Notes_Ag_Business_Politics_GildedAge
advertisement

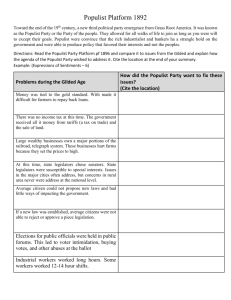
Agriculture, Business & Politics of the Late 19th Century Agriculture The Plight of the Farmer Over production – producing more than the “World” needs More land being farmed, better soil than before, better technology Result: decrease in demand, leads to falling prices Farmers don’t stop: continue to buy more land, equip, etc. Problem: borrow $ to do so, debt increases, income remains the same. Disaster hits Plague (1874) Drought (1886) Banks call in loans Farms foreclosed upon “In God We Trusted, In Kansas We Busted” Farmers become Ranchers With the loss of Buffalo, Cattle became the staple of the GP Demand grows due to the R.R. & Growth of Cities The Cattle Town Chisholm Trail - drives cattle from San Antonio, TX to Abilene, KS Abilene connects to Chicago Chicago to Eastern cities Cowboys learn from Vaqueros Spanish had brought both the Cow and Horse here in the 1500s 55,000 worked as Cowboys Majority white, but 25% black, 10% Hispanic As young as 15 as old 40 10-14 hr days Spring round-up to 3-month “long-drive” o 1 cowboy to 250 cattle Owned a saddle, but not usually the horse Short-lived Overgrazing, bad weather, and the invention of barbed wire ends “Open Range” era Business National Economics Economics: the study of how people use goods and services to satisfy their needs and wants Chain Stores: sold, repaired farm equipment (along with other products) McCormick Harvesting Company (1847) – would become International Harvester in 1902 Deere & Company (1868) Steel plow-wagon-planters-cultivators Retail Stores: warehouse of consumer goods Marshall Field’s (Chicago - 1852), Macy’s (NYC - 1858), Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Company (1859) Introduce charge accounts, customer service dept, door-to-door salesmen & advertising Railroads Play Important Role Refrigerated RR cars spur the growth of meat “packing” industry Swift & Company (1878) sending meat from Chicago to San Francisco & New York City George Pullman Creates the Pullman “Sleeper” RR car Gains national attention when Pres. Lincoln’s dead body is transported from Washington, D.C. to Springfield, IL on a Pullman Car (1865) By 1880 Pullman cars in such high demand that a town is built for employees - Pullman, IL Provided all necessities for employees: housing, medical care, social activities Claims of restricted freedoms: assembly, choice – alcohol Pullman Strike (1894) results in annexation of Pullman into Chicago Magnates & Robber Barrons Def: an individual who has immense power and influence over a particular industry; whose business practices are often questionable Ex: Andrew Carnegie, Henry Clay Frick, Cornelius Vanderbilt, & John D. Rockefeller Union Pacific uses profits to buy their influence in Congress James Garfield, later Pres, when in Congress took RR $$$ Republican Party embarrassed by the $$$ Politics Problems with RR Misuse of gov’t land grants Suppose to sell their land to settlers, were selling their land to businesses Fixed prices because they controlled the transportation Charged different customers different rates: rural v. urban locations Action taken States in Munn v. Illinois allowed to regulate RR Congress passes Interstate Commerce Act (1887) to overrule Munn Def: est. Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) and declared the fed gov’t had sole power to regulate trade that spanned multiple states Economic Panic RR Financial Problems contribute to Nationwide Depression Corporate abuses, mismanagement, “flooded” market 600 Banks close, 15,000 businesses fail, 4 million ppl unemployed (20%) Investment firms gobble up RRs 7 companies gain control of 66% of RRs JP Morgan & Co Populist Party created (1892) Alternative to Republican and Democrat Parties Purpose: “restore government to ‘plain people’” Farmers, laborers, reformers Mid-Western ideals Leaders of the party are from MN, IA, KS, & NE Reason: depression of 1892 left 4 million unemployed Populist Party Platform: Mint silver = create increase in prices for goods & services Graduated income tax: as you make more, you pay more in taxes Election of Senators by popular vote Term limits for Pres & VP Est. of 8 hr work day Immigration restrictions Election bids 1892: Populist Party Presidential Candidate - James Weaver (IA) 10% of Pres. Vote in 1892 - loses to Grover Cleveland 5 Senators elected 3 Governors elected 1500 state legislators (most success, most impact) 1896 Republicans o Who: business owners, bankers, Northeasterners o Nominee: William McKinley Democrats & Populists Unite o Who: farmers, daily laborers, Southerners & Westerners o Nominee: William Jennings Bryan Issues o Bimetallism v. Gold Standard Bimetallists = gold for silver in exchange for “paper” currency Democrats & Populists Stimulate econ with more $$$ in circulation (liberal) Gold Standard = paper currency only for gold Republicans Stable econ with “expensive” currency (conservative) Results o Victor: McKinley Carries the “East” & industry of Midwest o Populism crumbles Voice of the “little guy” heard Democrats adopt Populist platform Reforms were coming Lasting Legacy Ideals of the Populist Party live on within Democratic Party Democrats absorb Populist Party members