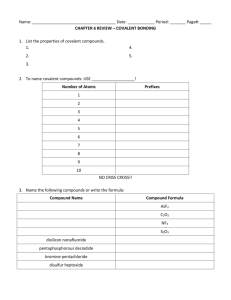
Unit 5: Soap Name Date You are to complete a minimum of 3

Unit 5: Soap
Name ___________________________________________ Date ___________________________
You are to complete a minimum of 3 learning opportunities and all required activities for each unit. Required activities will be done in class while learning opportunities will be done primarily at home. The first 10 minutes of each day will be given to you to work on the LO’s. If additional time is needed, you will have to complete them at home.
1 LO = 60% 2 LO’s = 70% 3 LO’s = 80% 4 LO’s = 90% 5 LO’s = 100 %
At the end of this unit, the student will:
Standards Learning Opportunities (LO) Required activities Section
5.1
Types of Bonds
5.2
Drawing Molecules
5.3
Molecules in 3D o Describe metallic bonds: “metal ions plus
‘sea’ of mobile electrons” o Apply the concept that sharing electrons form a covalent compound that is a stable (inert gas) arrangement o Determine that a bond is predominately ionic by the location of atoms on the periodic table
(metals combined with nonmetals) *or when
ΔEN > 1.7 o Determine that a bond is predominately covalent by the location of atoms on the periodic table (nonmetals combined with nonmetals) *or when ΔEN < 1.7 o Draw Lewis (dot diagram) structures for simple compounds and diatomic elements indicating single, double or triple bonds o Predict chemical formulas of compounds using Lewis structures o Appropriately use the term cation as a positively charged ion and anion as a negatively charged ion o Apply Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Theory (VSEPR) for these electron pair geometries and molecular geometries and bond angles – Electron pair – Molecular
(bond angle); Linear framework – linear;
Trigonal planar framework; trigonal planar, bent; Tetrahedral framework – tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, bent; Bond angles
(include distorting effect of lone pair electrons) no specific angles, conceptually o only. o Reading Guide 5.1 ,online o CYNTK Practice 5.1 o Draw a visual representation with a full explanation for each type of bond. o Reading Guide 5.2,online o CYNTK Practice 5.2 o Reading Guide 5.3,online o CYNTK Practice 5.3
Introductory Activity
Read Glencoe o pp210 – 220 o Pp 228 – 231 o Pp 241 - 247
Lab 5.1: Types of Bonds
Section Quiz
Drawing Molecules
Activity/worksheet??
Read Glencoe o Pp 252 - 258
Section Quiz
Lab 5.3: Covalent Molecules in 3D
Read Glencoe o Pp 259 - 261
VSEPR Theory worksheet/notes sheet
Section Quiz
Unit 5: Soap
5.4
Polarity of
Molecules o Describe bond polarity. Polar/nonpolar molecules (relate to symmetry)
5.5
Intermolecular
Forces
5.6
Intermolecular
Forces and
Properties o Describe intermolecular forces for molecular compounds o H-bond as attraction between molecules when H is bonded to O, N, or F. o Dipole-dipole attractions between polar molecules o London dispersion forces (electrons of one molecule attracted to nucleus of another molecule) – i.e. liquefied inert gases o Relative strengths
(H>dipole>London/van der Waals) o Explain why intermolecular forces are weaker than ionic, covalent or metallic bonds. o (*Explain how) ionic bonding in compounds determines their characteristics: high MP, high BP, brittle, and high electrical conductivity either in molten state or in aqueous solution o (*Explain how) covalent bonding in compounds determines their characteristics: low MP, low BP, poor electrical conductivity, polar nature, etc o (*Explain how) metallic bonding determines the characteristics of metals: high MP, high
BP, high conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster o relate polarity to solubility – “like dissolves like”
Unit 5 Test
o Reading Guide 5.4,online o CYNTK Practice 5.4 o Reading Guide 5.5,online o CYNTK Practice 5.5 o Reading Guide 5.6,Online o CYNTK Practice 5.6 o
Practice worksheet
Read Glencoe o Pp 263 - 264
Section Quiz
Practice Worksheet
Read Glencoe o 265 - 267
Section Quiz
Lab 5.3: Intermolecular Forces and
Evaporation
Glencoe reading (spread throughout the other readings for this unit)
Section Quiz