein: Transports glucose and water; support Midrib: Central rib of the leaf What is a Cross Section? Leaf Cross Section A. A. Cuticle: Cuticle: Function Location Non-cellular outer layer that Outermost surface; layer on waxy the surface of a leaf prevents water loss A B. Upper Upper Epidermis: Epidermis:Function Location Helps protect level the internal tissues fromtop damage; First cellular of the leaf on the part analso the transparent to bottom allow sunlight the leaf part oftoa penetrate leaf B C. Palisade Palisade Mesophyll: Mesophyll:Function Location Found beneath the upper epidermis; Vertically Contain large amounts of chloroplasts; where elongated cells photosynthesis occurs in the leaf C D. Vascular Vascular Bundle: Bundle:Function Location Found within theand mesophyll; in circlesthe in Location of xylem phloem; typically xylem transports water and the phloem crosstransports section glucose D SpongyMesophyll: Mesophyll:Function Location E.E.Spongy beneath mesophyll; typically TheFound air spaces allowthe forPalisade the transport of gases in and very spacious out of the leaf E F. Stomata: Location F. Stomata: Function Found beneath on the lower epidermis on the Allows water and gases to move in and out of the leaf underside of a leaf; appear as small pores/opening F