Cost Management: Quality
advertisement

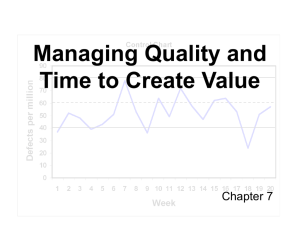
Cost Management: Issues of Quality ACCT7320, C. Bailey Quality as a Competitive Weapon TQM a key issue of the 1990’s-Present high costs associated with quality--15-20% in many organizations. Baldrige Quality Award ISO 9000 and ISO 14000 Conceptual linkage between Quality and Profitability (Exhibit 17.1—see next slide) Exhibit 17.1 17-3 What is quality? Quality Definitions fitness for use degree to which a product satisfies customer wants conformance to design specifications Conformance Quality; Design Quality Next slide… Meeting the customer’s needs Two Aspects of Quality Actual Performance Design Specifications Conformance Quality Failure Customer Requirements Quality of Design Failure Costs of Quality The cost incurred to prevent, or the costs arising as a result of, a low-quality product. Traditional Categories • • • • Prevention Appraisal Internal failure External failure Prevention Cost …incurred to preclude the production of products/ services that do not conform to specifications. Areas for consideration: Design Engineering Process Engineering Supplier evaluations Preventive equipment maintenance Quality training New materials used to manufacture products Appraisal Cost …..incurred to detect which of the individual units of products do not conform to specs. Areas for consideration: • • • Inspection Online product manufacturing & process inspection Product testing Internal failure costs …..incurred on a defective products before it is shipped to customers. Areas for consideration: Spoilage Rework Scrap Breakdown maintenance Manufacturing/process engineering on internal failure Opportunity costs External failure costs …..incurred on a defective products after it is shipped to customers. Areas for consideration: • • • • • Customer support Manufacturing/process engineering for external failures Warranty repair costs Liability claims Opportunity costs Cost of Quality Report Evaluating Quality Performance Advantages of Costs of Quality Measures Focus attention on how costly poor quality is. Estimate benefits of different qualityimprovement programs; setting priorities for cost reduction. Help evaluate trade-offs among prevention and failure costs. Evaluating Quality Performance, Cont’d. Advantages of Nonfinancial Measures Often easy to quantify and to understand. Direct attention to physical processes Provide immediate feedback on whether efforts have succeeded in improving quality. A balanced scorecard combines financial and nonfinancial measures so management can evaluate trade-offs between areas of improvement. Cost Of Quality: Traditional View Costs Total Costs Prevention & Appraisal) Internal & External Failure) Lowest Quality Point of “enough quality” Highest Quality Problems with the Traditional View Accountants do not traditionally measure some important costs Opportunity costs Cost to reduce failure may be lower than thought Deming’s principles Cost Of Quality: Revised Failure more expensive, P & A Less Costly than believed Costs Total Costs Prevention & Appraisal) Internal & External Failure) Lowest Quality New point of “enough quality” Highest Quality End of Presentation