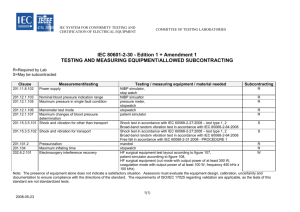
Software Integrity Levels in Safety-Critical Industries
advertisement
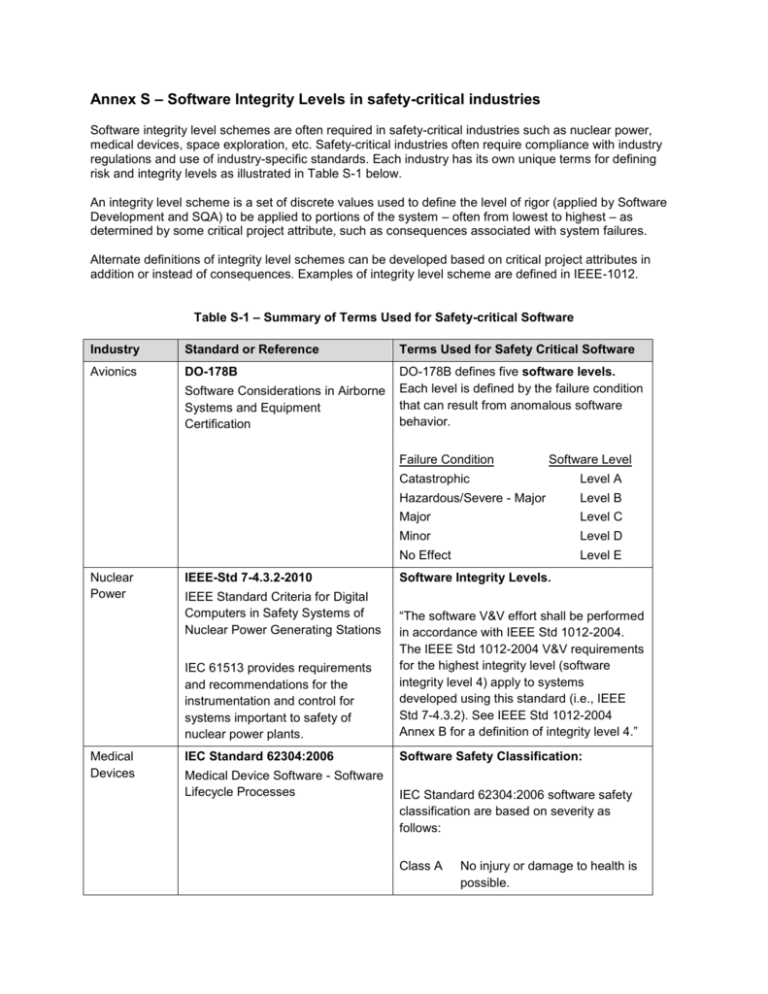
Annex S – Software Integrity Levels in safety-critical industries Software integrity level schemes are often required in safety-critical industries such as nuclear power, medical devices, space exploration, etc. Safety-critical industries often require compliance with industry regulations and use of industry-specific standards. Each industry has its own unique terms for defining risk and integrity levels as illustrated in Table S-1 below. An integrity level scheme is a set of discrete values used to define the level of rigor (applied by Software Development and SQA) to be applied to portions of the system – often from lowest to highest – as determined by some critical project attribute, such as consequences associated with system failures. Alternate definitions of integrity level schemes can be developed based on critical project attributes in addition or instead of consequences. Examples of integrity level scheme are defined in IEEE-1012. Table S-1 – Summary of Terms Used for Safety-critical Software Industry Standard or Reference Terms Used for Safety Critical Software Avionics DO-178B DO-178B defines five software levels. Each level is defined by the failure condition that can result from anomalous software behavior. Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification Failure Condition Nuclear Power Medical Devices IEEE-Std 7-4.3.2-2010 IEEE Standard Criteria for Digital Computers in Safety Systems of Nuclear Power Generating Stations Software Level Catastrophic Level A Hazardous/Severe - Major Level B Major Level C Minor Level D No Effect Level E Software Integrity Levels. IEC 61513 provides requirements and recommendations for the instrumentation and control for systems important to safety of nuclear power plants. “The software V&V effort shall be performed in accordance with IEEE Std 1012-2004. The IEEE Std 1012-2004 V&V requirements for the highest integrity level (software integrity level 4) apply to systems developed using this standard (i.e., IEEE Std 7-4.3.2). See IEEE Std 1012-2004 Annex B for a definition of integrity level 4.” IEC Standard 62304:2006 Software Safety Classification: Medical Device Software - Software Lifecycle Processes IEC Standard 62304:2006 software safety classification are based on severity as follows: Class A No injury or damage to health is possible. Industry Space Exploration Transportation Standard or Reference Terms Used for Safety Critical Software Class B Non-serious injury is possible. Class C Death or serious injury is possible. NASA Technical Standard 8739.8 2004 Software Class: Class A Human Rated Software Systems Software Assurance Standard Class B Non-Human Space Rated Class C Mission Support Software Class D Analysis and Distribution Software Class E Development Support Software IEC 61508 Safety Integrity Level Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems The Safety Integrity Level (SIL) is determined from the probability of failure. For systems that operate continuously the allowable frequency of failure must be determined. For systems that operate intermittently the probability of failure is specified as the probability that the system will fail to respond on demand. Rail EN 50128 provides a specific interpretation of IEC 61508 for railway applications. SIL Low demand mode: average probability of failure on demand High demand or continuous mode: probability of dangerous failure per hour 1 ≥ 10-2 to < 10-1 ≥ 10-6 to < 10-5 2 ≥ 10-3 to < 10-2 ≥ 10-7 to < 10-6 3 ≥ 10-4 to < 10-3 ≥ 10-8 to < 10-7 4 ≥ 10-5 to < 10-4 ≥ 10-9 to < 10-8 Automotive Software The development of software for safety related automotive systems is predominantly covered by the Motor Industry Software Reliability Association guidelines. The MISRA project was conceived to develop guidelines for the creation of embedded software in road vehicle electronic systems. In November 1994 Development guidelines for vehicle based software was published. This document provides the first automotive industry interpretation of the principles of the emerging standard IEC 61508. Additional information on the definition and use of integrity levels can be found in ISO-15026-Part 3.