Student Worksheets
Name:
Date:
Who’s Polluting the River?
Student Handout
Introduction:
New mayor Karen Heck believes that someone is polluting the Kennebec River in
Waterville. She has contacted your well-respected lab to conduct the preliminary investigation.
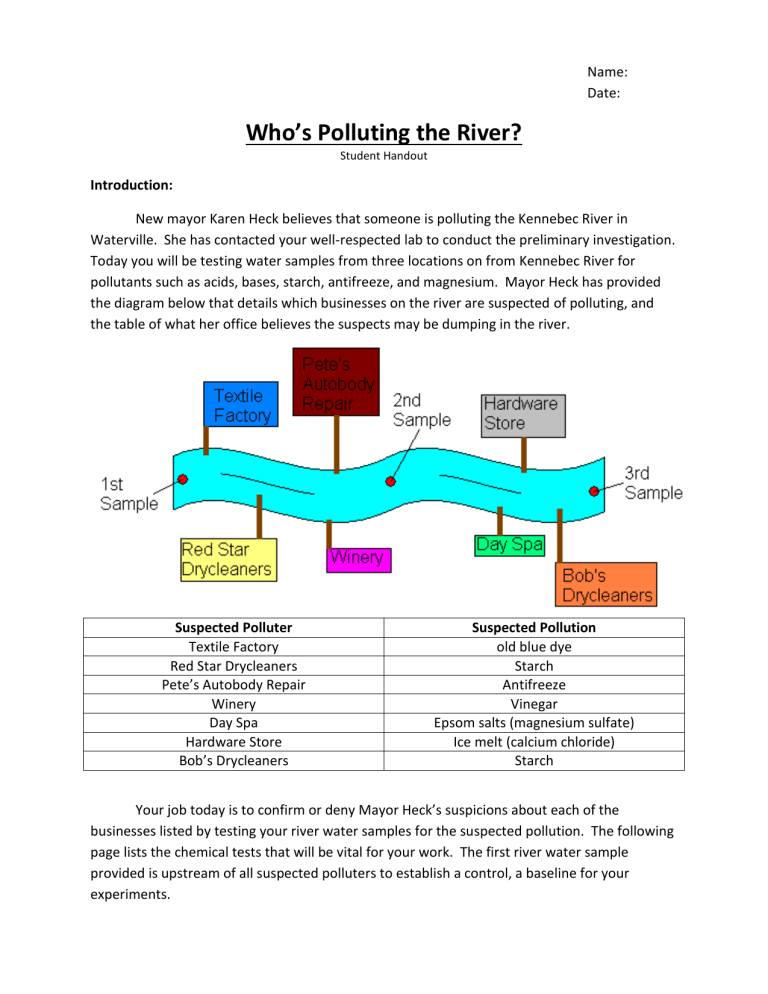
Today you will be testing water samples from three locations on from Kennebec River for pollutants such as acids, bases, starch, antifreeze, and magnesium. Mayor Heck has provided the diagram below that details which businesses on the river are suspected of polluting, and the table of what her office believes the suspects may be dumping in the river.
Suspected Polluter
Textile Factory
Red Star Drycleaners
Pete’s Autobody Repair
Winery
Day Spa
Hardware Store
Bob’s Drycleaners
Suspected Pollution old blue dye
Starch
Antifreeze
Vinegar
Epsom salts (magnesium sulfate)
Ice melt (calcium chloride)
Starch
Your job today is to confirm or deny Mayor Heck’s suspicions about each of the businesses listed by testing your river water samples for the suspected pollution. The following page lists the chemical tests that will be vital for your work. The first river water sample provided is upstream of all suspected polluters to establish a control, a baseline for your experiments.
Identifying the Pollution: An Explanation
Blue dye in the river can be indentified by the use of a spectrophotometer. A spectrophotometer measures the absorbance of a sample placed between its light source (known as a spectrometer) and a detector (a photometer). First, the spectrophotometer must be calibrated with pure water, free of all pollutants. A sample of river water may then be placed in the spectrophotometer. To confirm the presence of
blue dye the sample spectra should have a characteristic peak at 627nm.
Epsom salts are a commonly used bath additive, especially for spa treatments. Epsom salts and washing soda dissolved in water produce a white precipitate, magnesium carbonate. To confirm the presence of Epsom salts add 2-4 drops of washing soda. A
white precipitate should form and settle to the bottom. o MgSO
4(aq)
+ Na
2
CO
3(aq)
===> MgCO
3(s)
Corn starch and iodine react to produce a dark blue complex. To confirm the presence of starch, add 2-4 drops of iodine. A dark blue cloud should settle to the bottom. o Beta amylose + I
2(aq)
==> I
5
-1 (a dark blue complex)
Vinegar in the river water will turn the solution acidic. Red cabbage juice is a natural pH indicator due to the presence of anthocyanin, a pigment that changes color due to pH. .
To confirm the presence of vinegar add 2-4 drops of red cabbage juice. The solution
should turn pink. In a strongly acidic solution the anthocyanin would turn red.
Ice melt will turn the river water basic. Red cabbage juice is a natural pH indicator due to the presence of anthocyanin, a pigment that changes color due to pH. To confirm the presence of Ice melt add 2-4 drops of red cabbage juice. The solution should turn bluish-
green.
Antifreeze is made with a fluorescent, black light reactive tracer dye to aid in identification of spills. To confirm the presence of antifreeze expose the sample to a black light. If there is antifreeze dissolved in the solution, the solution will appear to glow.
Procedure:
1. Add 10-15 drops of river water sample #1 to each of three spot plate wells using a disposable pipette.
2. Add 2-4 drops of iodine to the first well, red cabbage juice to the second, and washing soda to the third. Record your results in the Data Table below.
Iodine test: if a sample has starch in it, it will turn dark blue .
Cabbage juice test: if a sample has acid in it, it will turn red . If a sample has base in it, it will turn bluish-green .
Washing soda test: If a sample has Epsom salts in it, a white solid will form.
3. Repeat this procedure for river water samples #2 and #3.
Data Table:
River Water Sample Iodine Test Red Cabbage Test Washing Soda Test
#1
#2
#3
4. For river water sample #2, have one member of your group bring the test tube of river water to the Ocean optics spectrometer. There a teacher will assist you in the use of the spectrometer and reading the spectrum for your sample.
Remember, a sample with blue dye will have a characteristic peak at 627nm.
Does your sample contain blue dye? Yes No
5. For each of the samples, test them with the black light.
Remember, a sample with antifreeze will fluoresce under black light.
Does your sample contain antifreeze? Yes No
When you believe your group has identified the polluters inform the instructor who you believe is polluting the river and why you believe so. A small worksheet to help you organize your argument has been provided on the back.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Is the Textile Factory polluting the river?
How do you know?
How do you know?
How do you know?
Is Red Star Drycleaners polluting the river?
Is the winery polluting the river?
Is Pete’s Autobody Repair polluting the river?
How do you know?
5.
Is the day spa polluting the river? Yes No
How do you know?
6.
Is the hardware store polluting the river? Yes No
How do you know?
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
7.
Is Bob’s Drycleaners polluting the river? Yes No
How do you know?