Vitamins and Minerals
advertisement

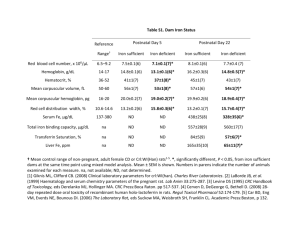
Sodium: Functions 0 Fluid and electrolyte balance. 0 Associated with blood pressure and pH balance in the body. 0 Required for nerve impulse transmission. 0 Assists in the transport of certain nutrients into body cells. Recommended intake: 0 Need at least approximately 200mg/day (varies by source and country) is required 0 Upper limit is 2,300mg/day Sources of Sodium: Processed foods are surprisingly high in sodium What are the consequences of over consumption of Sodium? 0 Hypernatremia is abnormally high blood sodium concentration 0 Can happen to patients with congestive heart failure or kidney disease 0 Results in high blood volume, edema, and high blood pressure 0 There is a relationship between the consumption of high sodium diets and hypertension. Hypertension: 0 Hypertension is a chronic condition 0 0 0 0 characterized by high blood pressure. Optimal blood pressure is less than 120/80 mm Hg. Blood pressure greater than or equal to 140/90 mm Hg is considered hypertension. This disease is considered “the silent killer” because there are initially no symptoms. A person could have high blood pressure for years and not know it. Hypertension increases a person’s risk for many chronic diseases. Chloride: Functions 0 Helps maintain fluid balance 0 Aids the immune system 0 Makes up part of hydrochloric acid, which is the acid in your stomach that aids in digestion Recommended intake: 0 Minimum recommendation is 750mg/day Sources of Chloride: 0 Chloride can be found attached to sodium, therefore salt is our main source. What are the consequences of overconsumption of Chloride? 0 May lead to hypertension in salt-sensitive patients What are the consequences of under consumption of Chloride? 0 Deficiencies are rare but can occur in people with eating disorders Potassium: Functions 0 Potassium is involved in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance 0 It is very important in muscle contractions and transmission of nerve impulses 0 It also helps regulate blood pressure Recommended intake: 0 2,000 to 4,000 mg/day Sources of Potassium: Fresh fruit and vegetables and whole grains are good sources of potassium. As food is processed, the sodium content increases while the potassium content decreases. What are the consequences of overconsumption of Potassium? 0 Hyperkalemia is high blood potassium level 0 This can occur in patients with kidney disease 0 The inability to excrete potassium can lead to Hyperkalemia. High blood potassium can alter normal heart rhythm resulting in a heart attack 0 People with normal kidney function seldom develop this condition Calcium: Functions 0 The majority of calcium can be found in bones and teeth 0 The one percent of calcium in the blood is responsible for helping muscles contract (like the heart muscle), assisting with enzyme activity, transmission of nerve impulses, and maintaining healthy blood pressure. 0 Serum calcium levels are so important that the body has an orchestrated hormonal system that maintains this balance in a very narrow range. Recommended intake: 0 values vary from 1,000 mg to 1,300 mg per day. Sources of Calcium: Dairy products and green leafy vegetables are good sources of calcium. What are the consequences of overconsumption of Calcium? 0 Too much calcium in the form of supplements can upset mineral balance, may cause constipation and lead to kidney stones What are the consequences of under consumption of Calcium? 0 Associated with kidney disease and vitamin D deficiency. 0 Osteoporosis is a condition that leads to weakened and brittle bones. Phosphorus: Functions 0 Phosphorus is a major component in bone 0 It can be found in the phospholipid bi-layer of cell membranes 0 It is a component of ATP, RNA and DNA Recommended intake: 0 700 mg/day. Sources of Phosphorus: Protein-containing foods such as milk, meats, and eggs are high in phosphorus as well as cereals, nuts and fish It is also used as a food additive in processed foods Phosphoric acid is used to acidify dark colas. What are the consequences of under consumption of Phosphorus? 0 Because phosphorus is so widely distributed in foods, deficiencies are rare in healthy adults Magnesium: 0 A large portion of magnesium can be found in the bones and is required to maintain healthy bones due to its influence on calcium and vitamin D. Functions 0 Magnesium is a part of bone structure 0 It aids in the activation in over 300 enzymatic reactions 0 It is required for the production of ATP, DNA, and proteins 0 It plays a role in regulating blood pressure Sources of Magnesium: 0 It is found in a variety of foods such as green leafy vegetables, whole grains, seeds, nuts, seafood, beans, and some dairy products. What are the consequences of overconsumption of Magnesium? 