5th Edition
PPT 7-1
Chapter 7
Retail Locations
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
PPT
7-2
Levy/Weitz:
Retailing Management, 5/e
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Retailing Strategy
Human Resource
Management
Chapter 9
Retail Market and
Financial Strategy
Chapter 5, 6
Retail Locations
Chapter 7
Site Locations
Chapter 8
Information and
Distribution
Systems
Chapter 10
PPT 7-3
Customer
Relationship
Management
Chapter 11
What Are the
Three Most Important Things in Retailing?
Location! Location! Location!
PPT 7-4
Retail Locations
Shopping Centers
– Strip Shopping Centers
– Shopping Malls
City or Town Locations
– Inner City
– Main Street
Free Standing Sites
Other Location Opportunities
PPT 7-5
Types of Strip Shopping Centers
Traditional
Mom and Pop Local Merchants,
Children’s Place, GapKids,
Blockbuster Video
Power Centers
Target, Home Depot, Office Depot,
PetsMart, Best Buy, Sports Authority,
Toys R Us
PPT 7-6
Elements in Retail Mix
Location Strategy
Customer
Service
Store Display
And Design
Communication
Mix
PPT 7-7
Merchandise
Assortment
Pricing
Strip Shopping Centers
PPT 7-8
Types of Shopping Malls
Regional Centers
Superregional Centers
Lifestyle Centers
Fashion/Specialty Centers
Outlet Centers
Theme/Festival Centers
Merchandise Kiosks
PPT 7-9
Shopping Malls
PPT 7-10
The Largest U.S. Shopping Malls
PPT 7-11
Problems Facing Regional Malls
• Competition from Alternative, More
Convenient Locations
• Focus on Apparel – Weak Apparel Sales
• Aging
• Demographic Shifts
PPT 7-12
The Most Expensive Shopping
Streets in the World
Street
PPT 7-13
Location
Cost / sq foot / year
Fifth Avenue (48th to
58th St.)
New York City
$580
57th Street (5th Ave.
to Madison Ave.)
New York City
$500
Oxford Street
London
$400
Madison Avenue (57th New York City
to 72nd St.)
$375
Ave. des Champs
Elysee
$360
Paris
Tradeoff Between Locations
There are relative advantages
and disadvantages to consider
with each location.
Rent
Traffic
PPT 7-14
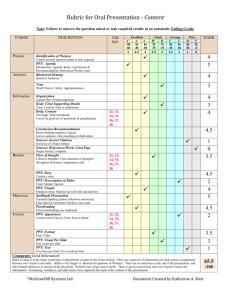
Relative Advantages
of Major Retail Locations
Location
City
Issues
Strip
Center
Shopping
Free
Mall
Standing
Large size
draws people
to area
+
-
+
-
People
working/living
in area
provided source
of customers
+
+
-
-
Source of
entertainment/
recreation
?
-
+
-
Protection
against weather
-
-
+
-
PPT 7-15
Relative Advantages
of Major Retail Locations
Location
CBD
Issues
Shopping
Free
Center
Mall
Standing
-
+
+
+
+
Planned
shopping
area/balanced
tenant mix
-
-
+
-
Parking
-
Occupancy
costs
(e.g. rent)
?
+
+
-
+
+
Security
Long, uniform
hours of
operation
PPT 7-16
Strip
Relative Advantages
of Major Retail Locations
Location
City
Issues
Strip
Shopping
Center
Mall
Free
Standing
Pedestrian
traffic
+
-
+
-
Landlord
+
+
-
+
Strong
competition
+
+
-
+
Tax
incentives
?
?
?
?
control
PPT 7-17
Other Retail Location Opportunities
Mixed Use Developments
Airports
Resorts
Hospitals
Store within a Store
PPT 7-18
Matching Location to Retail Strategy
• Department Stores Regional Mall
• Specialty Apparel Central Business District,
Regional Malls
• Category Specialists Power Centers,
Free Standing
• Grocery Stores Strip Shopping Centers
• Drug Stores Stand Alone
PPT 7-19
Types of Leases
Percentage
Fixed - Rate
Percentage leases – lease based on a % of sales.
Retailers also typically pay a maintenance fee
based on a percentage of their square footage of
leased space.
Most malls use some form of percentage lease.
PPT 7-20
Variations of Percentage Leases
Percentage lease with specified maximum percentage of sales up to a maximum amount.
Rewards retailer performance by allowing retailer
to hold rent constant above a certain level of sales
Percentage lease with specified minimum retailer must pay a minimum rent no matter how
low sales are.
Sliding scale - percentage of sales as rent
decreases as sales go up.
PPT 7-21
Fixed Rate Leases
Fixed Rate Leases - used by community and
neighborhood centers.
-Retailer pays a fixed amount per month over the life
of the lease.
-Not as popular as percentage leases
Graduated Lease - a variation of the fixed rate
lease
-Rent increases by a fixed amount over a specified
period of time.
PPT 7-22
Percentage or Fixed Rate Leases
Maintenance-increase-recoupment lease
- used with either a percentage or fixed
rate lease.
Rent increases if insurance, property
taxes, or utility bills increase beyond a
certain point.
Net lease - retailer is responsible for all
maintenance and utilities.
PPT 7-23
Prohibited Use Clause
Limits the landlord from leasing to certain tenants.
Some tenants take up parking spaces and don’t
bring in shoppers: bowling alley, skating rink,
meeting hall, dentist, or real estate office.
Some tenants could harm the shopping center’s
wholesome image: bars, pool halls, game parlors,
off-track betting establishments, massage parlors
and pornography retailers.
PPT 7-24
Exclusive Use Clause
Prohibits the landlord from leasing to retailers
selling competing merchandise
Specify no outparcels
Specify if certain retailer leaves center, they can
terminate lease.
Escape Clause
Allows the retailer to terminate its lease if sales don’t
reach a certain level after a specified number of
years, or if a specific co-tenant in the center
terminates its lease.
PPT 7-25
Environmental Issues
“Above-ground” risks - such as asbestos-containing
materials or lead pipes used in construction.
Hazardous materials - e.g. dry cleaning chemicals,
motor oil, that have been stored in the ground.
Retailers’ Protection
Stipulate in the lease that the lessor is responsible
for removal and disposal of this material if it’s
found.
Retailer can buy insurance that specifically
protects it from these risks.
PPT 7-26
Other Legal Issues
Zoning and Building Codes
Zoning determines how a particular site can be
used.
Building codes determine the type of building,
signs, size, type of parking lot, etc. that can be
used
Signs
Restrictions on the use of signs can also impact
a particular site’s desirability
Licensing Requirements
Some areas may restrict or require a license for
alcoholic beverages
PPT 7-27