Antidiabetic drugs and renal failure
advertisement

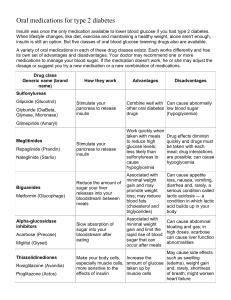
Antidiabetic and Antilipid drugs and renal failure DR M.MORTAZAVI NEPHROLOGIST Goal To understand the use and side effects of anti-diabetic medications and be able to educate patients. Guidelines for Glycemic, BP, & Lipid Control American Diabetes Assoc. Goals HbA1C Preprandial glucose Postprandial glucose < 7.0% (individualization) 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/l) < 180 mg/dL Blood pressure < 130/80 mmHg Lipids LDL: < 100 mg/dL (2.59 mmol/l) < 70 mg/dL (1.81 mmol/l) (with overt CVD) HDL: > 40 mg/dL (1.04 mmol/l) > 50 mg/dL (1.30 mmol/l) TG: < 150 mg/dL (1.69 mmol/l) HDL = high-density lipoprotein; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; PG = plasma glucose; TG = triglycerides. ADA. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:S11-63 Nine to Know Brand & Generic Name Mechanism of action Therapeutic effect Relevant pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Dosing by route Adverse reactions and contraindications Monitoring parameters Drug-drug and drug food interactions Comparisons between agents w/in the same class of drugs Main Pathophysiological Defects in T2DM pancreatic insulin secretion incretin effect - gut carbohydrate delivery & absorption pancreatic glucagon secretion ? HYPERGLYCEMIA + hepatic glucose production peripheral glucose uptake Adapted from: Inzucchi SE, Sherwin RS in: Cecil Medicine 2011 Type 2 Diabetes High blood glucose Impaired GI motility 1. Defective beta cell function • • Diminished phase 1 insulin release Delayed phase 2 insulin release 2. Overproduction of glucagon 1. Tissues less sensitive to insulin 2. Liver produces excess glucose Image Obtained From: Diabetes 101: Overview of Drug Therapy by Jennifer Danielson, RPh, CDE Type 2 Video from diabetes.com ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 3. ANTI-HYPERGLYCEMIC THERAPY • Therapeutic options: Oral agents & non-insulin injectables - Metformin - Sulfonylureas - Thiazolidinediones - Meglitinides - a-glucosidase inhibitors - Bile acid sequestrants Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] Biguanides Metformin Glucophage 500, 850, 1000 mg tablets (Glucophage XR) 500, 750 mg XR tablets Indication Type II Diabetes Mellitus, Antipsychotic-induced weight gain MOA Decrease hepatic glucose production, decrease intestinal absorption of glucose and increase insulin sensitivity therefore increasing peripheral glucose uptake Biguanides (cont) Patient Info Upset stomach/dyspepsia – take with food Metallic taste Minimal Weight Loss Alcohol may increase likelihood of lactic acidosis Does not cause hypoglycemia Biguanides (cont) Special Population Considerations: Geriatric: limited data suggests starting doses should be 33% lower for geriatric patients than that of an adult dose. Titration should also to a lower limit. Cautions/Severe Adverse Reactions Black Box Lactic Acidosis: D/C immediately and notify practitioner if: myalgia, malaise, hyperventilation, unusual somnolence. Alcohol potentiates this reaction Biguanides (cont) CONTRAINDICATIONS Renal disease or renal dysfunction (Scr > 1.5 mg/dL in males, >1.4 mg/dL in females) Abnormal Scr from any cause including: shock, acute MI, or septicemia Metabolic acidosis (including diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)) Heart failure requiring pharmacologic therapy; active liver failure Sulfonylureas Gliclazid 80 mg Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL) (2.5), 5, 10 mg (XL) tablets Glyburide (DiaBeta) 1.25, 2.5, 5 mg tablets Indications Adjuncts to diet and exercise to lower blood glucose in patients w/ type II diabetes mellitus MOA Stimulating insulin release from beta-cells of pancreatic islets Where does it work? Image Obtained From: Diabetes 101: Overview of Drug Therapy by Jennifer Danielson, RPh, CDE Sulfonylureas (cont) Patient Info Hypoglycemia GI upset/abdominal pain Dizziness Weight gain Heartburn/epigastric fullness Onset: glucose lowering effect: 30 minutes with peak at 1.5-3 hours lasting 24 hours Sulfonylureas (cont) Special Population Considerations: Pediatric: safety and efficacy not established for pts under