The Metric System - Grosse Pointe Public School System
advertisement

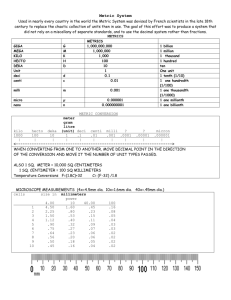
The Metric System The Metric System • • • All scientific measurements are made using the Metric System. It is also called the SI System (La Systeme International d’Unites) The Unites States is the only major country that does not use this system. Very Easy To Use Based on multiples of 10 (10 and 100 and 1,000 and 10,000 … etc.) Much easier conversions because of the 10’s • Think of how hard it is to work with conversions in our system! How many inches in a foot? Feet in a mile? Ounces in a pound? Very Easy To Use It’s a decimal system… Can you think of a system we use every day that is a decimal system? How many pennies in a dime? How many dimes in a dollar? How many $1 dollar bills are in a $10? How many $10 dollar bills in $100? Each measurement has a base unit and a prefix Base unit • the last name of a measurement (tells which family you belong to) and helps you determine what we are measuring Prefix • the first name of a measurement (separates you from the other members of your family) and helps you determine the size of what we are measuring Metric Base Units What we’re measuring Metric Base Unit Length Mass Volume (how long it is) Density (how much matter in a given g/L (for liquids) amount of space) g/m3 (for solids) (how much heat it has) °Celsius second Temp. Time (how much matter is in it) (how much space it takes up) (how long it takes) meter gram liter (for liquids) meter3 (for solids) How Do We Measure Them? Length Temperature Volume Time Mass Length The length, width, or height of an object tells us the distance between two points on that object We use a ruler, meter stick, or tape measure to find this measurement in meters Mass • • The mass is the amount of matter in an object and won’t change. We use a triple beam balance to find the mass of an object in grams. Mass vs. Weight • • Mass is NOT the same as weight! The weight of something is the amount of gravity acting on an object and will change if you go somewhere with more or less gravity. Volume • • For easy-to-measure solids (like a tissue box), we use a ruler to find the volume in cubic meters (m3). Volume (m3) = Length x Width x Height Volume • • The volume is the amount of space an object takes up. For liquids or oddly-shaped solids, we use a graduated cylinder or beaker to find the volume in liters (or mL). Volume • • The surface of the liquid might look slightly curved. This curve is called the meniscus and we read the amount from the lowest point of the meniscus. Density • • • Density is the amount of matter (mass) in a given space (volume) Density = Mass (g) ÷ Volume (mL or m3) For example, water’s density is 1 g/mL which means that there is 1 gram of matter in every mL of water. Density Think of it like a suitcase… the more clothes you try to fit in a suitcase, the more packed it gets. More packed = More dense Density When you compare the density of two or more objects, the denser objects will sink below the less dense objects. Sink or Float? Density REMEMBER: Denser objects sink below less dense objects! • Number your paper 1 – 4 • Order the following objects from least dense (#1) to most dense (#4): • Water (blue), Syrup, Rubbing Alcohol (red), and Vegetable Oil The length of the yellow line in meters (there will be a decimal) is _______ m Use the triple beam balance to find the mass of a football in grams? Use the meniscus (lowest point of the water’s surface) to find the volume of the water (there will be a decimal). The volume is about _______ L. Metric Prefixes kilo hecto deka 1000 base units 100 base units 10 base units BASE UNIT 1 deci 1/10 (0.1) of a base unit centi 1/100 (0.01) of a base unit milli 1/1000 (0.001) of a base unit Moving the Decimal for Length Larger Units, Smaller Number Smaller Units, Larger Number Base Unit kilo (km) Hecto (hm) Deka (dka) METER (m) Deci (dm) Centi (cm) Milli (mm) Moving the Decimal for Mass Larger Units, Smaller Number Smaller Units, Larger Number Base Unit kilo (kg) Hecto (hg) Deka (dkg) GRAM (g) Deci (dg) Centi (cg) Milli (mg) Moving the Decimal for Volume Larger Units, Smaller Number Smaller Units, Larger Number Base Unit kilo (kL) Hecto (hL) Deka (dkL) LITER (L) Deci (dL) Centi (cL) Milli (mL)