Stability in Bonding
advertisement

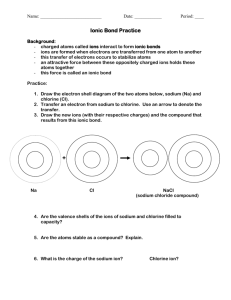
Stability in Bonding Combined Elements Some of the matter around you is in the form of uncombined elements such as copper, sulfur, and oxygen. When the conditions are right, these and other chemicals will combine to form compounds. The green coating on the Statue of Liberty is an example of these chemical changes. This new compound is copper sulfate. (copper, sulfur, and oxygen combined) These new compounds have their own unique properties. Sodium chloride (table salt) is a compound made from sodium (a shiny, soft, silver metal) and chlorine ( a poisonous greenish-yellow gas). Formulas A chemical formula tells what elements a compound contains and the exact number of the atoms of each element in a unit of the compound. Example: NaCl stands for Sodium Chloride and tells you that there is one atom of sodium and one atom of chlorine in each unit. H2O shows that there are two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen in each unit or molecule of water. Some Familiar Compounds Familiar Name Chemical Name Formula Sand Silicon dioxide SiO2 Cane sugar Sucrose C12 H22 O11 Lime Calcium oxide CaO Vinegar Acetic acid HC2H3O2 Stomach acid Hydrochloric acid HCl Atomic Stability Atoms combine when the compound formed is more stable than the separate atoms. However, some of the atoms are stable by themselves. The Unique Noble Gases To understand the stability of the noble gases, you must look at electron dot diagrams. Electron dot diagrams show only the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom. Ex. Elements in Group 1 have one electron in the outer energy level, Group 2 has two, Group 13 has 3, Group 14 has 4, and so on to Group 18 which has 8. An atom is chemically stable when the outer energy level is complete. The noble gases are stable because they each have a complete outer energy level. Energy Levels and Other Elements Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17 do not have a full outer energy level, so they are more stable when they are found in compounds. For example, hydrogen only has one electron in its outer energy level, which means its outer energy level is not complete. This is why there are so many hydrogen-containing compounds found on earth. Outer Energy LevelsGetting Their Fill Atoms with partially stable outer energy levels can lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a stable outer energy level. They do this by combining with other elements that have partially complete outer energy levels. This helps them both become stable. Example: sodium and chlorine Stability is Reached Sodium has only one electron in its outer energy level, which is lost to combine with chlorine in sodium chloride. Now we look to next level down in sodium and see that it is full, so now both elements have a complete energy level and both are now stable. When atoms gain, lose, or share electrons, an attraction forms between the atoms, pulling them together to form a compound. This attraction is called a chemical bond. A chemical bond is the force that holds atoms together in a compound.