age 16 Hepatic/Renal Dysfunction: conservative dosing and titration recommended. Caution/Severe Adverse Reactions Syndrome of Inappropriate Anti-diuretic Hormone (SIADH) CONTRAINDICATIONS Diabetes complicated by ketoacidosis Type I DM Diabetes w/ pregnancy. Pregnancy Cat: C (except glyburide: B) Thiazolidinediones (TZD) Pioglitazone (Actos) 15, 30, 45 mg tablets Rosiglitazone (Avandia) 2, 4, 8 mg tablets Indications As adjunct to diet and exercise for type II diabetes MOA Increase insulin sensitivity by affecting PPAR-γ (peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor) at adipose tissue, skeletal muscle and in the liver. Where does it work? Image Obtained From: Diabetes 101: Overview of Drug Therapy by Jennifer Danielson, RPh, CDE TZD (cont) Patient Info Weight gain Edema Hypoglycemia esp. when used with other antidiabetic medications and insulin (not w/ metformin) May cause or exacerbate heart failure with risk of fluid retention Myalgia Headache TZD (cont) Cautions/Severe Adverse Reactions Black Box: Heart Failure (for all thiazolidinediones, mainly due to rosiglitazone) Hepatic failure Anemia Bone loss Ovulation in premenopausal women Pregancy Cat: C TZD (cont) Special Populations Considerations: Congestive Heart Failure: should be initiated at lowest approved dose with longer intervals between dose increases for NYHA class II. Use is not recommended in patients with NYHA Class III or IV CHF CONTRAINDICATIONS NYHA Class III-IV heart failure Active liver disease (ALT > 2.5 upper limit of normal) Insulin Indications Type I diabetes mellitus, type II diabetes mellitus, hyperkalemia, DKA/diabetic coma MOA Stimulating peripheral glucose uptake and inhibiting hepatic glucose production Patient Info Hypoglycemia (BG < 70 mg/dL) esp with higher doses Anxiety, blurred vision, palpitations, shakiness, slurred speech, sweating Weight gain Indication for insulin therapy: Where does it work? Image Obtained From: Diabetes 101: Overview of Drug Therapy by Jennifer Danielson, RPh, CDE Insulin: the Movie from diabetes.org Insulin (cont) Administration: Subcutaneous injection Rotate site Check blood sugars regularly Storage: Refrigerate until use Once vial is punctured, it is good for 28 days and can be left at room temperature (except for glargine which is 90 days) Insulin (cont) Dosing: Starting daily dose: 0.5-1 unit/kg/day in divided doses Adjust according to fasting (premeal) blood glucose of 80-130 mg/dL and peak postprandial blood glucose < 180 mg/dL Provide 50% as long acting insulin and 50% as prandial insulin 1 unit of can account for 30 grams of carbohydrate (14-50) 1 unit can lower 50 mg/dL blood glucose (10-100) Special Population Consderations: Renal dysfunction CrCl 10-50 mL/min: 75% of normal dose CrCl < 10 ml/min: 25-50% of normal dose; monitor closely Exercise??? ---- Acute Stress??? ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 3. ANTI-HYPERGLYCEMIC THERAPY • Therapeutic options: Insulin Insulin level Rapid (Lispro, Aspart, Glulisine) Short (Regular) Intermediate (NPH) Long (Detemir) Long (Glargine) 0 2 4 6 8 Hours 10 12 14 16 Hours after injection 18 20 22 24 Insulin Dosing Long-acting Long-acting & Short-acting Normal insulin secretion 70/30 pre-mixed Insulin Comparison Chart courses.washington.edu/pharm504/Insulin%20Chart.pdf Class Mechanism Advantages Disadvantages Cost Biguanides • Activates AMP-kinase • Hepatic glucose production • Extensive experience • No hypoglycemia • Weight neutral • ? CVD • Gastrointestinal • Lactic acidosis • B-12 deficiency • Contraindications Low SUs / Meglitinides • Closes KATP channels • Insulin secretion • Extensive experience • Microvasc. risk • Hypoglycemia • Weight gain • Low durability • ? Ischemic preconditioning Low TZDs • PPAR-g activator • insulin sensitivity • No hypoglycemia • Durability • TGs, HDL-C • ? CVD (pio) • Weight gain • Edema / heart failure • Bone fractures • ? MI (rosi) • ? Bladder ca (pio) High a-GIs • Inhibits aglucosidase • Slows carbohydrate absorption • No hypoglycemia • Gastrointestinal • Nonsystemic • Dosing frequency • Post-prandial glucose • Modest A1c • ? CVD events Table 1. Properties of anti-hyperglycemic agents Mod. Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] Class Mechanism Advantages Disadvantages Cost DPP-4 inhibitors • Inhibits DPP-4 • Increases GLP-1, GIP • No hypoglycemia • Well tolerated • Modest A1c • ? Pancreatitis • Urticaria High GLP-1 receptor agonists • Activates GLP-1 R • Insulin, glucagon • gastric emptying • satiety • Weight loss • No hypoglycemia • ? Beta cell mass • ? CV protection • GI • ? Pancreatitis • Medullary ca • Injectable High Amylin mimetics • Activates amylin receptor • glucagon • gastric emptying • satiety • Weight loss • PPG • GI • Modest A1c • Injectable • Hypo w/ insulin • Dosing frequency High Bile acid sequestrants • Bind bile acids • Hepatic glucose production • No hypoglycemia • GI • Nonsystemic • Modest A1c • Post-prandial glucose • Dosing frequency • CVD events High Dopamine-2 agonists • Activates DA receptor • Modulates hypothalamic control of metabolism • insulin sensitivity • No hypoglyemia • ? CVD events • Modest A1c • Dizziness/syncope • Nausea • Fatigue High Table 1. Properties of anti-hyperglycemic agents Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] Class Insulin Mechanism • Activates insulin receptor • peripheral glucose uptake Advantages • Universally effective • Unlimited efficacy • Microvascular risk Table 1. Properties of anti-hyperglycemic agents Disadvantages • Hypoglycemia • Weight gain • ? Mitogenicity • Injectable • Training requirements • “Stigma” Cost Variable Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 4. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS • Comorbidities Metformin: CVD benefit (UKPDS) - Coronary Disease Avoid hypoglycemia - Heart Failure ? SUs & ischemic preconditioning - Renal disease ? Pioglitazone & CVD events - Liver dysfunction - Hypoglycemia Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 4. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS • Comorbidities - Coronary Disease Metformin: May use unless - Heart Failure condition is unstable or severe Avoid TZDs - Renal disease - Liver dysfunction - Hypoglycemia Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 4. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS • Comorbidities - Coronary Disease - Heart Failure Increased risk of hypoglycemia - Renal disease Metformin & lactic acidosis - Liver dysfunction - Hypoglycemia US: stop @SCr ≥ 1.5 (1.4 women) UK: dose @GFR <45 & stop @GFR <30 Caution with SUs (esp. glyburide) Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 4. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS • Comorbidities - Coronary Disease - Heart Failure - Renal disease - Liver dysfunction - Hypoglycemia Most drugs not tested in advanced liver disease Pioglitazone may help steatosis Insulin best option if disease severe Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] ADA-EASD Position Statement: Management of Hyperglycemia in T2DM 4. OTHER CONSIDERATIONS • Comorbidities - Coronary Disease - Heart Failure - Renal disease - Liver dysfunction - Hypoglycemia Emerging concerns regarding association with increased mortality Proper drug selection in the hypoglycemia prone Diabetes Care, Diabetologia. 19 April 2012 [Epub ahead of print] Antilipid Drugs DR.M.MORTAZAVI NEPHROLOGIST Lipoproteins Low-density lipoproteins (LDL): Elevation of LDL: Atherosclerotic plaque formation Increases the risk for heart disease High-density lipoproteins (HDL): Take cholesterol from the peripheral cells and transport it to the liver Cholesterol Levels HDL cholesterol: Protects against heart diseases Higher the LDL level: Greater the risk for heart disease Drugs used to treat hyperlipidemia: Bile acid sequestrants HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors Fibric acid derivatives Niacin HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Actions Statins** HMG-CoA reductase: An enzyme that is a catalyst during the manufacture of cholesterol Inhibits the manufacture of cholesterol or promotes the breakdown of cholesterol Lowers the blood levels of cholesterol and serum triglycerides Increases blood levels of HDLs HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Uses As adjunct to diet in the treatment of hyperlipidemia For primary prevention of coronary events MI For secondary prevention of