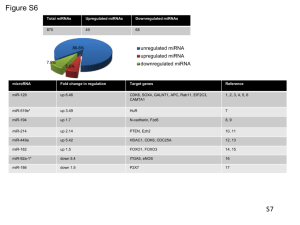
MYC activation
advertisement

Molecular markers in NKTL A/Prof Chng Wee Joo Department of Haematology-Oncology National Cancer Institute of Singapore National University Health System Senior Principle Investigator Cancer Science Institute, Singapore National University of Singapore Research Clinical Care Education Extranodal nasal-type Natural Killer/T-cell lymphoma (NKTL) • Distinct clinicopathologic entity most commonly affecting Asians and Central and South Americans • characterized by a clonal proliferation of NK or T cells with a cytotoxic phenotype. • There is a strong association with Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), which manifests a type II latency – expression of LMP-1 and EBNA-1, – absence of EBNA-2. • EBV detected in the neoplastic cells in a clonal episomal form, supporting the role of the virus in tumor pathogenesis Clinical Spectrum of Extra-nodal Natural Killer / T-cell Lymphoma Kwong YL. Leukemia 2005; 19:2186 Proposed model of NKTL pathogenesis EBV infection P53 mutations LMP-1 or other factors MYC activation Regulate NF-KB activation p53 Deregulation Induce Survivin Proliferation Anti-apoptotic Ng SB, et al. J Pathol. 2011 Mar;223(4):496-51 microRNAs: small molecules with a big impact • MicroRNAs (miRNA) are a class of small, non-coding RNAs (~20 nts long) that repress gene expression (in most cases) – Degrading or repressing mRNAs – Important class of gene regulators that controls most biological processes. – Latest in human: 1527 precursors, 1921 mature miRNAs (miRbase 19) • Each miRNA can have hundreds of different conserved or nonconserved targets • Samples: – 30 cases of NKTL FFPE – 6 NK cell lines (KHYG-1, NK-92, HANK-1, SNT-8, SNK-6 and NK-YS) – 3 paired samples of normal NK cells (unstimulated and stimulated) isolated from buffy coat packs of whole blood samples from blood bank – 2 cases each of normal skin, intestinal, nasal and lymph node FFPE tissue were also included as control tissue miRNA are predominantly downregulated in NKTL • miRNA deregulation in NKTL – In both NK cell lines and FFPE NKTL samples compared to normal NK cells, among the miRNAs showing at least 2-fold and statistically significant difference (p<0.05) in expression: • 2 upregulated (miR-155 and miR-378) • 39 were down-regulated: miR-342-5p, miR-26b, miR363, miR-150 and miR28-5p – Validation of MEP results • Real-time RT–PCR quantification of miRNAs • Correlation with microRNA transcriptome of NK cell using sequencing method quantitative-PCR validation of selected miRNAs consistent with MEP data miR-155 Upregulated miRNA miR-378 1000 100 100 10 10 1 1 0.1 Normal NKTL 0.1 NK Cell Lines Normal NKTL NK Cell lines Downregulated miRNA miR-26b miR-363 10 10 miR-342-5p 10 1 1 1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.001 0.001 0.001 Normal NKTL NK Cell Lines Normal NKTL NK Cell Lines Normal NKTL Nk Cell lines Selection of high probability predicted target genes of deregulated miRNA mirBase pictar targetScan mirtarget2 miRanda tarBase Predicted targets Intersect with our previous GEP data to narrow down target genes whose expression is inversely correlated with expression of deregulated miRNAs Final list Gene expression profile list (J Pathol. 2011 Mar;223:496-51) 226 target genes of 41 deregulated miRNA Validation of miRNA targets: Re-expression of miRNA using lentiviral vector • Target genes of miR-101, miR-26a, and miR-26b selected (STMN1, BCL2, IGF1, EZH2) • Lentiviral vectors used to re-express these miRNAs in NKYS cell line • Results – reduced growth of NKYS – modulated the expression of their predicted target genes – suggesting the potential functional role of the deregulated miRNAs in the oncogenesis of NKTL Relative expressions mRNA expression changes upon overexpression of miRNAs by Lentiviral transduction Mir-101 precursor control mir-26b precursor control mir-26b precursor Relative mRNA levels Relative mRNA expressions control control BCL2 IGF1 mir-101 precursor Immunohistochemistry reveals overexpression of target proteins of suppressed miRNAs in NKTL • IHC for selected target proteins (MUM1/IRF4, BLIMP1, STMN1) of deregulated miRNAs performed on 38 cases of NKTL for validation BLIMP1 MUM1 STMN1 17/34 (50%) 20/38 (53%) 20/35 (57%) Mechanism of miRNA deregulation in NKTL Role of MYC • MYC is known to cause extensive repression of miRNA expression (Chang TC, et al. Nat Genet. 2008;40:43-50) • Indeed, in our cohort, tumor samples with increase expression of BLIMP1, MUM1 and STMN1 proteins, regulated by their underexpressed miRNAs, showed higher MYC nuclear expression, consistent with MYC activation EZH2 overexpression in majority of NKTL. 6 8 10 12 A B P=0.003 P=0.002 Inhibition of EZH2 with DZNep induced cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in NK malignant cells. Proposed model of NKTL pathogenesis EBV infection JAK3 mutations P53 mutations LMP-1 or other factors STAT activation MYC activation Regulate miRNA EZH2 Proliferation NF-KB activation P53 P53 Deregulation Deregulation Induce Survivin Anti-apoptotic Future Studies • MYC-EZH2 in about 50%, JAK3 mutation in about 35% – Do they signify 2 molecular groups of NKTL i.e are these abnormalities mutually exclusive or overlapping ? – What are the clinical implications if such subtypes exist? – Opportunity to answer these questions as collaborative projects within the Asian lymphoma study group • STAT3 and p53 mutation • EZH2, MYC and NFKB protein by IHC Acknowledgement YAN Junli Viknes Ng Siok Bian Koh Tze Loong Acknowledgement and thanks National University Health System, Singapore Jim Liang-Seah Tay Baohong Lin Chonglei Bi Joy Tan Gaofeng Huang Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong Yok-Lam Kwong Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Japan Norio Shimizu Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan Katsuyuki Aozasa Funding from NMRC, NRF, MOE