0 There are no known toxicities from magnesium in food, however supplements like Milk of Magnesia can cause diarrhea, nausea, cramps and dehydration What are the consequences of under consumption of Magnesium? 0 Because magnesium is found in so many foods, deficiencies are rare except for in people who abuse alcohol and those with certain medical condition. Sulfur: 0 Sulfur is found in proteins and it is used as a food additive. If you have ever eaten dried fruit, you will find sulfur on the ingredient label as sulfur dioxide. It helps prevent foods from oxidizing. In the body, sulfur aids in the detoxification processes of the liver and protein synthesis. There are no known toxicities or deficiencies. Iron: Functions 0 Iron is a component of the hemoglobin and myoglobin molecules. Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body while myoglobin carries oxygen in muscle cells. 0 In plays an important role in the energy production pathways Recommended intake: 0 RDA ranges from 8 mg/day for adult men to 27 mg/day for pregnant women. Sources of Iron: 0 Meat, poultry, fish, clams, oysters, enriched cereals and breads 0 Iron is available in two forms: 0 Heme iron 0 Non-Heme iron Sources of Iron: 0 Heme iron is iron that is available in meat. It is easily absorbed by the body. 0 Non-Heme iron is the iron found in plant tissues and enriched cereals. This video explains a little about iron deficiency anemia and rich food sources of iron: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFeCIsJEoM8&feature=fvwrel Many people find out that they may be iron deficient when they try to give blood. The American Red Cross has an excellent, and colorful list of foods that are rich sources of iron: http://www.redcrossblood.org/learn-about-blood/health-andwellness/iron-rich-foods What are the consequences of overconsumption of Iron? 0 You will find this statement on all iron containing products. 0 “Accidental overdose of iron-containing products is a leading cause of fatal poisoning in children under 6. Keep this product out of reach of children. In case of accidental overdose, call a doctor or poison control center immediately.” 0 Iron poisoning can cause shock and liver failure. One large single dose or moderate doses taken over a period of time can cause toxicity. 0 Our body regulates iron by increasing or decreasing absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). Iron supplements can overcome this compensatory mechanism. 0 Symptoms of iron toxicity include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness and confusion. 0 There is a condition called hemochromatosis, where excess accumulation of iron in the body occurs due to increased absorption of iron through the GI tract. The best treatment for this condition is frequent blood transfusions. What are the consequences of under consumption of Iron? 0 Iron deficiency is the most common nutrient deficiency in the world. 0 The most vulnerable people include infants, young children, preadolescent girls, premenopausal women, and pregnant women. Iron deficiency anemia 0 If iron deficiency is not treated, iron deficiency anemia can develop. Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by small, pale red blood cells that cannot deliver adequate oxygen to the cells. 0 There is a long list of symptoms associated with iron deficiency anemia and you can view this list here: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/irondeficiency-anemia/DS00323/DSECTION=symptoms Who is at risk for iron deficiency anemia? The National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute describes the populations who are most at risk: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/ida/ida_whoisatrisk.html Remember that the body regulates iron levels by increasing or decreasing absorption. There are many factors in the diet and in the body that enhance and inhibit iron absorption. Enhancers: 0 Iron absorption increases with increased need in the body 0 There is a factor called MFP which is found in meat, fish, and poultry that enhances iron absorption 0 Eating a vitamin C rich food along with an iron rich food increases iron absorption 0 Hydrochloric acid in the stomach helps the absorption of iron. 0 Cooking in cast iron cookware increases the iron content of food. It is not the best absorbed, but every little bit counts. Inhibitors: 0 Phytates, a compound found in legumes, rice and whole grains that inhibit absorption. 