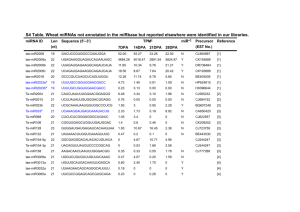
microRNAs and their applications
advertisement

miRNAs and their Applications Laura Martí Sánchez Genomics Advanced Genetic Master December, 2015 INDEX Introduction History Biogenesis Applications: • Cancer • Rossetta Genomics kit Bibliography Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography miRNAs non-coding RNA sequences (average length of 22 nucleotides) founded in eukaryotes (animals, plants and viruses) Regulation of gene expression thereby controlling many cellular processes Human genome may encode 28645 miRNAs Todd Smith. May, 2009 FinchTalk. Small RNAs get smaller Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography First miRNA: lin-4 (1993) By efforts of Victor Ambros (1987) and Gary Ruvkun (1988) in lin-4 Study of the gene lin-14 en C. Elegans development Negative regulation of gene lin-14 They showed that this RNA doesn’t encode a protein In December 1993, in the same issue of Cell, Ambros and Ruvkun independently reported that the small and non-protein coding transcript lin 4 regulates the gene lin-14 Lin-4 Transcripts and Complementarity between lin-4 and lin-14 Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography Processing of miRNA Transcription Nuclear Processing Nuclear Export Cytoplasmatic Processing Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography miRNA inhibition pathways Interaction with protein translation process: M1: Preventing assembling of the initiation process M2: Recluting 60S ribosomic subunit M3: on the translation process M6,7: Degradation Introduction History The development of miRNA microarrays, RT-PCR platforms and deep sequencing is a good advantage for the knowledge of these RNAs. During the past decade, our knowledge about role of miRNA in human diseases has grown exponentially, specially in cancer Biogenesis Applications Bibliography Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography miRNAs and Cancer Utilizing a signature of altered miRNA expression to differentiate cancer tissue from normal tissue Profiling circular blood or tumor derived exosomal miRNAs, surprassing the invasive procedures to aid in early detection of cancers Use of miRNA based classifier to identify tissue of origin for cancers of unknown primaries miRNAs in Cancer Diagnosis Distinguishing tumor subtypes using a panel of miRNAs that show differential expression with one cancer type Study SNPs in the miRNA genes, miRNA binding sites in the target mRNA genes or in the miRNA processing/machinery pathway genes to predict cancer predisposition Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography mi-LungTM Test (Rosetta Genomics) miRNA Function Uses Hsa-miR-106a regulates the tumor suppressor retinoblastoma High levels in retinoblastoma Hsa-miR-125a-5p Hsa-miR-129-3p Hsa-miR-205 involved in the invasion and migration of NSCLC cells has not yet been demonstrated regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition High levels in NSCLC underexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma be used to distinguish squamous from nonsquamous NSCLC Hsa-miR-21 Epidermal growth factor receptor at higher levels in NSCLC versus SCLC Hsa-miR-29b acts as a tumor suppressor via the targeting of methyltransferases at higher levels in NSCLC versus SCLC Hsa-miR-375 regulates cancer growth up-regulated in lung cancers with neuroendocrine features Hsa-miR-7 regulate epidermal growth factor receptor High levels in NSCLC 451 samples Nonsquamos Agilent microarray (675 probes) Squamous cell Carcinoma RT-qPCR Types of lung Cancer Small cell Carcinoid Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography mi-LungTM Test (Rosetta Genomics) Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography Other tests from Rosetta Genomics Introduction History Biogenesis Applications Bibliography • Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P, Tuschl T(2011): miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol 223:102–115 • Gilad S, Lithwick-Yanai G, Barshack I, Benjamin S, Krivitsky I, Edmonston TB, Bibbo M, Thurm C, Horowitz L, Huang Y, Feinmesser M, Hou JS, St Cyr B,Burnstein I, Gibori H, Dromi N, Sanden M, Kushnir M, Aharonov R (2012) Classification of the four main types of lung cancer using a microRNA-based diagnostic assay. J Mol Diagn 14(5):510-7 • Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75(5):843-54 • Moura RS, Vaz-Cunha P, Silva-Gonçalves C, Correia-Pinto J. (2015) Characterization of miRNA processing machinery in the embryonic chick lung. Cell Tissue Res 362(3):569575 • Leonov G, Shah K, Yee D, Timmis J, Sharp TV, Lagos D. (2015) Suppression of AGO2 by miR-132 as a determinant of miRNA-mediated silencing in human primary endothelial cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 69:75-84 • Jacek Krol, Inga Loedige & Witold Filipowicz. (2010) The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nature Reviews Genetics 11, 597-610 Thanks for your attention! Laura Martí Sánchez