12-SNC2D-ScientificNotationSignftDigits
advertisement

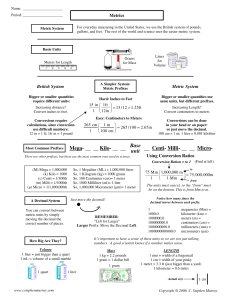
SNC2D Physics Unit Name: _____________________________ SCIENTIFIC NOTATION Scientists often have to work with very large or very small numbers. We tend to use a simpler form of these numbers called: scientific notation. In scientific notation, all numbers are written in the form: 𝑎 × 10𝑛 In this form, a can be greater than or equal to 1 but less than 10 and b can be any value. For large numbers, move the decimal place to the left. The number of times you move the decimal point to the left will be equal to the exponent on the base 10. o Example: 1500 (the exponent will be +3) 1.5 x 103 For small numbers, move the decimal place to the right. Note, the exponent on the base is negative. o Example: 0.0505 (the exponent will be -2) 5.05 x 10-2 On a scientific calculator, enter using the following sequence: 5 . 0 5 EXP or EE +/- 2 Practice converting the numbers below from standard form into scientific notation 8,200,000 = ______________________ 50,880,000,000,000 = ______________________ 0.00012 = ________________________ 0.00000000458 = _________________________ SNC2D Physics Unit Name: _____________________________ UNIT CONVERSIONS FOR METRIC SYSTEM Metric system: the system of units used by most scientists. Also known as System International (SI) units. In the metric system, different units for the same quantity are related to one another by prefixes. Each prefix represents a multiple of 10. The table at right summarizes common metric prefixes. Prefix Symbol Meaning kilo- k 103 = 1,000 hecto- h 102 = 100 Base unit - 100 = 1 deci- d 10-1 = 1/10 centi- c 10-2 = 1/100 milli- m 10-3 = 1/1,000 micro- μ 10-6 = 1/1,000,000 nano- n 10-9 = 1/1,000,000,000 All the conversions are multiples of 10. Converting from one unit to another, such as from meters to centimeters, simply involves shifting the decimal point to the left or right. Example: 12.56 meters = 1,256 centimeters = 0.01256 kilometers. Use the diagram from the handout to help remember how to convert from one metric system to another. Tips for solving unit conversion problems: Always be aware of the unit you start with and the unit you have been asked for. Set up the conversion factor so that it cancels the unit in the prior term. If this unit is in the numerator, the unit in the conversion factor should be in the denominator. SNC2D Physics Unit Name: _____________________________ METRIC CONVERSION PRACTICE Use the staircase to help convert the following to the requested metric unit. 1. 3 meters = __________ centimeters 2. 40 meters = __________ decameters 3. 600 millimeters = __________ meters 4. 5 kilometers = __________ hectometers 5. 70 centimeters = __________ meters 6. 900 millimeters = __________ centimeters 7. 550 mm = __________ cm 8. 2.5 km = __________m 9. 82 cm = __________ mm 10. 980,000 cm = __________ km 11. 9.2460 m = __________ mm 12. __________ m = 6968 cm 13. 240 __________ = 24 cm 14. 45,000 __________ = 450,000 m 15. 0.0123 __________ = 1.23 cm 16. 975.4 __________ = 0.9754 km 17. __________ mm = 44.7 cm 18. 2544 mm = __________ m