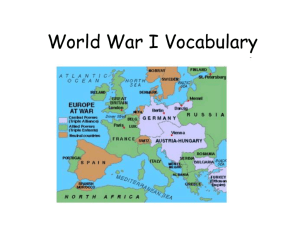
Triple Alliance
advertisement
The Great War -- Terms and Concepts: Modern Ideas German Naval Buildup Triple Alliance Black Hand Dual Alliance Nicholas II Franco-Russian Alliance Anglo-Russian Entente Worker’s unions and worker’s parties Vladimir Lenin Spread of industry in Europe “Young Turks” these new ideas challenged the old views of life and the universe (mostly based on the era of the Enlightenment and the Christian religion in Europe and North America). They included Einstein’s atomic theory, modern psychology from Freud, and evolution from Darwin a program to build up the German navy and improve naval weaponry; worsened relations between rivals Britain and Germany Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy; signed in 1882 a Serbian militant group, financed by Serbian government with aim to enlarge Serbian territory with Austrian lands the alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary signed in 1879 Tsar (emperor) of Russia, also played a part in beginning of World War I, and his decision to take field command helped bring on the revolution alliance between Russia and France in 1894 to counter the Triple alliance alliance between England and Russian signed in 1907; finalized the addition of England to the Franco-Russian alliance; finalized the Triple Entente created to give more power to workers for wages and working conditions, they . They ranged from trade unions to socialist parties to communism and anarchism Russian head of the international Communist party (Bolsheviks), who led the successful revolution in Russia in 1917 changed the population, with more people living in cities, with larger countries needing colonies for selling its industrial goods, and creating tariffs to prevent other countries from selling goods to home and colonies Term given to the group of younger Turkish officers, like Enver Pasha, helped change the government in Turkey Balkan Wars Triple Entente Eastern European selfdetermination Archduke Franz Ferdinand Gavrilo Princip Austrian demands Central Powers Italy Trench Warfare tactics Battle of Verdun Battle of Somme Hindenburg and Ludendorff The U-boat Wars fought in 1912 and 1913, in which Turkey lost most of its territory west of the Bosporus. This caused further tensions and encouraged Turkey to seek allies in Europe Britain, Russian and France; Later joined by Romania, Greece and the United States; also called the Allies the want of the Eastern European ethnic minorities to be able to be given the freedom to decide whether or not to become an individual nationalistic state heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary; assassinated in Sarajevo, triggering the events that led to war assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand, one of six assassins attempting to do so; a member of the Black Hand Sent out on July 23; responded to on July 25; caused Austria to declare war on Serbia on July 28 Germany, Austria-Hungry, Turkey, Italy, Bulgaria; new name of the Triple Alliance switched sides on April 29, 1915 in the Treaty of London in return for territorial concessions in Turkey and the Adriatic dragged out the war due to effectiveness against infantry charge; tactics to defeat trench warfare included heavy artillery bombardment and frontal attaches which only resulted in huge casualties Germans attached a key French fortress to force the Allies into a peace settlement in February 1916; huge numbers of casualties due to superior defense over offense British counter attach to the Battle of Verdun into German territory, Somme, also in 1916; huge numbers of casualties due to superior defense over offense The principal field marshals, first in the East, then created the late 1915 strategy of defensive on land in the west, creating the Hindenburg line, until Russia was forced out. They then renewed unrestricted submarine warfare and launched a major offensive against British troops in France Germany’s best hope of forcing Britain out of the war by starving the home front with merchant losses. After the US threatened intervention in 1915, the submarines were confined to warning before attacking ships. French mutiny Zeppelins Kaiser William II Trench warfare Poison gas Munitions “canaries” “shell shock” “Lafayette Escadrille” 14 Points American Neutrality Lusitania Zimmerman Telegram Ludendorff Offensive A “strike” by French troops following heavy losses at Verdun, which forced France to act defensively while Britain launched an attack in 1917. German weapon for attacking Great Britain from the air. Emperor of Germany and formal commander of German forces, he occasionally interfered in strategy – which harmed his image when battles failed the military stalemate in France from 1915 to 1918 that caused millions of casualties in pointless attacks against fortified positions and destroyed military morale a variety of gases (usually mustard, chlorine or phosgene) used by all forces through the war British women who worked in munitions plants were given this nickname because the chemicals affected their skin and, like canaries in mines, the work was so dangerous term to describe a number of injuries related to the damage that constant shell bursts did to men’s nervous systems while Americans joined the French Foreign Legion as early as 1914 and served as ambulance drivers with the French army, American fliers joined the French Air Service and in late 1915 formed this special squadron Woodrow Wilson’s plan for a postwar settlement, stressing national self-determination, no secret treaties, disarmament, freedom of trade and a League of Nations to promote peace. US stays out of World War I from 1914 to 1917, but lends money to Britain and sells arms to Britain and France, angering Germany the death of over 100 Americans when a German submarine sinks this British ship in 1915 moves American closer to war against Germany British agents intercept this telegram from Germany to Mexico, offering military help to Mexico for an attack on the United States. Helps trigger US declaration of war against Germany in 1917 The final German effort to win the war in France before American troops arrived in force, consisting of attacks from March 1918ninto late April. The failure to break the Allied League of Nations Treaty of Versailles "War Guilt" Clause “Lost Generation” lines exhausted the German army and allowed the Allies to begin their own attacks in the summer. the international congress (1st United Nations, in effect) created by Treaty of Versailles for promoting peace. US does not join League even though it was Wilson’s idea ended World War I and imposed serious penalties on the Triple Alliance powers a clause in the Versailles Treaty that stated the war was provoked by Germany, thus giving the Allies their claim to reparations term for those who had died or lost their innocence in the Great War.