01 Population Dynamics intro v2
advertisement

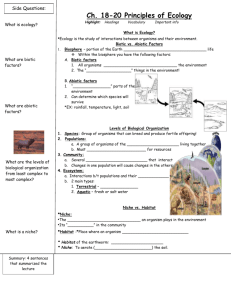
What do terms like biosphere, ecosystem, population, and ecology make you think of? Work with 3-4 partners and quickly sketch a concept map. SBI4U RHSA http://teachers.saschina.org/dbister/files/2010/11/Biology_Biosphere1.jpg Ecology is the study of the abundance of plants, animals, bacteria, fungus and other organisms as well as their distribution and environmental interactions with each other. The environment consists of all the biotic and abiotic components that surround an organism. Name biotic and abiotic factors in this ecosystem. Describe some interactions between the biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic or living parts of the environment include plants, animals and other organisms. Abiotic or non living parts include physical and chemical parts of the environment such as temperature, light, water, nutrients or concrete. AGAIN - Name biotic and abiotic factors in this ecosystem. Describe some interactions between the biotic and abiotic factors. Ecologists focus their research on one of four categories: 1. Organism - individuals of a species (e.g. fish) 2. Population –a group of individuals of the same species living in the same geographical area e.g. a school of fish 3. Community -all the organisms in all the interacting populations in a given area e.g. all the fish, plants, algae, coral in a reef 4. Ecosystem - a community of living organisms together and the abiotic factors that surround and affect it. e.g. wind, water, sunlight around the reef community Use the grade 9 terms organism, population, producer, consumer, autotroph, heterotroph, community and ecosystem while describing this photo of the Asian steppes. Biomes are generalized ecosystems with specific climate and the species evolved to succeed there. Example: cacti in a desert biome. Name the other biomes shown. Choose one organism inferred in the picture and describe its’ habitat and its’ niche. A habitat is a specific set of biotic and abiotic characteristics in which individuals of a species can thrive. This is different than an ecological niche which is the task an organism plays in the habitat. For example a beaver lives in a boreal forest habitat but it’s niche is to be a consumer of trees and to modify the habitat to convert rivers to ponds for other organisms. Succession Change is a major factor in ecology. Populations change due to predation, competition for food or rainfall changes. The change in a population of grass will affect the population of sparrows in the community. Ecological succession is the process of successive change in species composition. Types of Succession Primary Succession occurs where no living species were previously found. e.g. a new island. The first species to arrive are pioneer species like lichen which form soil from rock. Secondary succession occurs when patches of a community are disturbed by fire, flood or logging. Colonizers are the species that thrive in open disturbed areas and their growth gives shade for other species. A stable self perpetuating community is called a climax community. How lichen work – symbiosis! A fungus and an algae or photosynthetic bacteria work together. What What What What happened in picture 1? evidence supports your hypothesis? changes can be seen in picture 2? type of succession is occurring? Describe the type of succession that is occurring – where, when , why and how does this happen?