WLTP-DHC-09-02
advertisement

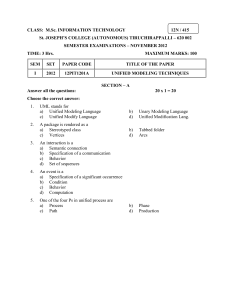
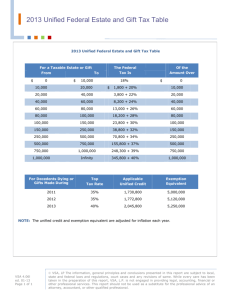
WLTP-DHC-09-02 Development of World-wide Light-duty Test Cycle ~ Introduction of the WLTC 1st ver.~ Prepared by Japan DHC group under GRPE/WLTP informal group 6-7 July 2011 Stockholm, Sweden 1 Table of contents 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. WLTP-DHC-09-02 Purpose In-use data collection Regional weighting In-use driving data analysis Development of WLTC 1st version WLTP driving cycle 1st version 2 1. Purpose WLTP-DHC-09-02 Develop the world wide harmonized light duty test cycle (WLTC) which will represent typical driving conditions around the world. The WLTC are developed based on combination of collected in-use data and suitable weighting factors. Data collection CP’s: EU, India, Japan, Korea, USA (and China) 3 WLTP-DHC-09-02 2. Overview of In-use data collection Total amount of data collection Region Japan (JP) Korea (KR) India (IN) China (CN) USA (US) Belgium (BE) Germany (DE) Spain (ES) France (FR) Italy (IT) EU+CH Poland (PL) Slovenia (SI) Switzerland (CH) United Kingdom (UK) Sweden (SE) (Unit: km) Vehicle type No. of vehicles PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV Chased car PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV PC LDCV 11 13 6 2 16 4 0 0 156 20 11 0 8 0 6 4 42 0 8 0 9 0 18 0 26 4 10 12 5 2 Urban 13,605 13,233 8,480 2,558 11,783 3,218 0 0 0 0 7,538 4,986 0 7,865 0 800 2,815 23,568 0 9,827 0 9,438 0 14,662 0 6,021 518 7,174 0 0 0 Rural 1,301 1,325 6,943 3,261 11,832 3,713 0 0 0 0 2,365 24,667 0 11,051 0 729 4,093 53,520 0 23,964 0 4,796 0 24,351 0 3,763 57 9,750 0 0 0 Motorway 10,764 12,727 10,610 2,551 18,189 7,042 0 0 0 0 19,635 21,292 0 4,498 0 1,090 140 31,828 0 23,854 0 413 0 9,920 0 12,886 374 566 0 0 0 Undefined 130,188 114,271 14,290 18,525 18,426 Total 25,670 27,285 26,033 8,370 41,804 13,974 0 0 130,188 0 29,538 165,216 0 23,414 0 2,619 7,047 108,916 0 57,646 0 14,648 0 48,934 0 22,670 949 17,491 14,290 18,525 18,426 52,955 34,403 55,778 0 159,726 165,216 23,414 9,666 108,916 57,646 14,648 48,934 23,619 31,781 36,951 4 WLTP-DHC-09-02 3.1. Regional weighting Regional weighting when developing the unified driving characteristic is set based on Traffic volume ratio 100% 90% IN, 0.22 IN, 0.16 KR, 0.04 80% KR, 0.06 IN, 0.10 KR, 0.04 JP, 0.02 JP, 0.12 US, 0.55 70% Regional weighting IN, 0.00 KR, 0.01 JP, 0.01 JP, 0.16 60% IN US, 0.55 KR 50% US, 0.23 JP US, 0.44 US 40% EU 30% EU, 0.43 20% EU, 0.33 EU, 0.24 10% EU, 0.29 0% Low Middle High Ex-High 5 WLTP-DHC-09-02 3.2. Internal weighting for Europe and US Internal WF for European counties was set based on Traffic statistics (TREMOVE) and in-use driving data (vehicle speed and amount of in-use data). Internal WF for US data was set based on US and Mr. Steven’s advice. [Internal WF for Europe] SE CH 6% 4% [Internal WF for US] BE 15% BE DE UK 14% ES DE 12% SI 5% PL 4% FR US customer data 16% IT US EPA data PL US customer data SI UK ES 9% IT 10% CH SE US EPA data 84% FR 21% 6 500 Low Middle 2000 1000 0 High Extra-high 30 25 20 Low EU US 45 Middle High KR IN 