0 Calcium supplements taken along with iron inhibits absorption 0 Soybeans can inhibit iron absorption 0 Tea and coffee contain tannins and it is this compound that inhibits absorption Those are the dietary factors that influence iron absorption. This table indicates circumstances that improve and diminish iron status. Zinc: Functions 0 Zinc is involved in the function of at least 300 enzyme systems 0 It is involved in the immune system 0 It aids in the growth and repair of body tissues Recommended Intake 0 RDA is 8 mg/day for women, 11 mg/day for men. Sources of Zinc: 0 Red meats, whole grains, enriched grains and cereals 0 Like iron, zinc is better absorbed from animal sources than from grain. This is mainly due to the phytates found in grains. 0 Oysters - contain the most zinc than any other food (source: http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/) What are the consequences of overconsumption of Zinc? 0 Toxicity can occur from using zinc supplements. Symptoms may include intestinal pain, cramps, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. 0 Speaking of supplements, does the use of zinc lozenges (such as Zycam) have an effect on the common cold? Go to this website and scroll down to disease and common cold and you can read about current research findings: http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/infocenter/minerals/zinc/ 0 Too much zinc can interfere with copper absorption. What are the consequences of under consumption of Zinc? 0 Deficiencies are uncommon in the US 0 Symptoms are growth retardation, diarrhea, delayed sexual maturation, poor immune function 0 Phytates and fiber strongly inhibit zinc absorption. Iodine: Functions 0 Iodine is necessary for the manufacturing of thyroid hormones 0 Thyroid hormones regulate body temperature and resting metabolic rate Sources of Iodine 0 Iodized salt, seafood, plants grown near the sea, dairy products What are the consequences of overconsumption of Iodine? 0 Blocks synthesis of thyroid hormones 0 Thyroid tries to make more hormones 0 Results in goiter – enlarged thyroid What are the consequences of under consumption of Iodine? 0 Iodine deficiency isn’t very common in the US thanks to the 0 0 0 0 iodization of salt. Iodine deficiency results in hypothyroidism and goiter. This website at the Mayo Clinic provides a definition of goiter: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/goiter/DS00217. The picture to the right depicts a woman with a goiter. Cretinism can result in mental retardation during embryonic development if the mother suffers from iodine deficiency. This is a very informative video from Mort Satin, Technical Director of the Salt Institute on the history of Iodized salt: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9dMHVSWRuU 0. Copper: Functions 0 Copper is necessary for the function of many enzyme systems. 0 It is required for iron transport Recommended Intake 0 RDA for adults is 900 mg/day. Sources of Copper 0 Copper is found in a variety of foods What are the consequences of overconsumption of Copper? 0 Copper toxicity is not very common but is seen in people with Wilson’s disease 0 Wilson’s disease is a genetic disorder that prevents the body from getting rid of excess copper 0 To learn more about Wilson’s disease click on this website: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/wilsons-disease/DS00411 What are the consequences of under consumption of Copper? 0 Because copper is available in a variety of foods, deficiency is rare. Fluoride: Functions 0 Supports the development and maintenance of teeth and bones 0 Protects teeth from cavities Recommended Intake 0 The adequate intake is 3-4 mg/day for adults Sources of Copper 0 The most common source of fluoride is fluoridated water What are the consequences of overconsumption of Fluoride? 0 Fluorosis (excess fluoride) creates porous tooth enamel and the teeth become stained and pitted. See the picture below. What are the consequences of under consumption of Fluoride? 0 Dental caries (cavities) Chromium: Functions 0 Chromium assists in the action of insulin, aiding glucose uptake in cells and normalizing blood sugar Sources of Chromium 0 Mushrooms, eggs, dried beans, prunes, dark chocolate, nuts, whole grains-basically it is widely distributed. What are the consequences of overconsumption of Chromium? 0 There are few side effects of chromium toxicity. 0 Chromium supplementation is on the rise due to interest related to weight loss, glucose control and lipid metabolism. The Office of Dietary Supplements from the National Institute of Health reviews the latest research on chromium and these three areas. Click on this website http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/chromium/ and scroll down to “what are the current issues and controversies.” What are the consequences of under consumption of Chromium? 0 People who are deficient in chromium may have glucose intolerance. Glucose tolerance is not improved in people who have diabetes and are not deficient in chromium.