Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer Lecture
advertisement

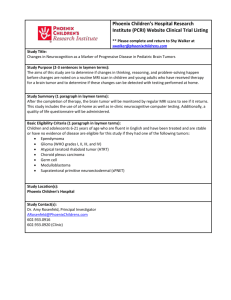
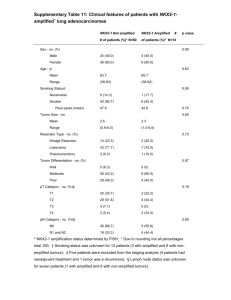
CELL CYCLE REGULATION & CANCER NORMAL CELL CYCLE • Cyclins: proteins • CDKs (Cyclin dependent kinases): enzymes • Cyclins and CDKs bind together to activate parts of the cell cycle NORMAL CELL CYCLE • G1 checkpoint • G2 checkpoint • M checkpoint • If something is wrong, cycle will STOP ABNORMAL CELL CYCLE • CANCER: when cell cycle regulations fail • Crowd out normal cells • Spend less time in Interphase ABNORMAL CELL CYCLE • Apoptosis:cell death( if damaged) • Cancer: no apoptosis TUMOR: MASS OF CANCER CELLS • TWO TYPES OF TUMORS • Benign: stays contained • Malignant: spread to nearby tissue or other organs WHY ARE TUMORS BAD? • Angiogenesis: when tumors get a blood supply • nutrients and oxygen go to tumor WHY ARE TUMORS BAD? • Metastasis: pieces of tumor travel through blood to other organs CAUSES OF CANCER • Gene Mutations: changes in genes that control cell cycle • What causes these mutations? CANCER CAUSES • Carcinogens: cancer causing substances • EX: tobacco smoke, asbestos • Radiation • EX: UV light from sun, X-rays CANCER CAUSES • Virus • EX: Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) • Hereditary • EX: breast • Sporadic (no reason) TREATMENTS • Prevention!!!!! • Diet, exercise, healthy weight, no smoking, limit alcohol • Screenings • Catch it early! • Mammograms • Pap smear • Colonoscopy TREATMENTS • Surgery • Remove tumor and surrounding tissue • Radiation • Directly kill tumor • Chemotherapy • Drug treatment Incidence Rates: Male (From CDC) Incidence Rates: Female Death Rates: Male Death Rates: Female http://www.bozemanscience.com/what-is-cancer/