15 10 5 High 0.05 disregard 0.108 0.155 0.117 0.144 0.164 0.139 0.162 0.156 0.174 0.142 0.188 0.245 0.225 0.192 0.142 0.176 0.134 0.086 0.114 0.103 0.10 22.1 Middle IN 14.5 35 disregard JP KR 15.5 17.1 12.2 50 46.2 Unified US 22.8 40 34.2 Low 21.5 18.4 20.1 2500 EU 24.6 22.4 [Average ST duration] 39.8 Extra-high 0.192 JP 22.3 0 0.177 0.200 Unified 25.6 0.15 RPA (m/s2 ) 0.25 16.6 IN 0.20 24.9 29.2 23.1 21.9 KR 86.8 120 26.5 High 67.6 [Average speed] 15.6 disregard 80 Average IDLE duration (s) US 824 1621 86.2 83.1 90.1 100 disregard Middle 1158 1082 62.9 55.6 59.7 53.9 56.1 58.0 60 IN 601 1500 1157 EU KR 446 JP 691 Low US 458 473 284 642 40.1 39.9 37.0 34.1 39.5 38.4 40 EU 238 20 19.8 20.0 18.8 17.2 21.1 19.8 Average speed (km/h) JP 161 221 125 201 66 68 63 64 148 84 Average ST duration (s) 4.1. driving characteristics WLTP-DHC-09-02 [RPA] 0.30 Unified 0.00 Extra-high [Average IDLE duration] Unified 0 Extra-high 7 WLTP-DHC-09-02 4.2. Unified speed acceleration distribution [Low phase] [Middle phase] 16 16 Unified Middle Unified Low 12 Acceleration (km/h/s) Acceleration (km/h/s) 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -16 -16 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 Speed (km/h) 120 140 160 [High phase] 0 20 40 60 80 100 Speed (km/h) 120 140 160 [Extra-high phase] 16 16 Unified High 8 4 0 -4 -8 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -16 -16 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 Speed (km/h) 120 140 Unified Extra-high 12 Acceleration (km/h/s) 12 Acceleration (km/h/s) -20 160 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 Speed (km/h) 120 140 160 8 WLTP-DHC-09-02 4.3. Speed frequency distribution [Middle phase] 45 90 70 30 60 Unified Low Japan Low EU Low US Low Korea Low India Low Unified Low 15 10 5 40 30 20 30 100 90 Unified High Japan High EU High US High Korea High India High Unified High 70 60 50 40 30 20 25 Frequency (%) 80 Cum. frequency (%) 25 10 20 15 Unified Extra-high Japan Extra-high 100 90 EU Extra-high US Extra-high Korea Extra-high 80 70 60 Unified Extra-high 50 40 10 30 20 5 10 Vehicle speed (km/h) 10 0 180 0 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 Frequency (%) 20 [Extra-high phase] 30 5 30 Vehicle speed (km/h) [High phase] 10 40 0 0 10 20 30 Vehicle speed (km/h) 15 50 0 180 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 10 5 0 60 Unified Middle Japan Middle EU Middle US Middle Korea Middle India Middle Unified Middle 15 10 0 20 70 Cum. frequency (%) 20 50 20 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 25 90 80 Frequency (%) 80 35 100 25 Cum. frequency (%) 40 Frequency (%) 30 100 180 50 Cum. frequency (%) [Low phase] Vehicle speed (km/h) 9 WLTP-DHC-09-02 4.4. Frequency distribution on Short trip duration [Middle phase] 10 90 70 6 60 Unified Low Japan Low EU Low US Low Korea Low India Low Unified Low 4 2 50 40 30 Frequency (%) 80 90 80 70 6 60 Unified Middle Japan Middle EU Middle US Middle Korea Middle India Middle Unified Middle 4 2 20 10 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1 51 101 151 201 251 301 351 401 451 501 551 601 651 701 751 801 851 901 951 1001 