Cardiovascular System
advertisement
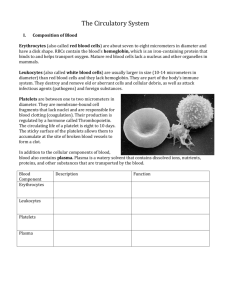
Cardiovascular System Aka: The Circulatory System What does it do? • • • • Moves the blood Protects the body Transports nutrients Removes metabolic waste • Regulates body temperature Structure • Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood Blood Blood is made of… • Erythrocytes (RBC) • Leukocytes (WBC) • Platelets • Plasma Differentiated Blood Cells Erythrocytes • Red Blood Cells (RBC) • Transport Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide • Flattened Doughnuts with depressed center for increased surface • Flexible to get through vessels • No nucleus – last 120 days broken down in spleen Leukocytes • White Blood Cells (WBC) • Protects body from foreign microbes and toxins • Found in blood stream and some tissue • Last 18-36 days • Three types Types of Leukocytes • Lymphocytes: Immune function • Granulocytes: Destroy bacteria, viruses, parasites • Macrophages: Break down old blood cells and foreign matter like dust and asbestos Platelets • Aka: Thrombocytes • Clot blood • Release coagulating chemicals • No nucleus • Fragments of Megakaryocytes • Stimulate Immune System and Fight Infections Plasma • Clear liquid protein and salt part of the blood • 55% of our blood volume • 95% of plasma is H2O • Contains: nutrients, clotting factor, hormones, antibodies, vitamins, lipids, sugars, other proteins, metabolic waste Blood Formation - Hematopoiesis • Bone Marrow produces red blood cells, most white blood cells and platelets • All blood cells originate from stem cells • Production is based on body need such as infection or bleeding The Heart - Structure • Four cavities that fill with blood • Two are Atria (Upper “Round” Half) • Two are Ventricles (Lower “pointed” Half) • Points to left side of chest at the bottom • Size of fist • Pumps 4300 gallons / day Four Steps of Circulation • Step 1: From right side of heart to lungs to collect O2 turning blood bright red and CO2 leaves the capillaries through diffusion. • Step 2: Oxygenated blood returns to the left side of the heart. (Pulmonary Circulation) • Step 3: Blood is pumped to all parts of the body distributing O2 and nutrients • Step 4: Blood returns to the right side of the heart a reddish-blue color to be oxygenated again (Systemic Circulation) How blood circulates…. • Closed system of blood vessels • Four chambers of the heart • Review the steps from the previous slide Heart - Function • Connects to Aorta at the top. Main artery carrying blood away • Pulmonary Artery connects heart to lungs • Two largest veins = Carry blood into heart are superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. Heart - Function • Cardiac Muscle • Contracts 70-80 times per minute • Nerves connected to the heart regulate speed of muscle contraction Blood Vessels - Structure • Three Types: 1. Arteries - thick and flexible due to forceful bloodflow 2. Veins- appear blue, thinner walls than arteries, less forceful flow 3. Capillaries – tiniest vessels, connect arteries and veins. Very thin walls Blood Vessel - Function • Arteries: Carry oxygenated blood from heart to tissues. Large to small: Arteries to Arterioles to capillaries • Veins: Carry deoxygenated blood to heart. Small to large: Capillaries to Venuoles to Veins • Capillaries: gas exchange and absorb metabolic waste Pulse • Rhythmic contractions of arteries can be felt through the skin. • Keeps pace with heart beat. • A way to measure vital health statistics Blood Pressure • The force of blood pushing against artery walls • Strongest when heart contracts (systolic or the higher number) • Weakest when heart relaxes (diastolic or the low number) • 120/80 is considered normal BP http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E 5huVSebZpM • http://depts.washington.edu/learncpr/video demo/two-step-cpr.html