Supreme Court Cases
advertisement

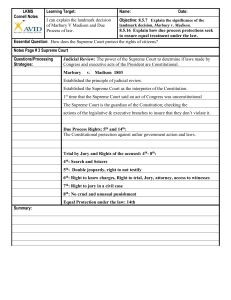
Supreme Court Cases: The Top 30 Directions: Using http://www.streetlaw.org/en/home, http://oyez.org/, or your textbook for each of the following cases include the following in the chart provided: Summary of the case o Who was involved? o What happened? o Where and when did it occur? o How and why was it brought to the Supreme Court? The decision: o What was the Supreme Court ruling? o Explain why this is a landmark case This assignment must be hand written, not typed. Grading: 2 points each summary, 1 point each precedent = 90 points total DUE DATE: April 4th 1. Marbury v. Madison 2. McCulloch v. Maryland 3. Gibbons v. Ogden 4. Engel v. Vitale 5. Lemon v. Kurtzman 6. Reynolds v. United States (1879) 7. Oregon v. Smith 8. Schenck v. United States 9. New York Times v. Sullivan 10. Roth v. Unites States 11. Tinker v. Des Moines Independent School District 12. Texas v. Johnson 13. Barron v. Baltimore 14. Gitlow v. New York 15. Weeks v. United States 16. Mapp v. Ohio 17. Gideon v. Wainwright 18. Miranda v. Arizona 19. Dred Scott v. Sandford 20. Plessy v. Ferguson 21. Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka 22. Regents of the University of California v. Bakke 23. Grutter v. Bollinger 24. Griswold v. Connecticut 25. Roe v. Wade 26. Baker v. Carr 27. Wesberry v. Sanders 28. Korematsu v. Unites States 29. United States v. Nixon (1974) 30. Buckley v. Valeo Court Case Marbury v. Madison Who was involved? William Marbury, James Madison What happened? Marbury and several others were appointed to government posts created by Congress in the last days of John Adams's presidency, but these were never fully finalized. March 2, 1801,Washington DC Where and when did it occur? How and why was it brought to the Supreme Court? Based on Judiciary Act of 1789 SCOTUS had jurisdiction What was the Supreme Court ruling? Explain why this is a landmark case Judiciary Act of 1789 is unconstitutional because it conflicts with the Constitution. Establishes the SCOTUS’ power of judicial review