1051 1101 1151 1201 0 1 11 21 31 41 51 61 71 81 91 101 111 121 131 141 151 161 171 181 191 201 211 221 231 241 251 261 271 281 291 301 0 Short trip duration (s) Short trip duration (s) [Extra-high phase] 10 100 30 20 Unified Extra-high 60 Japan Extra-high 50 EU Extra-high 40 US Extra-high 30 Korea Extra-high 20 Unified Extra-high 10 2401 2601 0 2001 2201 0 1401 1601 1801 3401 3601 3201 2801 3001 2401 2601 2001 2201 1401 1601 1801 1201 601 801 1001 0 1 201 401 2 10 0 Short trip duration (s) 4 1201 2 40 601 801 1001 4 50 3401 3601 60 Unified High Japan High EU High US High Korea High India High Unified High 70 6 1 201 401 6 80 3201 70 90 8 Frequency (%) 80 Cum. frequency (%) 90 8 100 2801 3001 10 Cum. frequency (%) [High phase] Frequency (%) 100 8 Cum. frequency (%) 8 Frequency (%) 10 100 Cum. frequency (%) [Low phase] Short trip duration (s) 10 WLTP-DHC-09-02 4.5. Frequency distribution on Idling duration [Middle phase] 20 18 12 60 Unified Low Japan Low EU Low US Low Korea Low India Low Unified Low 8 6 4 2 40 30 20 Unified Middle Japan Middle EU Middle US Middle Korea Middle India Middle Unified Middle 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 Idling duration (s) Idling duration (s) 20 100 18 70 12 60 Unified High Japan High EU High US High Korea High India High Unified High 4 2 30 20 10 80 14 12 10 70 Unified Extra-high 60 Japan Extra-high 50 8 EU Extra-high 40 6 US Extra-high 30 4 Korea Extra-high 20 10 2 Unified Extra-high 10 0 0 40 30 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 20 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 0 50 90 16 Frequency (%) 80 14 Cum. frequency (%) 16 6 40 100 18 90 8 50 [Extra-high phase] 20 10 60 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 10 [High phase] Frequency (%) 70 12 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 0 50 80 14 Cum. frequency (%) 10 90 16 Frequency (%) 70 Cum. frequency (%) 80 14 100 18 90 16 Frequency (%) 20 100 Cum. frequency (%) [Low phase] Idling duration (s) Idling duration (s) 11 WLTP-DHC-09-02 5.1. Determination of test cycle duration The total test cycle duration is set at 1800 s, same as WHDC and WMTC The test cycle duration in each phase is determined based on traffic volume ratio between L/M/H/ExH phases(*) Low: 589 s, Mid.: 433 s, High: 455 s, Ex-High: 323 s [Traffic volume in million vehicle-hour] EU US JP KR IN World-wide propotion Cycle duration Low 23,338 15,898 11,126 4,053 15,629 70,044 0.327 Middle 12,444 22,578 6,157 1,838 8,466 51,484 0.240 589 433 High Ex-High Total 15,748 16,380 67,911 29,541 21,254 89,271 1,164 328 18,775 2,087 443 8,420 5,641 64 29,800 54,181 38,470 214,178 0.253 0.180 1.000 455 323 1800 (*) Traffic volume ratio between L/M/H/ExH phases is obtained by using compensated WF and amount (duration) of data when converted from U/R/M to L/M/H/ExH 12 WLTP-DHC-09-02 5.2. Determination of No. of Short trip and Idling section The No. of short trip and idling section in each phase are determined by using the following equation number of short trip (NST, i) = drive cycle duration in each phase (Ti) - average idling duration average short trip duration + average idling duration number of idling section (NI, i) = number of short trip (NST, i) + 1 [No. of ST/IDLE section] Target cycle Average ST duration duration s s Average IDLE duration s No. of ST No. of IDLE # # Low 589 84 22 5 6 Middle 433 238 22 1 2 High 455 446 23 1 2 Extra-high 323 824 14 1 2 13 WLTP-DHC-09-02 5.3.1. Determination of Short trip duration in each phase [Low] 100 70 60 35 50 19 40 30 1 80 70 380±6s 3 60 50 2 40 30 1 20 20 10 10 0 0 1 51 101 151 201 251 301 351 401 451 501 551 601 651 701 751 801 851 901 951 1001 1051 1101 1151 1201 0 1 11 21 31 41 51 61 71 81 91 101 111 121 131 141 151 161 171 181 191 201 211 221 231 241 251 261 271 281 291 301 0 Short trip duration (s) Short trip duration (s) [High] Cycle duration for high phase is determined based on Idling ratio [Extra-high] 5 100 100 60 Combined cycle: 428 s 50 2 40 30 1 20 4 Frequency (%) 3 90 Actual ST: 317±4 s Cum. frequency (%) 70 Actual ST: 428±6s 80 Combined cycle: 317 s 70 3 60 50 2 40 30 1 20 10 Short trip duration (s) 10 3601 3201 3401 2801 3001 2601 2201 2401 1801 2001 1601 1201 1401 801 1001 601 0 201 401 0 1 3601 3201 3401 2801 3001 2601 2201 2401 1801 2001 1601 1201 1401 801 1001 601 0 201 401 0 1 Frequency (%) 80 Cycle duration for Extra-high phase is determined based on Idling ratio 5 90 4 Cum. frequency (%) 90 4 Frequency (%) Frequency (%) 80 54 3 100 90 249±1s Cum. frequency (%) 88±1s 4 5 Cum. frequency (%) 5 2 Cycle duration for middle phase is determined based on Idling ratio [Middle] Short trip duration (s) 14 5.3.2. Determination of Idling duration in each phase [Low] [Middle] 100 90 80 70 20 60 15 50 86 18 30 20 5 20 80 7 46±6 s 60 15 50 40 10 30 20 5 10 10 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 0 Idling duration (s) Idling duration (s) [High] [Extra-high] 30 100 30 100 90 70 60 25±6 s 15 50 40 10 30 20 5 Frequency (%) 2 90 25 Cum. frequency (%) 80 80 1 70 20 60 15 50 5±4 s 40 10 30 20 5 10 0 10 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200 Frequency (%) 25 20 70 Cum. frequency (%) 28 40 90 25 Frequency (%) 8 13 10 30 Cum. frequency (%) Frequency (%) 100 Cum. frequency (%) 30 25 WLTP-DHC-09-02 Idling duration (s) Idling duration (s) 15 WLTP-DHC-09-02 5.3.3. Selection of each ST duration it is necessary to reduce number of combinations ST selection criteria ST within average ±1σ in each ST duration Average vehicle speed Acceleration duration ratio Deceleration duration ratio Smaller chi-squared value is higher priority The number of candidate STs in each ST duration Longest ST has big influence on chi-square value => Not reduce Shorter ST => reduce candidate STs to make total number of combinations approximately 108~9 . 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 X 1 X2 X3 X4 X5 sec. Y sec. 0 50 100 N * X1/Y units ・・・ N * X4/Y -10 0 150 N * X5/Y units 200 250 300 350 N units 16 5.4. The characteristics of first ST and Idling of a day WLTP-DHC-09-02 Order of Idling sections Average Idling duration of first Idling of a day is 28 s. Select 28 s The final Idling duration would be more than 5 s because of stable sampling. Select 8 s Order of Short trips Average speed of first short trip of a day is approx. 