Bio200-Plant Transport
advertisement

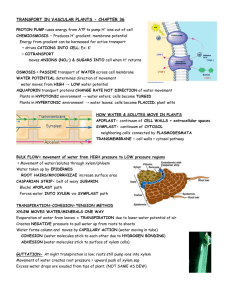
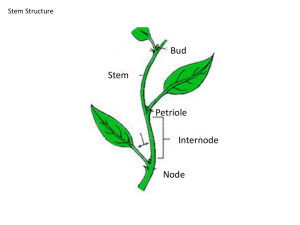
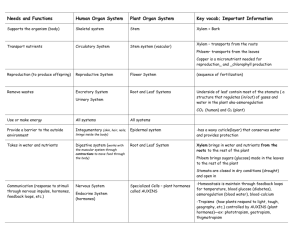
Plant Transport Relevant Portions of Text CH 36: Pg 779, 36.2-36.5 Objectives and Study Questions 1. What is the symplast? Apoplast? 2. What are plasmodesmata/plasmosdesma (plasmodesmata is plural, plasmodesma singular) 3. Compare and contrast symplastic transport and apoplastic transport 4. How does water cross the plasma membrane of a cell? Can the permeability to water be increased or decreased? 5. How do ions and large polar molecules cross the plasma membrane of a cell? 6. What is water potential? Solute Potential? Pressure potential? 7. If the pressure potential inside a cell is greater than the solute potential what effect does that have on water movement? 8. What effect does increasing the solute concentration have on the solute potential (and by extension water potential)? 9. What effect does “pushing” on water have on pressure potential (and by extension water potential)? 10. What effect does tension, “pulling”, on water have on pressure potential (and by extension water potential)? 11. Which direction does water move relative to water potential? 12. Explain how water moves from soil into the xylem within roots? 13. What is the role of then endodermis in water and mineral movement into xylem? 14. What is the casparian strip? 15. How does active transport of solutes by the endodermis relate to the movement of water into the root xylem? 16. What is bulk flow? 17. What is xylem sap? 18. What is phloem sap? 19. What is root pressure and how is it created? 20. Is root pressure a significant mechanism in the bulk flow of xylem sap? 21. What is transpiration? 22. What is cohesion? When we say there is lots of cohesion among water molecules what does that mean? 23. Explain how xylem sap moves due to cohesion-tension and transpirational pull beginning with the evaporation of a water molecule out the stoma on a leaf? 24. Does the plant expend energy to move xylem sap by bulk flow. 25. Describe a stomata including the stoma and guard cells? 26. What are the function of stomata (i.e., what happens at them/what do they allow to occur)? 27. Explain how guard cell cell wall structure and the movement of K+ and water cause guard cells to open and close. 28. From the plants perspective what are the pros and cons (i.e, benefits and consequences) of having the stomata open? Closed? 29. When are stomata typically closed? Open? 30. What causes the daily opening of stomata? 31. Under what conditions would the stomata close during the day? 32. Describe common adaptions that reduce water loss. 33. How does C4 and CAM photosynthesis reduce water loss? 34. What is a sugar sink? Sugar Source? 35. Explain how sources and sinks can change with seasons (or conditions). 36. Explain how phloem sap moves by translocation including the role of active sugar transport, osmosis, and pressure.