cardiovascular events TIA/stroke HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Adverse Reactions Central nervous system reactions: Gastrointestinal reactions: Headache, blurred vision, dizziness, insomnia Flatulence, abdominal pain, cramping, constipation, nausea Other: Elevated CPK level, Rhabdomyolysis with possible renal failure Pharyngitis with use of rosuvastatin/Crestor HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Contraindications And Precautions Contraindicated in patients: With hypersensitivity to the drugs, serious liver disorders During pregnancy and lactation Used cautiously in patients with: History of alcoholism, acute infection, hypotension, trauma, endocrine disorders, visual disturbances, and myopathy Nursing alert Pts taking cyclosporine, Asians and those with severe renal insufficiency are at risk for myopathy/rhabdomyolysis when taking rosuvastatin/Crestor HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Interactions Interactant Drug Macrolides, erythromycin, clarithromycin Amiodarone Niacin Effect of Interaction Increased risk of severe myopathy or rhabdomyolysis Increased risk for myopathy and for severe myopathy or rhabdomyolysis Increased risk for severe myopathy or rhabdomyolysis Bile Acid Sequestrants: Actions and Use Bile: Manufactured, secreted by liver -Stored in the gallbladder, emulsifies fat, lipids Used to treat: Hyperlipidemia; Pruritus associated with partial biliary obstruction Bile Acid Sequestrants: Adverse Reactions Constipation Aggravation of hemorrhoids Abdominal cramps Nausea Increased bleeding tendencies related to vitamin K malabsorption, and vitamin A and D deficiencies Bile Acid Sequestrants: Contraindications And Precautions Contraindicated in patients : With known hypersensitivity to the drugs With complete biliary obstruction With liver disease Used cautiously in patients: With liver disease, kidney disease During pregnancy and lactation Bile Acid Sequestrants : Interactions Drug Interactant Anticoagulants Thyroid hormone Ursodiol Effect of Interaction Decreased effect of the anticoagulant (cholestyramine) Loss of efficacy of thyroid; also hypothyroidism (particularly with cholestyramine) Reduced absorption of ursodiol (particularly cholestyramine and colestipol) Fibric Acid Derivatives: Actions Clofibrate: Stimulates liver to increase breakdown of very–low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs) to lowdensity lipoproteins (LDLs); Decreases liver synthesis of VLDLs and inhibites cholesterol formation Fenofibrate: Reduces VLDL; Stimulates catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins; Decreases plasma triglyceride, cholesterol Fibric Acid Derivatives: Actions (cont’d) Gemfibrozil: Increases Reduces liver Lowers excretion of cholesterol in the feces the production of triglycerides by the serum lipid levels Fibric Acid Derivatives: Uses Clofibrate and gemfibrozil: Used to treat individuals with very high serum triglyceride levels who are at risk for abdominal pain, pancreatitis Fenofibrate: Used as adjunctive treatment for reducing LDL, total cholesterol, triglycerides in patients with hyperlipidemia Fibric Acid Derivatives Adverse Reactions: Nausea, vomiting, GI upset, diarrhea, cholelithiasis or cholecystitis Contraindicated in patients: With hypersensitivity to the drugs and those with significant hepatic or renal dysfunction or primary biliary cirrhosis Used cautiously in patients with: Peptic ulcer disease, diabetes, during pregnancy and lactation Miscellaneous Antihyperlipidemic Drugs: Niacin Action: Lowers blood lipid levels Uses: Adjunctive therapy for lowering very high serum triglyceride levels in patients who are at risk for pancreatitis Adverse reactions: Gastrointestinal reactions: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea Other reactions: Severe generalized flushing of the skin, sensation of warmth, Miscellaneous Antihyperlipidemic Drugs: Contraindications And Precautions Contraindicated in patients: With known hypersensitivity to niacin, active peptic ulcer, hepatic dysfunction, and arterial bleeding Used cautiously in patients with: Renal dysfunction, high alcohol consumption, unstable angina, gout, pregnancy Thank you