IAFNR.NR.4.PP.2.3 - NAAE Communities of Practice
advertisement

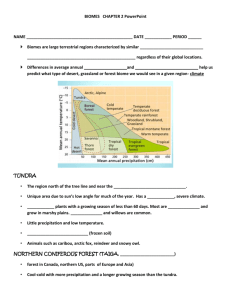
Forestry IAFNR MODULE 4 N AT U R A L R E S O U R C E S Our Forests • What is a Forest? – Community of associated trees, shrubs, other plants, and animals that interact and play a part in the ecosystem • Historic thoughts of forests – Enemy • Jamestown, the first permanent English settlement – Trees were a barrier for expansion and survival and had to be cleared – Friend • Valuable products to build wood homes and furniture • Provided summer cooling (shade), and heat for winter (fuel) • European shipping industry depended on America’s Forests Today’s Forests • How much is there? – 33% of total US Land Area is covered by forests • 1/3 of US forest and woodland is considered non-commercial forestland – Not suitable for tree production (Ex: swamps, mountainous land, parks, and preservation areas) • Other 2/3 are commercial forests – Capable of producing useful forest, but not all being used for this purpose • Forest Regions – In US, there are 860 species of trees – Six major forest regions West Coast Forests • • • Pacific coast from central California to Canada Major Species: Douglas Fir, coast redwood, Western red cedar, Sitka spruce, Sugar pine Most lumber, softwood, polywood comes from this region Central Hardwoods • • From New York State to N. Georgia to W. Texas, to N Minnesota Major Species: Shortleaf pine, Virginia pine, Eastern White Pine, Red Cedar, Birch, White Oak, Hickory, Elm, White Ash, Red Maple Northern Forests • • Maine south along the mountains to Georgia, also northern Michigan and Minnesota Major Species: Many Pines, Spruces, and Oaks, White Cedar, Black Cherry, Walnut, and Birches Western Forests • • Mountainous regions from SW Texas to Wyoming Major Species: Ponderosa pine, Idaho White pine, Sugar Pine, White fir, Western larch Tropical Forests • • Southern Tips of Florida and Texas Major Species: Mahogany, Mangrove, Bay Tree Southern Forests • • Coast of Virginia to Eastern Texas and Missouri Major Species: Lobolly pine, Longleaf pine, Shortleaf pine, Slash pine, Bald Cypress, Oaks, Willow, Cottonwood Forest Regions Key • West Coast Forests • Western Forests • Central Hardwoods • Tropical Forests • Northern Forests • Southern Forests Indiana’s Forestland Morgan-Monroe State Forest • Indiana has 4.7 million acres of forestland • 95% of Indiana’s Forests are classified as hardwood forest types • Oak, Hickory, Elm, Ash, Cottonwood • Rankings • 9th nationally in total lumber production • 3rd in hardwood lumber production http://www.in.gov/dnr/forestry/4816.htm Forest Products and Benefits • Wood – Different grades of lumber • Shop and Factory grade: Furniture, barrels, cabinets, etc. • Structural grade: Joists, planks, laminated wood • Yard wood grade: Boards and finish lumber • Converted Wood – Products like paper, charcoal, sponges, artificial hair, and imitation vanilla – Almost impossible to spend a day and not work with a wood product • Benefits – Climate Moderation • Temperature can be almost 8 degrees cooler in a forest • Provides shade in sun and break from harsh winds – Water and Soil Conservation • Forests are most effective vegetative cover for soil and water control – Wildlife Habitats and Recreation Forest Management • Measurements – Special units of measure in forest management – Monitoring Tree diameters, Heights, and Timber Volume • Cuttings – Intermediate Cuttings • Harvests taken from trees before planned maturity – Most likely for tree improvement, sanitation, or salvage – Harvest Cuttings • Cuttings for production – Whole or partial removal of trees for production and seeding Forest Management • Reproducing Forests – Seeding • Natural – Allow trees to reseed themselves in area naturally • Direct – Apply tree seeds to the desired area by hand, spreaders, or planes and helicopters – Cuttings • Replanting cuttings of certain tree species that grow readily by this method – Seedlings • Planting nursery produced seedlings – Quickest method, but also requires the most labor Forest Enemies Our Forests are fighting to grow and stay alive!! Image retrieved from: http://www.fs.fed.us/projects/hfi/field-guide/web/page09.php Forest Enemies Insects Disease • Insects have been known to kill more trees than any other forest enemy • Forest Pathology is the study of tree diseases – Common Insect Enemies • • • • • • Bark Borers Defoliators Wood Borers (Termites) Tip Feeders Sap Suckers Root Feeders – Non-infectious diseases • Caused by environmental problems – Infectious diseases • Caused by parasites – Fungus Caused Disease • Spores spread disease through large areas – Stem and Root diseases cause the most damage Forest Enemies Wildlife Environment • Any animal living in the forest gets its food from the forest • Can range from minor to extreme – Wildlife population determines the damage on the forest • When population is great not only does the forest suffer, but so do animals – Extreme Example • A whole forest is wiped out from a tornado – Minor Example • Tree limbs have broken off from ice storm effects • Good Forest management is the only way to minimize this kind of damage FIRE!! A Forest’s greatest enemy! Image retrieved from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/capital-weathergang/wp/2013/10/17/report-western-wildfires-growing-more-intense-insurers-deeply-concerned/ As a Management Tool • Prescribed Fire – Planned fire used as a part of forest management plan – Produces many benefits for the forest, wildlife, and people • Reduces wildfire hazard • Removes undesirable trees • Controls forest diseases • How does it work? – Trained foresters start and control these fires • Small areas at a time • Only performed in specific humidity and temperature levels Image retrieved from: http://www.fs.usda.gov/detail/conf/landmanagement/planning /?cid=fsm9_029220 Wildfires Image retrieved from: http://www.elitefire.co.u k/news/basics-firetriangle/ • Causes – The Fire Triangle • Types of wildfires – Ground Fire • Common in wet, bog type areas – Surface Fire • Most common type of fire – Crown Fire • Most violent and dangerous • Prevention – Smokey Bear Campaign Image retrieved from: http://www.fs.usda.gov/bitterroot/ 2013 Colorado Wildfires https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFcZ_RsZtgE References • Camp, W., & Heath-Camp, B. (2009) Managing our Natural Resources. New York: Delmar. • 7 News– Denver Channel. (June 12, 2013). Black Forest Fire burns 7500-8000 acres. Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFcZ_RsZtgE