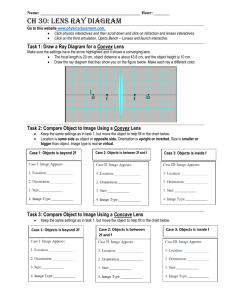
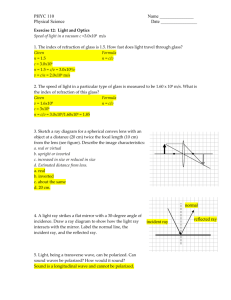
Blue Ray Light
advertisement

Blue Ray Light Blue Ray light is a color in the visible light spectrum that is found in both natural and artificial sources. While some blue ray light can help regulate our natural circadian rhythm and boost our mood, research has shown that increased exposure to blue ray light can have damaging effects on our health. What is Blue Ray Light? In order to understand blue ray light, we need to understand light in general. All light is made up of electromagnetic particles that emit radiation, but humans can only see some of this light. Human eyes are only sensitive to light on the visible light spectrum, and we see these as colors such as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. These colors all have their own wavelengths. Shorter wavelengths result in higher amounts of energy, while longer wavelengths produce less energy. Blue ray light falls into the visible light spectrum and has one of the shortest wavelengths and thus, produces a high amount of energy. The long wavelength of blue ray light allows it to produce a flickering effect, which then creates a strong glare. This glare can affect our vision negatively by reducing the sharpness, clarity, and visual contrast. Why it’s important Your tablet, computers, phones, LED lighting, compact fluorescent lamps, and even the sun have blue ray light. But today’s electronic evolution has made the effects of blue ray light a bigger problem than it was in the past. More and more humans are spending their waking hours staring at computer screens or tablets, whether it’s for work or for play. This has led researchers to begin studying the effects of blue ray light on our health, and the results aren’t ideal. In the 1980s, researchers took rhesus monkeys and conducted experiments on them to discover the prolonged effects of blue ray light on their retinas. They found that the monkeys developed lesions on the retina after being exposed to 1,000 seconds of blue ray light. Other studies have demonstrated the importance that blue ray light plays on the body’s sleep patterns. It is continuing to be studied today, but it is clear that blue ray light affects more than just a person’s eyes and their sleep patterns. Health Problems It should be noted that not all blue ray light is bad. In particular, the blue-turquoise light range is needed for our bodies to help regulate our natural sleeping cycle (also known as our circadian rhythm). This light range, which is from 465 nm to 495 nm, can help boost our mood, increase our overall feeling of well being, increase reaction time, and give us energy. However, if we receive insufficient light exposure or too much blue ray light out of this range, it can wreak havoc on our health. Eyes: The most common health concern from blue ray light is the effect it has on the human eye. Eyestrain is now the number one complaint for those who spend large amounts of time on a computer. Scientific studies have shown that increased exposure to blue ray light can lead to eye problems such as the following: Macular Degeneration: Research has shown that blue ray light can cause severe damage on the retina, leading to macular degeneration. Macular degeneration is a disease that leads to the deterioration of the macula, a small area by the center of the retina that is crucial for our sharp, central vision. The macular lets us see objects that are directly in front of us and the disease usually affects older people past their 50s, but our increased use of technology is seeing more and more young people with early signs of the disease. It does not lead directly to blindness, but it has a severe impact on performing everyday activities such as driving, reading, or writing. Dry Eye: Increased exposure to blue ray light can inhibit the body’s tear production, causing the eyes to become dry. Without this lubrication, eyes will become irritated and could lead to eyestrain. Eyestrain has its own possible effects, and a popular complaint among eyestrain sufferers is an increase in migraines. Reduced tear production can affect the eye long term and slowly lead to visual impairment. Cataracts: Studies have shown an increased susceptibility of cataracts in people who are exposed to too much blue ray light. The human eye may have some natural protection from blue light, but a high concentration of blue light will damage the lens over time. The UV and blue light that is absorbed by then lens is thought to be a major contributing factor to the onset of cataracts. Sleep: Blue ray light has a large impact on the body’s sleep cycles. In earlier times, the sun going down meant that humans had to rely on campfires or candles to see in the dark. These sources of light are in the yellow/orange spectrum of visible light and don’t impact our circadian rhythm. Now, we use technology such as LED lights that use blue ray light that trick our body’s into thinking it is still daytime. When it gets dark, the brain signals to the pineal gland to secrete melatonin that will make the body feel tired and want to sleep. Without this secretion of melatonin, our quality and quantity of sleep is severely disrupted. Numerous studies have been conducted that demonstrate the harmful effects of not getting between 7 and 9 hours has on the body. Without a good night’s sleep, the body can increase cortisol levels (the stress hormone), decrease memory and cognitive function, make it difficult to lose weight, and lead to many chronic diseases. Needless to say, sleep is important, and blue ray light can dramatically affect our sleep cycles. A Harvard study demonstrated how increased exposure to blue ray light could lead to issues such as diabetes and obesity. Researchers gradually shifted the circadian rhythms of 10 people and the results showed that their blood sugar levels increased while their leptin (the hormone that helps people feel full after a meal) levels went down. Getting a proper amount of sleep is key to a healthy life, and blue ray light can severely impact this. Positive Uses of Blue Ray Light As previously stated, not all blue light is bad. Many dermatological practices have begun using blue light as a treatment for skin ailments such as eczema and acne. Blue light therapy is also used to treat patients with mood disorders such as seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and delayed sleep phase disorder (DSPD). Skin Conditions: A study recently stated that short-term use of blue light for skin problems is safe and patients can see benefits from such treatments. Skin Cancer: Dermatologists are using blue light therapy to reduce the risk of skin cancer in patients with actinic keratoses. Actinic keratoses are rough, scaly bumps on the skin caused by increased exposure to the sun’s