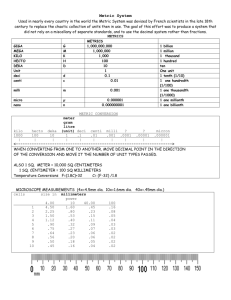
conversion factor
advertisement
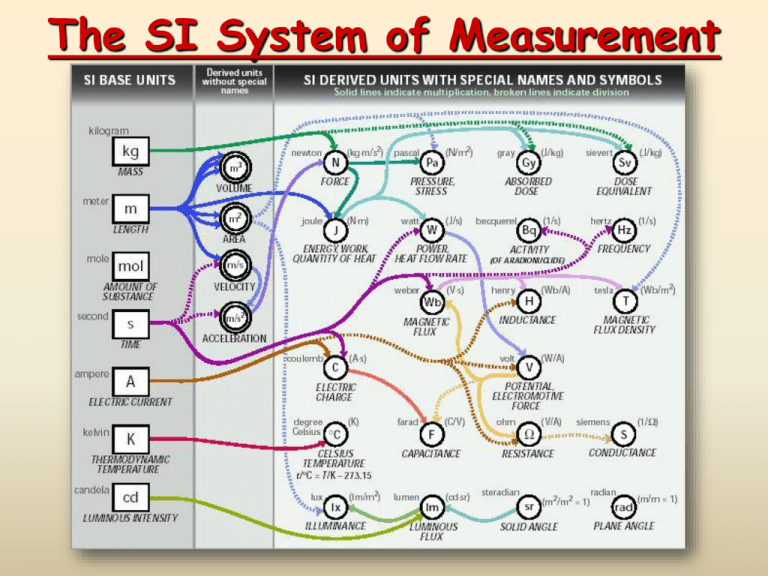
The SI System of Measurement The Nature of Measurement A Measurement is a quantitative observation consisting of TWO parts Part 1 - number Part 2 - scale (unit) Examples: 20 grams 6.63 x 10-34 Joule·seconds Derived SI Units Combinations of SI base units form derived units. pressure is measured in kg/m•s2, or pascals SI Prefixes Common to Chemistry Prefix Kilo Deci Centi Milli Micro Unit Abbr. k d c m Exponent 103 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-6 Metric Conversions 103 102 101 g m L kilo hecto deka Base unit 10-1 10-2 10-3 deci centi milli Conversions in the metric system are merely a matter of moving a decimal point. The “base unit” means the you have a quantity (grams, meters, Liters, etc without a prefix. Metric Conversions 103 102 101 g m L kilo hecto deka Base unit 18 L 10-1 10-2 10-3 deci centi milli 1 2 3 18 liters = 18 000 milliliters Example #1: Convert 18 liters to milliliters Metric Conversions 103 102 101 g m L kilo hecto deka Base unit 450 mg = 0.450 g 10-1 10-2 10-3 deci centi milli 3 2 1 450 mg Example #2: Convert 450 milligrams to grams Metric Conversions 103 102 101 g m L 10-1 10-2 10-3 kilo hecto deka Base deci centi milli unit 2 3 1 4 5 6 20 kg 20 kg = 20 000 000 mg Example #3: Convert 20 kilograms to milligrams Conversion Factors A conversion factor is a ratio derived from the equality between two different units that can be used to convert from one unit to the other. example: How quarters and dollars are related 4 quarters 1 1 dollar 1 dollar 1 4 quarters 0.25 dollar 1 1 quarters 1 quarter 1 0.25 dollar Conversion Factors, continued Dimensional analysis is a mathematical technique that allows you to use units to solve problems involving measurements. quantity sought = quantity given × conversion factor example: the number of quarters in 12 dollars number of quarters = 12 dollars × conversion factor 4 quarter ? quarters 12 dollars 48 quarters 1 dollar Factor Name Symbol Factor Name Symbol 1024 Yotta Y 10-1 Deci d 1021 Zetta Z 10-2 Centi c 1018 Exa E 10-3 Milli m 1015 Peta P 10-6 Micro μ 1012 Tera T 10-9 Nano n 109 Giga G 10-12 Pico p 106 Mega M 10-15 Femto f 103 Kilo k 10-18 Atto a 102 Hecto h 10-21 Zepto z 101 Deka da 10-24 Yocto y Using Conversion Factors Conversion Factors, continued Sample Problem B Express a mass of 5.712 grams in milligrams and in kilograms. Conversion Factors, continued Sample Problem B Solution Express a mass of 5.712 grams in milligrams and in kilograms. Given: 5.712 g Unknown: mass in mg and kg Solution: mg 1 g = 1000 mg Possible conversion factors: 5.712 g 1000 mg 1g and g 1000 mg 1000 mg 5712 mg g Conversion Factors, continued Sample Problem B Solution, continued Express a mass of 5.712 grams in milligrams and in kilograms. Given: 5.712 g Unknown: mass in mg and kg Solution: kg 1 000 g = 1 kg Possible conversion factors: 5.712 g 1000 g 1 kg and kg 1000 g 1 kg 0.005712 kg 1000 g