Exam-1-Test-Bank
advertisement

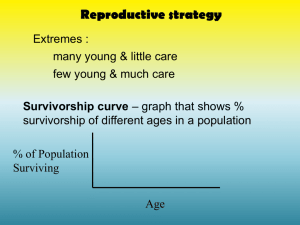
Exam 1 Test Bank: Topic 1: Definition of Ecology 1. The Cary institute definition of ecology is “the scientific study of the processes influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms, the interactions among organisms, and the interactions between organisms and the transformation and flux of energy and matter”. Which of the three components of this definition come from the definitions of: a. Ernst Haeckel b. Herbert Andrewartha and Charles Birch c. Eugene Odum Topic 2: Evolution 1. What two types of experiments are used to establish selection for locally adapted traits? 2. Consider a common garden experiment involving seeds of a species of orchid from mountain top and low elevation populations. On the mountain tops the orchid has a thicker stalk an a shorter overall stature; in the low elevation population, the stalks are thinner and grow taller. a. What experimental outcome would indicate that these populations had been selected for locally adapted traits? b. What experimental outcome would indicate that the observed differences between these populations was due to phenotypic plasticity? 3. Define phenotypic plasticity. 4. Define Convergent Evolution. 5. Define Parallel evolution. 6. What is the difference between allopatric and sympatric speciation? Topic 3: Measuring populations 1. What is the difference between a unitary and a modular organism? 2. What is the difference between a genet and a ramet? 3. What is the difference between strip transect sampling and distance sampling? 4. What is the goal of stratification in sampling design? 5. What are the 5 assumptions of mark-recapture sampling? 6. Consider a mark-recapture study to estimate the size of a fish population in a lake. On the first occasion 100 fish were captured and marked. On the second occasion, 200 fish were captured and 20 of these were marked individuals that had been recaptured. What is the estimate of the population size in the lake? Topic 4: Resources and Conditions 1. What is the difference between a resource and a condition? 2. Provide an example of something that may be both a condition and a resource? 3. What is the difference between a predator and a grazer? 4. What is the difference between a predator and a parasite? 5. What is the difference between a parasite and a grazer? 6. What is the definition of a niche given by G.E. Hutchinson? 7. What is the fundamental difference between the niche concept of Grinell and Elton and that of Hutchinson? Topic 5: Population Growth 1. What are the four processes that contribute to population growth and decline? 2. What is the difference between a static and a cohort life table? 3. Define the net reproductive rate (in words), 4. Give the equation for the net reproductive rate and define all terms. 5. What important assumption must be made in order to interpret a static life table? 6. In the panels below, label the x and y axes and draw the survivorship patterns characteristic of a Type I, Type II, and Type III survivorship. 7. Which of the 3 types of survivorship functions characterizes the setting in which the risk of mortality increases with age? 8. Which of the 3 types of survivorship functions characterizes the setting in which the risk of mortality is constant for all ages? 9. Which of the 3 types of survivorship functions characterizes the setting in which the risk of mortality decreases with age? 10. Define the cohort generation time (in words)? 11. What is the relationship between the net reproductive rate and the intrinsic growth rate for species with overlapping generations? 12. Define reproductive value 13. Describe why reproductive value is often low in older individuals 14. Describe why reproductive value is often low in young individuals 15. For the basic exponential growth model, how does extinction probability scale with : a. Initial population size? b. Generation time? c. Environmental variability? Topic 6: Intraspecific competition 1. What is the difference between exploitation and interference competition? 2. What is the difference between scramble and contest competition? 3. Which type of competition (scramble or contest) results in the greater variance in resource allocation among individuals? 4. Define carrying capacity. 5. In the logistic model of population growth, what is the relationship between the per capita contribution to population growth and population size? 6. What type of intraspecific competition is best characterized by the logistic model? 7. State the equation for logistic population growth and define all terms. 8. If density limits per capita growth (as in the logistic model), at what population size does the population grow fastest? 9. If density limits per capita growth (as in the logistic model), at what population size does the population have the highest recruitment? 10. In the space below, draw the expected relationship between recruitment (yaxis) and population size (x-axis) for a population that experiences intraspecific competition for resources. 11. Define the Allee effect. 12. Give two reasons why population growth rate may be lower when density is low. 13. Give two reasons why a population may exhibit an Allee effect. Topic 7: Life History Evolution 1. What is the difference between semelparous and iteroparous reproductive strategies? 2. What traits are commonly associated with r-selected species? 3. What traits are commonly associated with K-selected species? 4. In many settings, the observed clutch size is lower than that expected by Lack optimum. What characteristic can explain why the optimal clutch size would be lower than the Lack optimum? 5. In the space below, draw the expected relationship between recruitment and clutch size. a. 6. Following the re-introduction of wolves to Yellowstone, the population of elk declined. As a consequence, elk herbivory on adult willow plants declined significantly. Should the resulting decrease in the risk of adult willow mortality select for greater or smaller allocation to reproductive effort? 7. Consider two populations of frog – population A is in a pond where pollution reduces egg viability and results in high tadpole mortality, population B is in a pristine pond. In which population would you expect: a. Greater allocation of resources to reproductive effort? b. Faster maturation of adults? 8. What were two observed changes in the life history characteristics of fishes that were heavily harvested. 9. Buckling et al. showed that drug treatment of malaria resulted in a change in the relative production of blood-stage and transmission stage malaria parasites – what was that change? Explain why this change is predicted. Topic 8: Dispersal 1. What is the difference between passive and active dispersal? 2. What is the difference between potential and realized dispersal? Topic 9: Metapopulations 1. What is the difference between environmental and demographic variability? 2. What are the four conditions necessary for a metapopulation, according to Hanski’s definition? 3. In the space below, draw the relationship between the colonization of patches and the proportion of occupied patches according to the Levins metapopulation model. 4. In the space below, draw the relationship between the extinction of patches and the proportion of occupied patches according to the Levins metapopulation model. 5. According to the Levins model, what is the necessary condition for the proportion of occupied patches in a metapopulation to be greater than 0? 6. What are the 4 assumptions of the Levins metapopulation model? 7. Which type of variability (environmental or demographic) is likely to result in synchronous extinction probability in patches in a metapopulation? 8. Which type of variability (environmental or demographic) is likely to result in asynchronous extinction probability in patches in a metapopulation? Case Studies and Homework: Questions from the case studies that we discussed including the associated papers, are all fair game.