Microbiology of Mercury
advertisement

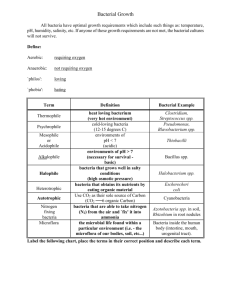
Microbial transformations of mercury in the environment lipophilic 2e- Hg0 [CH3-] [CH3-] Hg2+ CH3Hg+ (CH3)2Hg HS-, -S-R HgS, Hg+-S-R Algae Fish Children Women Fetus Infants Minnamata Bay Hg2+, Hg0 CH3-Hg+, (CH3)2Hg Anoxic sediment Pathology: constricted visual field, impairment of vibration sense, total blindness, ataxia, necrosis of Glia cells “Life is Redox Chemistry” AH2 + B A + BH2 Energy DG= -nFDE, DE= Eacceptor - Edonor DG<0 Redox pot ent ials for bact eria-mediat ed redox sequences ( St andard st at e condit ions at pH 7 ) DG o' = - nFDE o' Elect ron donor o' E [ mV] CH2 O CO2 H2 + DE o '=Eo' acceptor - Eo' donor Elect ron accept or o' E [ mV] -5 0 0 -4 7 0 -50 0 -47 0 -4 2 0 -42 0 CH2 O H2 CO2 H+ H 2+ CH4 H2 S H2 S CO2 So 24 SO Succinat e -25 0 -2 4 0 -2 2 0 -2 5 0 -2 2 0 Fe H2 S 0 +30 0 + 30 Fe( OH)3 24 Succinat e Fumarate FeCO3 FeCO3 Fe( OH) 3 + HCO -3 + 2 00 + 2 00 + NO3- - Fe( OH) 3 + HCO3+ NH4 NH 4 + 3 60 + 3 60 + 4 20 + 4 20 NO3- NO2- NO3 NO3 Mn 2+ Mn + 5 50 + 5 50 Mn4 + H2 O O2 NO3- 2+ 4+ Mn N2 N2 + 7 50 + 7 50 + 8 20 + 8 20 CH4 CO2 So SO Fumarate NO2- H2 S NO3- H2 O O2 Carbon and electron flow in sulfidogenic environments Complex organic matter Carbohydrates, nucleic acids proteins, lipids 1 Lactate Propionate Higher fatty acids Alcohols Aromatic compounds H2, CO2 Acetate 2 SO42- H2S, CO2 1 2 = fermentative bacteria, e.g., lactic acid bacteria, clostridia, enteric bacteria, propionibacteria = sulfate-reducing bacteria, e.g., Desulfovibrio spp, Desulfobacterium spp, Desulfobacter spp, Desulfotomaculum spp. Carbon and electron flow in methanogenic environments Complex organic matter Carbohydrates, nucleic acids proteins, lipids 1 Lactate Propionate Higher fatty acids Alcohols Aromatic compounds 2 H2, CO2 3 Acetate 4 1 CH4, CO2 2 = fermentative bacteria, e.g., lactic acid bacteria, clostridia, enteric bacteria, propionibacteria = proton-reducing, syntrophic bacteria, e.g., Syntrophomonas spp, Syntrophobacter 3 4 = homoacetogenic bacteria, e.g., Acetobacterium woodii, Clostrodium aceticum = methanogenic archaea, e.g., Methanosarcina spp, Methanobacterium spp., Methanospirillum spp. Carbon and electron flow in sulfidogenic environments Complex organic matter Carbohydrates, nucleic acids proteins, lipids 1 Lactate Propionate Higher fatty acids Alcohols Aromatic compounds H2, CO2 Acetate 2 SO42- H2S, CO2 1 2 = fermentative bacteria, e.g., lactic acid bacteria, clostridia, enteric bacteria, propionibacteria = sulfate-reducing bacteria, e.g., Desulfovibrio spp, Desulfobacterium spp, Desulfobacter spp, Desulfotomaculum spp. Sulfate-reducing bacteria - all sulfate-reducing bacteria are strict anaerobes - phylogenetically heterogeneous group: gram + : Desulfotomaculum spec., some Clostridia gram - : Desulfovibrio spec., Desulfobacterium spec., Desulfobacter spec., Thermodesulfobacterium spec. archaea: Archaeoglobus spec. General characteristics of catabolism in sulfate-reducing bacteria 2- SO 4 nXH 2 [H] ATP nX H2 S N.B.: All sulfate-reducers are specialized to use products of the primary fermenting bacteria - XH 2 = H2 , HCOO , Acetate, Propionate, Butyrate, Stearate (C 18 ), Fumarate, Succinate, Malate, Ethanol, Methanol, Alkane Benzoate, Phenylacetate, Toluene, Alanine, Glutamate, Cholin, Nicotinate, Indole Based on their metabolic properties sulfate-reducing bacteria can be subdivided into 2 groups: A) Incomplete oxidizers : organic substrates Acetate + CO2 e.g.: Desulfovibrio spec., Desulfobulbus spec., Desulfotomaculum (some) B) Complete oxidizers: organic substrates CO 2 (some acetate can be excreted) e.g.: Desulfobacter spec., Desulfococcus spec., Desulfosarcina spec., Desulfonema spec., Desulfobacterium spec., Desulfotomaculum acetoxidans N.B.: The complete oxidizers can use the citric acid cycle or the carbon monoxide dehydrogenase pathway for complete oxidation of acetyl-CoA. Oxidative carbon monoxide pathway in Sulfate-reducing bacteria QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Mercury in the environment lipophilic 2e- Hg0 [CH3-] [CH3-] Hg2+ CH3Hg+ (CH3)2Hg HS-, -S-R HgS, Hg+-S-R Algae Fish Children Women Fetus Infants