File - Kathleen Funck, MCD
advertisement

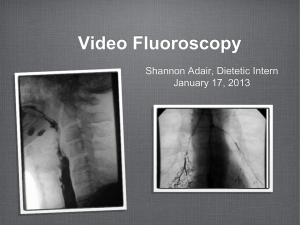
Dysphagia Dental Care Kathleen Funck About me Kathleen Funck, MCD, CCC-SLP • Who am I? – Kathleen Funck • Where did I graduate? – LSU Health New Orleans 2014 • Where do I work? – Veterans Affairs Medical Center • What’s my focus? – Degenerative Diseases Agenda What we will cover today: ✓ 1 Welcome 2 Dysphagia 3 Who is involved? 4 Evaluation and Treatment 5 Surprise Kathleen Funck Dysphagia What is it? •United States Department of Veterans Affairs Defines it as - A swallowing disorder •National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders Defines it as -having difficulty swallowing and may even experience pain while swallowing Kathleen Funck Etiologies Strokes 1 Approximately 71 to 73% of patients with a stroke have swallowing disorders Head Injuries 2 51% of patients admitted with severe hcad injury showed pharyngeal problems affecting swallowing Head and Neck Cancer 3 severity can depend on the tumor size, staging and location, and the type of surgical resection and reconstruction. No case is the same and no individual should be treated the same. Every case is unique and different. Progressive Neurologic Diseases 4 Approximately 300,000 to 600,000 people each year Kathleen Funck Terminology Aspiration Bolus entry of secretions, food, or any foreign material into the airway that travels below the level of the true vocal folds. the food, liquid, or other material placed in the mouth for ingestion Degluttion refers only to acts associated with bolus transfer and transport from the oral cavity to the stomach Laryngeal Penetration the entry of secretions, food/liquid, or any foreign material into the laryngeal vestibule above the level of the true vocal folds which are then ejected from the airway. This can occur normally and can also occur before, during, or after the pharyngeal swallow. Vallecula Silent Aspiration A channel, or depression between the base of the tongue and the epiglottis Material breaches vocal folds into trachea and potentially into lungs without any signs Kathleen Funck Phases of a Swallow Oral Phase 1 Oral Preparatory: reducing food to a bolus and position it for transport. Oral Transport: bolus is prepared for transport from the anterior to posterior oral cavity Pharyngeal Phase 2 • Velopharyngeal port closes • Hyoid bone and larynx begin ascent • Epiglottis folds down • Tongue to the posterior pharyngeal wall • Pharyngeal constrictors • Cricopharyngeus muscle • UES. Esophageal Phase 3 • • UES opens and food is propelled down through the esophagus LES opens and food goes into stomach Kathleen Funck Who is involved? Everyone Doctors and the Nursing Staff Speech, Physical, Occupational Therapy Dietians, Dental Care Family and Friends Kathleen Funck Multi-disciplinary Approach •Speech Language Pathologist The goal is to maximize the safety and efficiency of eating. -Feeding evaluations and treatments 84% in hospitals 90% in residential health care •Dental Care The goal is to provide daily dental and denture hygiene Your Logo Symptoms • Hesitation to swallow • Painful swallow • Constant feeling of a lump in the throat • Food sticking in the throat • Regurgitation • Hoarse voice • Repetitive swallowing • Coughing during or after swallow • The feeling having to “wash down” foods • Unexpected weight loss Kathleen Funck Evaluations Bedside Evaluation It includes a structural and functional evaluation of the 2 muscles and structures used in swallowing, functional evaluation of actual swallowing ability, and judgments of adequacy of airway protection and coordination of respiration and swallowing Instrumental Evaluation Videofluorscopic swallowing evaluation (VFSS) Fberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing (FEES) Standardized Testing Swallowing Ability and Function Evaluation (SAFE) Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability (MASA) Kathleen Funck Bedside Evaluation • • • • • • • • Past medical history Current medical status and medications Nutrition/Hydration Respiratory status Cognitive/Communicative history Posture and Movement Alertness and Awareness Auditory and Visual Acuity • Oral Motor Exam • Laryngeal Function • Respiratory Status • Trial Swallows Kathleen Funck Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study • • • • Bolus Size Texture Position of Patient Radiographic focus of the structures • More Accurate Kathleen Funck VFSS Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study VFSS Videofluoroscopic Swallow Study Treatment Supraglottic Swallow • Take a breath • Hold it while swallowing • Then cough after the swallow 1 Supersupraglottic Swallow same procedure as with the supraglottic swallow, but bear down while holding breath 2 Postures 3 • Head Down • Head Back • Head Turn • Head Tilt and turn Mendelsohn Maneuver 4 Turn head to weak side and tilt head to strong side learns to use muscles to keep the larynx elevated for several seconds after the swallow. Thermal and Tactile Stimulation Your own footer 5 • • • • Tapping or rubbing of the faucial pillars using frozen q-tips, or lemon ice Presenting a warm or cold bolus strong tastes or textures Pressing the spoon on the tongue when food is presented Your Logo Diets Level 1: Pureed Level 2: Mechanical Altered Level 4: Regular Level 3: Advanced Kathleen Funck This is placeholder text. Liquids Thin Thick Kathleen Funck This is placeholder text. Important? Patient Better quality of life Professional Staff Material aspirated is heavily colonized with bacteria. Rapid development of extensive bacterial colonies around the teeth will lead to colonization by respiratory pathogens. The risk becomes increasingly prevalent the longer a dependent patient resides in a health care environment. All of these patients are at elevated risk for aspirationrelated pneumonia if not provided good dental hygiene. Kathleen Funck Test your knowledge True OR False Kathleen Funck Stroke is the leading cause of neurologic dysphagia? True OR False Kathleen Funck More than 60,000 people die annually from complications related to dysphagia, making it the sixth leading cause of death in the United States? True OR False Kathleen Funck Videofluoroscopic examination is essential and the same assessment techniques may be used with all patients with dysphagia? True OR False Kathleen Funck THANK YOU! Contact me at: kfunck@lsuhsc.edu Your Logo



![Dysphagia Webinar, May, 2013[2]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005382560_1-ff5244e89815170fde8b3f907df8b381-300x300.png)