UV rays. When the bumps are left untreated, around 10 percent of these lesions turn into squamous cell carcinoma. By using blue light therapy, dermatologists are able to significantly reduce the amount of precancerous lesions in patients. Patients may experience burning or itching during treatment, but this will usually disappear within 24 hours. Swelling of the treated areas may occur afterwards. Acne Treatment: Blue light therapy is commonly used in dermatological practices in two different ways. One is called photodynamic therapy and is used for moderate to severe acne because it is a more serious procedure. It involves using a photosensitizing agent on the skin for three hours so that it is absorbed in to sebaceous glands. Once three hours has passed, blue light is shone on the affected area for about 20 minutes, activating the photosensitizing agent that works to kill the bacteria and shrink the oil glands. The other procedure does not use photosensitizers and is done at home. These at-home light therapy kits are used more commonly for light acne and do not respond well to severe acne. Using blue light (and sometimes red light as well), this procedure is usually administered twice a day on the sebaceous glands that will excite porphyrins. Porphyrins are a group of organic compounds inside the bacteria that will kill the bacteria when light is shone on them. Psoriasis: Those affected by psoriasis have found help in blue light therapy as well. Many doctors tell psoriasis patients to get 20 minutes of sun each day, but this can be damaging to the skin of patients aren’t careful. Many psoriasis patients buy blue light lamps that are to be used with a cream or pill called psoralen. This drug makes the skin more sensitive to light and helps the blue ray light work faster to clear up the skin. The downsides to this therapy are that it must be consistent in order to have the desired effect and it may result in side effects such as nausea, redness, and itchiness of the skin. Mood Disorders: Those with mood disorders can also benefit from blue light therapy. A study using 30 humans in a double-blind trial found that many symptoms were alleviated with blue light therapy. Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): This is a type of depression that usually occurs every year during the fall or winter when the days become increasingly short. The lack of light disrupts the body’s circadian rhythm and causes a lack of serotonin production. The lack of serotonin, which allows the brain to feel pleasure, can cause us to crave foods high in carbohydrates and sugar and get a poor night’s sleep. Many individuals have found relief in light therapy boxes, which are used to treat SAD by imitating the outside light. While light therapy boxes are designed to be safe, they have not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and should be used cautiously. Delayed Sleep Phase Disorder (DSPD): This circadian rhythm disorder affects the control of sleep, body temperature rhythm, the period of alertness, and hormonal rhythms of those affected. Light therapy in this disorder is not always effective, but many patients do find relief with it. In order to be effective, the patient should go out into the sunlight first thing in the morning or use a blue light lamp for ½ to 2 hours. To be successful, the timing has to be just right. There are times when light exposure before the body’s sleep period will have a negative effect by delaying the sleep cycle even further. Additionally, exposure to light too late after the sleep period will advance the sleep cycle too far. Note: Light therapy boxes can be found over the counter and come in many different sizes and intensities of light. Please consult a doctor before you decide which one is right for you. Protection Against Blue Ray Light We have some natural protection, but it isn’t sufficient with today’s increased use of electronic devices. The lens of our eyes and also the pigment in the back of the eyes work to block some blue ray light. Invest in blue-filtering lenses: Many people buy sunglasses that protect against UV rays, but most sunglasses are not made to block out blue light specifically. Sunglasses that protect against blue light contain lenses that have the perfect balance of melanin and ocular lens pigment to best protect your eyes. Whether you are outside or spend a lot of time at your computer, investing in a good pair of blue-filtering lenses is crucial. Wear wide-brimmed hats: People who spend a lot of time outdoors should wear wide-brimmed hats that will shield the face from the sun’s blue ray light. Not only will this help protect your eyes from the suns blue light rays, but it will protect your skin as well. Reduce the amount of time you spend on electronics in the evening: If you are required to be in front of a computer at work, try to cut down on the use of your electronics in the evening. If you use an eBook reader, try to buy a paper version to give your eyes a break. Instead of watching the television, pick up a hobby that doesn’t have you staring at a screen that emits blue ray light. Try reading by candlelight or invest in light bulbs that do not emit blue ray light. Alter your electronic devices: In most laptops and computers, you can adjust the screen brightness. Lower the brightness on your device as much as possible. In addition, there are many apps you can download to reduce the strain on your eyes. The f.lux app is a program you can install on your computer or phone that will automatically dim the brightness and color of your device based on your time zone. Artificial lens implants: Many people are turning towards intraocular lens (IOL), or artificial lens implants, to prevent the harmful effects of blue ray light. While they are usually used to treat eye diseases such as cataracts, the benefits of blocking harmful UV rays has made them become a popular request. Blue light-filtering IOLs may be colored in a transparent yellow color that will filter blue light. Block out as much light as you can at night: Invest in some high-quality blackout curtains. Due to Alaska’s proximity to the Arctic Circle, many people living there must invest in these curtains so that the increased hours of daylight do not disrupt their sleep. Not all blackout curtains are created equal, so find a quality brand. Sources http://www.bluelightexposed.com/#where-is-blue-light-found http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21552190 http://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/blue-light-has-a-dark-side http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20070834 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.17511097.1990.tb01972.x/abstract;jsessionid=7DDEB07753D5B69EB11F786A22E1B5 2D.f03t01 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19016463