Dihybrid Cross
advertisement
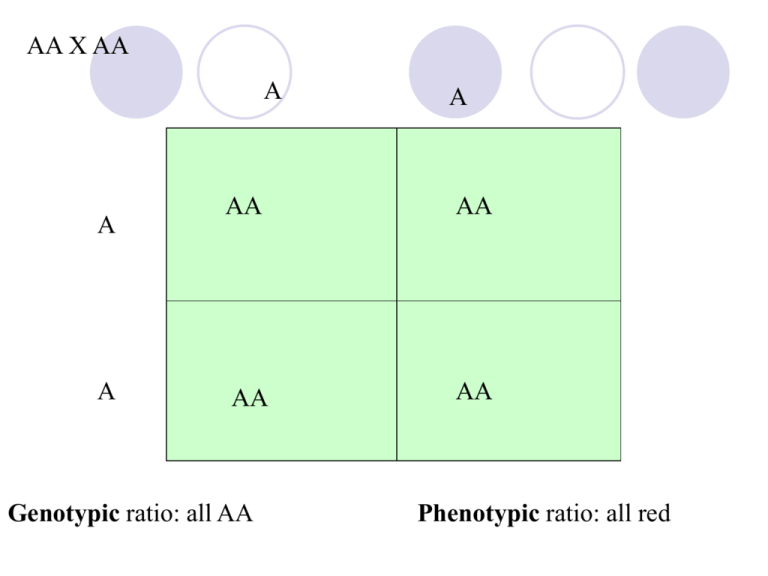
AA X AA A A A A AA AA AA AA Genotypic ratio: all AA Phenotypic ratio: all red AA X Aa A A a A AA AA Aa Aa Genotypic ratio: 1AA:1Aa Phenotypic ratio: all red AA X aa A a a A Aa Aa Aa Aa Genotypic ratio: all Aa Phenotypic ratio: all show dominant trait Aa X Aa A A a a AA Aa Aa aa aa Genotypic ratio: 1 AA:2Aa:1aa Phenotypic ratio: 3 not red:1 red Aa X aa A a a Aa Aa Aa Aa Genotypic ratio: 1 Aa:1 aa a aa aa Phenotypic ratio: 1 red: 1white aa X aa a a a a aa aa aa aa Genotypic ratio: all aa Phenotypic ratio: all white Complete Dominance vs. Incomplete Dominance Most traits display complete dominance the presence of one dominant allele masks the recessive allele Some traits display incomplete dominance the heterozygous condition results in a separate phenotype, neither allele is completely dominant-they blend together In some flowers, AA is red, Aa is pink, and aa is white Codominance Some traits are controlled by codominance: both alleles for a gene are expressed in heterozygous offspring. neither allele is dominant or recessive, nor do they blend; each is expressed equally. the best example of this is in a horse’s coat color; heterozygous = roan color where they have both white and red hairs. Dihybrid Cross dihybrid cross between individuals with two pairs of traits. Dihybrid Cross Rules First figure out what the gametes are that the parents can make. Use the FOIL method to do this. Parents: AaBb X AaBb Gametes: AB, Ab, aB, ab X AB, Ab, aB, ab Then place the gametes along the top and sides of the square and do the cross. Dihybrid Cross Gametes from Parent One (Female) Gametes from Parent Two (Male) AB Ab aB ab AB AABB AABb AaBB AaBb Ab AABb AAbb AaBb Aabb aB AaBB AaBb aaBB aaBb ab AaBb Aabb aaBb aabb Multiple Alleles Several alleles exist for a trait Sex Influenced Traits Traits expressed differently in males and females Example: baldness male female BB Bb bb bald bald not bald bald not bald not bald