Chapter 11 Notes (Heart and Vessels 2 of 4)
advertisement

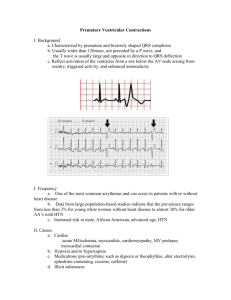
Ch 11 Heart Heart Physiology (PPT 2) Cardiac muscle characteristics: irritability contractility self-exciting rhythmic Control of the Heart Medulla oblongata (of brainstem) & the autonomic nervous system control heart rate SA node (intrinsic control)- cardiac muscle cells in RA, stimulated by neurons, stimulate other cardiac muscle cells to contract (i.e. starts the heartbeat!) SA node (in RA)- “pacemaker” of cardiac cycle, sends impulses in atria to stimulate AV node. Starts the heartbeat! AV node- (in RA) stimulates AV bundle (between ventricles), Purkinje fibers and ventricles Conduction system of the heart Starts the Heartbeat! “Pacemaker” video- conduction system of the heart Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle= 1 complete heartbeat = .8 sec Systole- contraction Diastole- relaxation “Atrial systole with simultaneous ventricular diastole, then atrial diastole with simultaneous ventricular systole” Cardiac Cycle Heart sounds = “LUBB DUPP” “LUBB”- AV valves (tricuspid and bicuspid) closing after atrial systole “DUPP”- semilunar valves (pulmonary and aortic) closing after ventricular systole Diagnostic technique EKG/ECG (Think back to nerve impulses and polarization, depolarization, repolarization) P wave (signals depolarization of atria…right before they contract) QRS complex (signals depolarization of ventricles, before they contract!) T wave (results from currents flowing during repolarization of the ventricles) EKG/ECG flatlining Practical applications Artificial pacemaker If SA node is defective, then electronic device called a pacemaker is implanted into heart to take SA node’s place. Practical applications Cardiac output (def.) volume of blood pumped by LV per minute (ml/min) CO= stroke volume (SV) x heart rate (HR) SV= volume of blood pumped from LV per beat (ml/beat) HR= heart beats per minute (b/min) Cardiac output sample problem CO= amt of blood in body, (because each drop of blood takes 1 minute to circulate through body) Approx. 5 Liters= 5000ml Average fitness CO= SV x HR 5000ml/min = 67 ml/beat x 75 b/min Always stays the same Average SV Average HR Cardiac output sample problems If a person is a couch potato….. then resting CO = 5000 ml/min= 50 ml/beat x 100 b/min But If they begin to exercise and are now of average fitness…… then resting CO= 5000ml/min = 67 ml/min x 75 b/min Cardiac output sample problems If they become even more fit or active resting CO= 5000ml/min 5000ml/min= 83 ml/beat x 60 b/min TAKE HOME MESSAGE: As person becomes more fit- heart becomes more fit at rest, pumps less beats per min., but more blood per beat! Cardiac Output Regulation of SV and HR- can be affected by exercise and fitness level TAKE HOME MESSAGE: As a person’s fitness level increases, their HR decreases, SV increases, but resting CO stays the same. Fitness = HR SV Homeostatic Imbalances Angina pectoris- crushing chest pain, can be symptom of MI Heart attack (myocardial infarction, AKA MI): Caused by blocked coronary artery due to either clot or atherosclerotic plaque, can lead to myocardial (muscle cell) death Myocardial infarction anticoagulants Homeostatic Imbalances Murmurs- occurs if valves don’t close correctly or if they leak Fibrillation- if atrial or ventricular chambers don’t contract simultaneously, ventricular fibrillation can be deadly Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation Can lead to death because ventricles tremble, but don’t contract (so no blood flow) Defibrillator Shocks heart to “reset” it Defibrillator Homeostatic Imbalances MVP- bicuspid valve leaks, blood flows backwards Pericarditis- inflammation of pericardium around heart Homeostatic Imbalances Cardiac arrhythmia- irregular heart beat, due to fibrillation or SA node problems CAD (Coronary Artery Disease): plaque/cholesterol in coronary arteries Coronary Artery Disease HDL’s- good cholesterol LDL’s- bad cholesterolclogs arteries Catheterization is a treatment, not a cure, because if one doesn’t change eating habits then it will just happen again Homeostatic Imbalances CHF- (Congestive Heart Failure)- heart weakening, not necessarily stoppage Due to: MI Atherosclerosis Hypertension CAD Other heart diseases