EE121 - The Citadel
advertisement
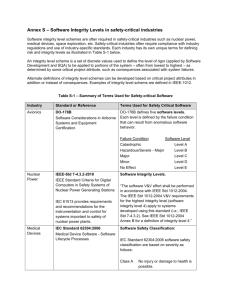
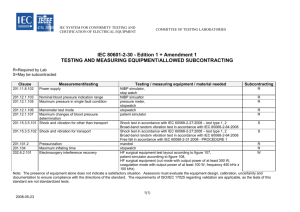
Requirement Definition Process Requirement Specification Marketing Requirement Description of customer need, “the product should be lightweight” Engineering Requirement Measurable engineering characteristics, “the product weighs 6.2 pounds” Requirement Specification, a collection of engineering and marketing requirements that satisfy a particular need. Functional Specification - description of inputs, outputs and functionality of important subsystems Technical Specification - complete details of the design Other Engineering Requirements Reliability and Availability Environmental MTBF and MTTR Energy consumption Pavg Ipeak Battery Life Shock and Vibration Temperature and Humidity Voltage and Frequency Software and Computing Data transfer formats Usability RASUI – Reliability, Availability, Serviceability, Usability and Installability Constraints Economic Environmental Ethical and Legal Health and Safety Manufacturability Political Social Sustainability Standards Internal External Governmental Trade/Professional Association Customer Voluntary Mandatory Cannot sell a product in a country unless it meets all applicable standards levied by that country. Umbrella Organizations ISO – Geneva, Switzerland ANSI – Washington, DC These organizations collect and disseminate standards in all types of industries. They also establish working groups to review and solicit standards with the goal of harmonizing conflicts among competing standards. Purposes Compatibility Screw threads Batteries Connectors on cables Protection Safety Hazardous materials Electromagnetic interference Sources of Standards Manufacturers Trade groups and professional societies Insurers Government regulatory agencies Department of Defense Manufacturers Test equipment interconnect HPIB Bus Cables and connectors Command set and protocol IEEE-488 Extended HP standard to the industry and allowed other manufacturers to participate. VXI/PXI/PCI/USB/RS-232 Professional Societies IEEE Set standards for nearly all aspects of EE “Color Books” Some well known IEEE1394 (FireWire) IEEE 802 (Wireless communications) IEEE 488.2 (GPIB instrumentation protocols) Insurers Fire safety Personnel safety Underwriters Laboratories (UL) Government Regulations Many government regulations are imposed to ensure that the product will not have a negative effect on its environment including its operators. Others are imposed to facilitate or control trade. Government Agencies OSHA -- Personnel safety EPA -- Environmental protection FCC -- Electromagnetic interference FDA -- Food and Drug Safety FAA -- Safety of flight Department of Defense Standards for military equipment Adopted by most nations Examples MIL-STD-28800D, Portable electronic equipment MIL-STD-461D, Electromagnetic compatibility MIL-STD-882D, System Safety MIL-STD-883F, Test Methods Standard Microcircuits MIL-STD/HDBKs often used commercially MIL-HDBK-217F, Reliability Predictions for Electronic Equipment Other Agencies CSA Personnel safety (Canadian) IEC Safety and electromagnetic interference (European) International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) First President was Lord Kelvin (1906) HQ: Geneva, Switzerland Prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies 61 member countries Promotes international cooperation and harmonization of standards Removes technical barriers to trade IEC Standards Terminology and symbols Electromagnetic compatibility Measurement and performance Dependability Safety and the environment. IEC Standards Currently 179 Technical Committees Members from around the world Covers all aspects; for example, Batteries Motors Components Often categorized by usage Industrial Laboratory Home Medical Political Context With the establishment of the European Economic Community (EEC), the IEC took on greater importance because it was chosen to establish standards to facilitate trade. The World Trade Organization (WTO) also uses the IEC, with the result that most national standards have migrated to the IEC. Assessment Companies are required to furnish proof of compliance. 100% test of all units produced is very expensive and generally not required. Typically a few units are tested for “type acceptance.” Testing can be done by the manufacturer or by a third party if the manufacturer does not have the necessary test facilities. Companies should have an audit plan where units off the production line are periodically tested. DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY Manufacturer’s Name: Agilent Technologies, Inc. Manufacturer’s Address: 1400 Fountaingrove Parkway Santa Rosa, CA 95403-1799 USA Declares that the products Product Name: Spectrum Analyzer Model Number: E4401B, E4402B, E4403B, E4404B E4405B, E4407B, E4408B, E4411B Product Options: This declaration covers all options of the above products. Conform to the following product specifications: EMC: IEC 61326-1:1997+A1:1998 / EN 61326-1:1997+A1:1998 Standard CISPR 11:1990 / EN 55011-1991 IEC 61000-4-2:1995+A1998 / EN 61000-4-2:1995 IEC 61000-4-3:1995 / EN 61000-4-3:1995 IEC 61000-4-4:1995 / EN 61000-4-4:1995 IEC 61000-4-5:1995 / EN 61000-4-5:1996 IEC 61000-4-6:1996 / EN 61000-4-6:1998 IEC 61000-4-11:1994 / EN 61000-4-11:1998 CERTIFICATE DELIVERED WITH THE NEW SPECTRUM ANALYZER RECEIVED BY THE ECE DEPARTMENT Limit Group 1, Class A 4 kV CD, 8 kV AD 3 V/m, 80–1000 MHz 0.5 kV sig., 1 kV power 0.5 kV L-L, 1 kV L-G 3 V, 0.15–80 MHz 1 cycle, 100% Safety: IEC 61010-1:1990 + A1:1992 + A2:1995 / EN 601010-1:1983 + A2:1995 CAN/CSA-C22/2 No. 1010.1-92 Supplementary Information: The products herewith comply with the requirements of the Low-Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and the EMC directive 89/336/EEC and carry the CEmarking accordingly. Santa Rosa, CA, USA 17 April 2000 Greg Pfeiffer/Quality Engineering Manager The 6 Hazards of Product Safety Risk of Shock Risk of Energy Risk of Fire Risk of Injury Radiation Hazards Chemical Hazards Risk of Shock Prevent access to hazardous voltages: 30 Vrms 60 Vdc Risk of Energy Prevent access to circuits capable of delivering 240 VA or more. Energy can melt bracelets, watches, and rings Risk of Fire Limit flammability of combustible materials Limit temperatures of flammable materials Prevent electrical discharge to flammable/explosive materials Containment of fire European standards used to aim at proof that there is no potential for fire. US focus is on fire containment. New international standards have adopted the US approach. Risk of Injury Limit access to hazardous moving parts, sharp edges, pinch points, etc. Prevent equipment tip-over Radiation Hazards Limit exposures Lasers CRT Non-ionizing & ionizing radiation Chemical Hazards Ozone Spillage of hazardous liquids Batteries Summary Standards help obtain compatibility between products. Mandatory standards must be met to sell products legally. Internal standards are often used to assure the quality and reliability of the product. External standards are imposed for compatibility and protection. Compliance with the applicable standards must be guaranteed by the manufacturer.