File - Latin is Fun!!!
advertisement

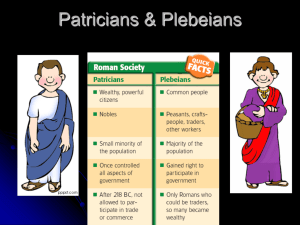
The Roman Villa Peter Thomann 7-1 Mrs. DiPalma Latin Common Vocabulary Used Villa- Country House Villa Rustica- Country House and Farm Patricians- Higher Class Romans Plebeians- Lower Class Romans Atrium- an open space in the house. It is a synonym for courtyard. Domus- is a self contained house Insulae- apartment buildings Villa Urbana- a villa in the city Villa Maritimae- country houses by the sea Vilicus- Overseer of the house Compare and Contrast between the Patricians and the Plebeians The Plebeians are the lower class Romans. They usually shared apartments with their extended family. They usually lived in the city. It was very tight and crowded. They lived in apartment houses, called flats, above or behind their shops. Even fairly wellto-do tradesmen might chose to live in an apartment-building compound over their store, with maybe renters on the upper stories. Their own apartments might be quite roomy, sanitary and pleasant. But others were not that nice. In the apartment houses, or flats, an entire family might all be crowded into one room, without running water. They had to haul their water in from public facilities. Fire was dangerous because people were cooking meals in crowded areas and some of the flats were made of wood. They didn't have toilets, and had to use the public facilities Compare and Contrast between the Patricians and the Plebeians The patricians were the upper class Romans. They lived very differently. Their homes were single family homes, which in ancient Rome meant the grandparents, parents, and kids of one family lived in a home together unlike having two different families in an apartment. Homes were made most of the brick with red tile roofs. The rooms were arranged around a central courtyard. The windows and balconies faced the courtyard to keep homes safe from burglars. There were painting on the walls and mosaics on the floor. There was very little furniture and no carpeting. Wealthy Romans might have a house with a front door, bedrooms, an office, a kitchen, a dining room, a garden, a temple, an atrium, a toilet, and a private bath. Compare and Contrast between the Patricians and the Plebeians Plebeians The Plebeians were the lower class. This was a typical apartment building. There is one door. There were separate floors. Usually two families lived in one apartment. This is a depiction of what an apartment looks like. Someone is throwing something out the window which was very common because sewers didn’t exist. Plebeians In Ancient Rome the Plebeians often lived in the city where it was very crowded. Plebeians Since the Plebeians didn’t have baths in their home they had to use the public baths and restrooms. Patricians The Patricians were the upper class. This included Gaius Cornelius’ family. They were people that were wealthy. Many of the Patricians were involved in government, just like Gaius Cornelius. Patricians also included kings and queens. Patricians The Patricians had beautiful mosaics on the floor. Patricians The Patricians homes were made of red tile roofs and were made of brick and stone. More Homes Shops Shops were a common feature on Roman streets in the front part of many houses and apartment. Most were single rooms but a large number also had rooms in the back for storage in addition to a living quarters. Some shops sold imported goods, while others, like bakeries, would make their wares onsite. During the empire, many shops were built in planned, concentrated markets. Other types of shops, such as inns were common. Animals in the Home The Romans may have had some animals that they used in their homes. A horse may have been used by Gaius Cornelius. Oxen and donkeys could have been used for farming or transportation. Some say the Romans used elephants for war and carrying large amounts. Dogs also may have been in the house. Slavery in the Home This was most likely the slave quarters of a home. The slaves often lived beneath the other rooms. Chores in the Home Unlike men, women were expected to stay at home every day so they could complete the chores around the house and watch the children while their husbands were at work. Very few women were allowed to hold jobs such as being a teacher or doctor. The men were the masters of the house and the family.. If you had been a rich man, you would have begun your day by putting on your toga and eating a breakfast. Before leaving for town, you would pray at the household shrine. The rich man would then begin his work. After a light lunch, you might take a nap, get a haircut, and finish your work for the day. In the late afternoon, all of the Roman men went to the public bathes, then home to enjoy a dinner with friends. Children of wealthy families in Rome started school when they were seven years old. Boys stayed at school longer than girls and learned different things. Girls who went to school learned how to spin, weave, cook, and clean. Girls of poor families learned all of these things at home since they could not afford to go to school. Almost all boys, except for those of very poor families went to school to learn how to read, write in Latin and Greek, do math, and make speeches. These skills were necessary for boys who wished to get a job in the government. Fun Facts The Romans usually lived with their family. Tradesmen looked for a shop that they could have a house behind. Finished