Chapter 4
advertisement

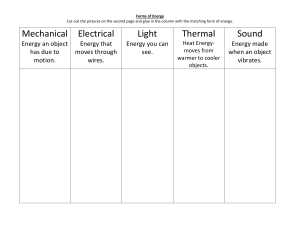
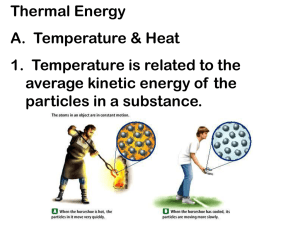
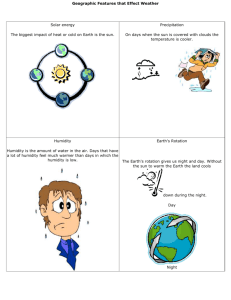
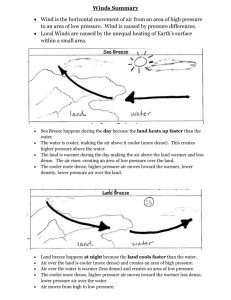
4.1- Temperature depends on particle movement. • 104- The kinetic theory of matter helps explain the different states of matter- solid, liquid, and gas. All particles in matter have kinetic energy. • 105- When kinetic energy in matter increases the temperature will increase. • 106- They have different numbers of degrees between the freezing and boiling points. They are similar in that they both measure temperature in terms of degrees. • 107- A thermometer works by the liquid expanding or contracting by a consistent amount due to a change in temperature. • 108- Objects expand when their temperature increases because the particles move faster and move apart from each other. 4.2- Energy flows from warmer to cooler objects. • 110- Heat is the flow of energy from warmer to cooler objects. • 111- Heat transfers from warmer to cooler objects. • 111- As heat transfers energy, the thermal energy of the warmer object decreases, and the thermal energy of the cooler object increases. • 112- Heat is measured in calories or joules. • 113- The greater the specific heat, the more energy is required to raise that substance’s temperature. • 114- The more mass that an object has, the more thermal energy it has. 4.3- The transfer of energy as heat can be controlled • 117- Conductors easily transfer energy, but insulators do not. Conductors often have low specific heats, and insulators often have high specific heats. • 118- The air is more dense (2) where the air is cool and less dense (1) where the air is warmer. • 119- Radiation transfers energy when electromagnetic waves strike an object, the waves transfer energy to the object. • 120- In both the hollow space in a polar bear’s hair and the empty space in a vacuum flask they both slow down the transfer of energy through conduction. In the hair, air is an insulator; in the vacuum flask, the empty space is the insulator. • 121- Insulation keeps a building warm by slowing the transfer of energy from the building to the cooler outside air.