Chapter 8: Production and
Cost in the Short Run
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Basic Concepts of
Production Theory
• Production function
• Maximum amount of output that can be produced
from any specified set of inputs, given existing
technology
• Technical efficiency
• Achieved when maximum amount of output is
produced with a given combination of inputs
• Economic efficiency
• Achieved when firm is producing a given output at
the lowest possible total cost
8-2
Basic Concepts of
Production Theory
• Inputs are considered variable or fixed depending
on how readily their usage can be changed
• Variable input
• An input for which the level of usage may be changed quite
readily
• Fixed input
• An input for which the level of usage cannot readily be
changed and which must be paid even if no output is
produced
• Quasi-fixed input
• A “lumpy” or indivisible input for which a fixed amount must
be used for any positive level of output
• None is purchased when output is zero
8-3
Basic Concepts of
Production Theory
• Short run
• At least one input is fixed
• All changes in output achieved by changing
usage of variable inputs
• Long run
• All inputs are variable
• Output changed by varying usage of all inputs
8-4
Sunk Costs
• Sunk cost
• Payment for an input that, once made, cannot
be recovered should the firm no longer wish
to employ that input
• Not part of the economic cost of production
• Should be ignored for decision making
purposes
8-5
Avoidable Costs
• Avoidable costs
• Input costs the firm can recover or avoid
paying should it no longer wish to employ that
input
• Matter in decision making and should not be
ignored
• Reflect the opportunity costs of resource use
8-6
Short Run Production
• In the short run, capital is fixed
• Only changes in the variable labor input can
change the level of output
• Short run production function
Q = f (L, K) = f (L)
8-7
Production Function
8-8
8-8
Average & Marginal Products
• Average product of labor
• AP = Q/L
• Marginal product of labor
• MP = Q/L
• When AP is rising, MP is greater than AP
• When AP is falling, MP is less than AP
• When AP reaches it maximum, AP = MP
• Law of diminishing marginal product
• As usage of a variable input increases, a point is
reached beyond which its marginal product decreases
8-9
Total, Average, & Marginal Products
of Labor, K = 2 (Table 8.2)
Number of
workers (L)
Total product (Q) Average product
(AP=Q/L)
Marginal product
(MP=Q/L)
0
0
--
--
1
52
52
52
2
112
56
60
3
170
56.7
58
4
220
55
50
5
258
51.6
38
6
286
47.7
28
7
304
43.4
18
8
314
39.3
10
9
318
35.3
4
10
314
31.4
-4
8-10
Total, Average, & Marginal Products
K = 2 (Figure 8.1)
8-11
Total, Average, & Marginal
Product Curves
Q2
Q1
Total
product
Panel A
Q0
L0
L1
L2
Panel B
Average product
L0
L1
L2
Marginal product
8-12
Law of Diminishing Marginal
Product (Returns)
• Only holds in the short-run
• As the quantity of the variable input (labor)
increases, the capital to labor ratio
declines
• Eventually an incremental increase in the
variable input adds less to output than the
previous incremental increase in the
variable input
8-13
8-
Change in Capital Stock
8-14
8-
Change in Capital Stock
8-15
8-
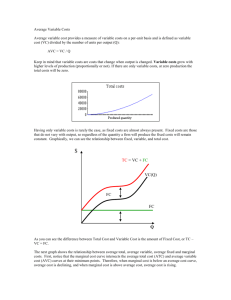
Short Run Production Costs
• Total variable cost (TVC)
• Total amount paid for variable inputs
• Increases as output increases
• Total fixed cost (TFC)
• Total amount paid for fixed inputs
• Does not vary with output
• Total cost (TC)
TC = TVC + TFC
8-16
Short-Run Total Cost Schedules
(Table 8.4)
Output (Q)
0
Total fixed cost
(TFC)
$6,000
Total variable cost
(TVC)
$
Total Cost
(TC=TFC+TVC)
0
$ 6,000
100
6,000
4,000
10,000
200
6,000
6,000
12,000
300
6,000
9,000
15,000
400
6,000
14,000
20,000
500
6,000
22,000
28,000
600
6,000
34,000
40,000
8-17
Total Cost Curves
(Figure 8.3)
8-18
Average Costs
• Average variable cost (AVC)
TVC
AVC
Q
• Average fixed cost (AFC)
TFC
AFC
Q
• Average total cost (ATC)
TC
ATC
AVC AFC
Q
8-19
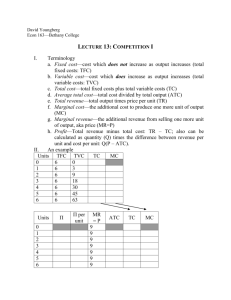
Short Run Marginal Cost
• Short run marginal cost (SMC) measures
rate of change in total cost (TC) as output
varies
TC TVC
SMC
Q
Q
8-20
Average & Marginal Cost Schedules
(Table 8.5)
Output
(Q)
0
Average
Average
fixed cost
variable cost
(AFC=TFC/Q) (AVC=TVC/Q)
--
Average total
cost
(ATC=TC/Q=
AFC+AVC)
Short-run
marginal cost
(SMC=TC/Q)
--
--
--
100
$60
$40
$100
$40
200
30
30
60
20
300
20
30
50
30
400
15
35
50
50
500
12
44
56
80
600
10
56.7
66.7
120
8-21
Average & Marginal Cost Curves
(Figure 8.4)
8-22
Short Run Average & Marginal
Cost Curves (Figure 8.5)
8-23
Short Run Cost Curve Relations
• AFC decreases continuously as output
increases
• Equal to vertical distance between ATC &
AVC
• AVC is U-shaped
• Equals SMC at AVC’s minimum
• ATC is U-shaped
• Equals SMC at ATC’s minimum
8-24
Short Run Cost Curve Relations
• SMC is U-shaped
• Intersects AVC & ATC at their minimum
points
• Lies below AVC & ATC when AVC & ATC
are falling
• Lies above AVC & ATC when AVC & ATC
are rising
8-25
Relations Between Short-Run
Costs & Production
• In the case of a single variable input,
short-run costs are related to the
production function by two relations
w
w
AVC
and SMC
AP
MP
Where w is the price of the variable input
8-26
Marginal Cost and Marginal Product
C
MC
q
VC ( wL) wL
MC
q
q
q
1
L
w
MC w
q
MPL
Marginal cost is inversely related to marginal product
8-27
Marginal Cost and Marginal
Product
• W = $10
• MP = 10
• MC =$1
• MP = 5
• MC = $2
8-28
8-
Average Variable Cost and Average Product
C
AVC
q
VC wL
AVC
q
q
1
L
AVC w w
q
APL
Average variable cost is inversely
related to average product
8-29
Short-Run Production and
Total Cost
8-30
8-
Short-Run Production and Marginal
cost
8-31
8-
Short-Run Production & Cost
Relations (Figure 8.6)
8-32
Relations Between Short-Run
Costs & Production
• When marginal product (average product)
is increasing, marginal cost (average cost)
is decreasing
• When marginal product (average product)
is decreasing, marginal cost (average
variable cost) is increasing
• When marginal product = average product
at maximum AP, marginal cost = average
variable cost at minimum AVC
8-33