Sample power point
advertisement

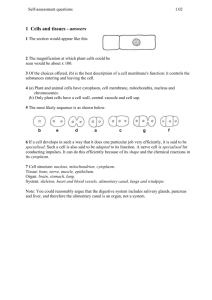
Click on part of the cell to see more A large, membrane-bound, usually spherical protoplasmic structure within a living cell, containing the cell's hereditary material and controlling its metabolism, growth, and reproduction. A small, typically round granular body composed of protein and RNA in the nucleus of a cell. It is usually associated with a specific chromosomal site and involved in ribosomal RNA synthesis and the formation of ribosomes. The double-layered membrane enclosing the nucleus of a cell. Also called nuclear envelope The semipermeable membrane that encloses the cytoplasm of a cell. A membrane network within the cytoplasm of cells involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of cellular materials. A membrane-bound organelle in the cytoplasm of most cells containing various hydrolytic enzymes that function in intracellular digestion. A minute round particle composed of RNA and protein that is found in the cytoplasm of living cells and serves as the site of assembly for polypeptides encoded by messenger RNA. The protoplasm outside the nucleus of a cell. A small cavity in the cytoplasm of a cell, bound by a single membrane and containing water, food, or metabolic waste. a net-like structure in the cytoplasm of animal cells (especially in those cells that produce secretions) A small region of cytoplasm adjacent to the nucleus that contains the centrioles and serves to organize microtubules. A spherical or elongated organelle in the cytoplasm of nearly all eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and many enzymes important for cell metabolism, including those responsible for the conversion of food to usable energy. Also called chondriosome.