Poetic Devices
advertisement

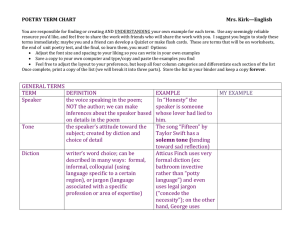
Poetic Devices Poetry • One of the three major genres (types) of literature; Difficult to define; Language being used in a special way; Art of playing with words and emotions Author’s Purpose • A reason for creating a particular work ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ To entertain To inform or explain To express an opinion To persuade 1. Figurative Language • Writing or speech which is not meant to be taken literally (word for word) • Examples: metaphor, simile, hyperbole, personification 2. Metaphor • A figure of speech which makes a comparison of two unlike things; saying something IS something else • Examples: Education IS a treasure, rich with opportunity 3. Simile • A figure of speech which makes a comparison of two unlike things AND uses the words “like” or “as” • Examples: My puppy is like a hairy hurricane, unpredictable and destructive. The Lighthouse The light house, the guardian angel of the night She shines her light for all the lost sailors passing by Her beam bright as the sun, flashing through the night sky The lighthouse, a soldier during the storms Standing tall, unafraid of the chaos Her light piercing through the storm like sharp knives The light house the night owl of the day Sleeping and cozzed away until the night Her beam off as silent as a deer not wanting to be found By: Katherine Sessor 4. Hyperbole • A figure of speech which uses exaggeration for effect • Examples: I have told you a million times not to…; I have a ton of homework. My Dog His bark breaks the sound barrier His nose is as cold as an ice box. A wag of his tail causes hurricanes His jumping causes falling rocks. He eats a mountain of dog food And drinks a water fall dry. But though he breaks the bank He’s the apple of my eye. 5. Personification • A figure of speech which gives human qualities, feelings, actions or characteristics to non-human things • Example: The leaves are dancing in the wind. Dinnertime Chorus The teapot sang as the water boiled The ice cubes cackled in their glass the teacups chattered to one another. While the chairs were passing gas The gravy gurgled merrily As the oil danced in a pan. Oh my dinnertime chorus What a lovely, lovely clan! 6. Imagery • Consists of words/ phrases that appeal to a reader’s five senses; Sensory details help readers imagine how things look, feel, smell, sound and taste 7. Alliteration • Repetition of initial consonant sounds: Used to create a rhythmic effect • Examples: Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers 8. Assonance • Repetition of vowel (a, e, i, o, u) sounds in the middle of words • Examples: moan, groan or spoon, moon An excerpt from “Bells” by Edgar Allan Poe: From the second stanza: Hear the mellow wedding bells, Golden bells! What a world of happiness their harmony foretells! Through the balmy air of night How they ring out their delight! From the molten-golden notes, And in tune, What a liquid ditty floats To the turtle-dove that listens, while she gloats 9. Onomatopoeia • Words that sound like their meaning; Use of words to imitate sounds • Examples: crack, snap, roar, sizzle Crack an Egg Crack an egg. Stir the butter. Break the yolk. Make it flutter. Stoke the heat. Hear it sizzle. Shake the salt, just a drizzle. Flip it over, just like that. Press it down. Squeeze it flat. Pop the toast. Spread jam thin. Say the word. Breakfast's in . 10. Rhyme • Repetition of ending sounds (at the end of words); Used to create a musical effect 11. Rhyme Scheme • A regular pattern of rhyming words in a poem; Lower case letters are used to indicate the rhyme scheme 12. Meter • A poem’s rhythmical pattern, determined by the number and types of stresses, or beats in a line • ....1................... 2......................3................4................... 5 Shall.I..|..com.PARE..|..thee.TO..|..a.SUM..|..mer’s DAY? 13. Stanza • A group of lines in a poem (such as a paragraph in an essay) 14. Repetition • The use (more than once) of any element of language (sounds, words, a phrase, a line, etc.) What Are Little Boys Made Of? What are little boys made of? What are little boys made of? Frogs and snails and puppy-dogs' tails, And that are little boys made of. What are little girls made of? What are little girls made of? Sugar and spice and all things nice, And that are little girls made of. 15. Refrain • A regularly repeated line or group of lines in a poem Assignment Using the song lyrics that you chose or “O Captain! My Captain!” on page. 780: • One paragraph written response • RACER strategy • Prompt: What poetic devices are used in your lyrics? • RACER Strategy • R- Restate the question • A- Answer the question • C- Cite examples from the story • E- Explain those examples (in your own words) • R-restate the question AGAIN