30 km/h. => ST of 245 s ST of lowest speed and IDLE of longest duration are connected in order to reflect traffic jam the order of short trips is set based on random [The characteristics of first ST and Idling of a day by Mr. Steven] average stop average short trip duration in speed in duration in s km/h s 24.0 208.4 29.3 maximum speed in km/h region sample number Europe 3271 USA 1492 32.0 144.7 29.8 55.5 Average - 28.0 176.5 29.6 52.2 48.8 17 WLTP-DHC-09-02 6.1. WLTP driving cycle 1st version 8.0 Low phase High phase Acceleration (km/h/s) 6.0 Middle phase Extra-high phase 4.0 2.0 0.0 -2.0 -4.0 -6.0 -8.0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 Time (s) 160 Low phase High phase 140 Speed (km/h) 120 100 Middle phase Extra-high phase TID1: 28 s Vave: 28.6km/h 80 60 40 20 0 0 200 400 600 800 Time (s) 18 WLTP-DHC-09-02 6.2. Characteristics of WLTC 1st version driving mode (*) Parameter Cycle duration Driving distanc e Averag e speed Max. speed Max. acceler ation Max. Deceler ation s (h) km km/h km/h km/h/s km/h/s Acceler ation ratio Deceler ation ratio Cruise ratio Idling ratio % % % % Low - - 19.8 60.0 - - 27.5 25.4 22.7 24.5 Unified characteris tics Middle - - 38.4 80.0 - - 31.4 27.5 28.8 12.2 High - - 58.0 110.0 - - 31.3 27.2 35.5 6.0 Worldwide Extra-high - - 86.8 194.7 - - 25.7 23.4 48.9 2.0 Unified - - 45.9 194.7 - - 29.1 26.0 32.1 12.8 Low 589 2.98 18.2 50.9 5.3 -5.3 26.1 27.8 19.7 26.3 Middle 433 5.01 41.6 72.5 5.4 -7.4 37.0 24.2 27.2 11.1 High 455 7.01 55.5 97.4 6.5 -7.7 29.0 28.8 35.2 7.0 Extra-high 323 8.06 89.8 125.5 6.4 -4.1 28.5 27.2 42.1 2.2 WLTCunified 1800 23.06 46.1 125.5 6.5 -7.7 29.9 27.1 29.6 13.4 WLTC 1st (*) The definitions for the driving modes are given by WMTC analysis (refer to Appendix) 19 WLTP-DHC-09-02 6.3. Speed acceleration distribution of WLTC 1st version Low Midle 12 12 Unified distribution-Worldwide Middle Unified distribution-Worldwide Low 8 Acceleration (km/h/s) Unified distribution Acceleration (km/h/s) 8 4 0 -4 -8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 12 -20 0 20 40 12 WLTC Middle WLTC Low 8 Acceleration (km/h/s) Acceleration (km/h/s) 8 WLTC ver.1 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 4 0 -4 -8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 20 WLTP-DHC-09-02 6.3. Speed acceleration distribution of WLTC 1st version High Ex-high 12 12 Unified distribution-Worldwide High Unified distribution-Worldwide Ex-high 8 Acceleration (km/h/s) Unified distribution Acceleration (km/h/s) 8 4 0 -4 -8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 12 -20 0 20 40 12 WLTC High WLTC Ex-high 8 Acceleration (km/h/s) Acceleration (km/h/s) 8 WLTC ver.1 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 4 0 -4 -8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -12 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Speed (km/h) 21 Appendix. Definition of driving modes WLTP-DHC-09-02 Source: TRANS-WP29-GRPE-2004-10e.pdf, page.18, http://live.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/trans/doc/2004/wp29grpe/TRANS-WP29-GRPE-2004-10e.pdf 22