Urban Geography Review2
advertisement

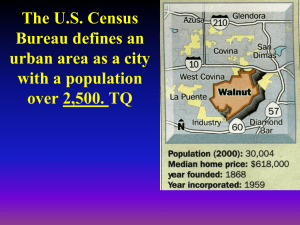
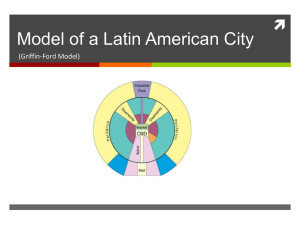
Esanye Ogbe and Michelle Ramsahoye CHAPTER 9: URBAN GEOGRAPHY When and why did people start living in cities? People first had to switch from hunting and gathering to agriculture. Components of agricultural surplus and social stratification had to enable the formation of cities. Urban morphology- the study of the physical form and structure of urban places First Urban Revolution Mesopotamia- 3500 BCE. Nile River Valley- 3200 BCE. Indus River Valley- 2200 BCE. Huang He and Wei River Valleys- 1500 BCE. Mesoamerica- 200 BCE. Greek vs. Roman Cities Greek Cities Acropolis Agora Theatres Mediterranean region Main Cities: Sparta, Athens Roman Cities Extensive transportation networks Forum Mediterranean Region, interior Europe and North Africa Focused on site Main City: Rome Second Urban Revolution Marked by the Industrial Revolution of Great Britain Improvements in agriculture: seed drill, hybrid, improved breeding practices for livestock Location of early industrial cities determined by the proximity of a power source Where are cities located and why? Trade area: region adjacent to every town and city within which its influence is necessary Rank-size rule: population of a city will be inversely proportional to its rank in the hierarchy Central Place Theory Developed by Walter Christaller Predicts how and where central places would be functionally and spatially distributed Central Places Today Sunbelt Phenomenon- movement of millions of Americans from northern and northeastern States to the South and Southwest CPT predicts that existing cities would increase production of technological goods and thus, increase economic reach to bypass others Reality: Atlanta, Dallas, and Phoenix became the Central Cities. Charlotte , Tampa, San Antonio, and Tucson rose to become secondary. Others participated less and remained where they were in the hierarchy How are city models organized and how do they function? Central Business District (CBD)- The concentration of business and commerce in the city’s downtown. Central city- the urban area that is not suburban, the older city compared to the newer suburbs Suburb- outlying, functionally uniform part of an urban area, and if often (but not always) adjacent to the central city Suburbanization- process by which lands that were previously outside of the urban environment become urbanized Ernest Burgess’s Concentric Zone Resulted from study of Chicago in the 1920s Zone 1= CBD Zone 2= Transition Zone 3= Independent workers’ homes Zone 4=Better residences Zone 5= Commuters’ zone Hector Hoyt Sector Model Focused on residential patterns based on the wealthy Core Education High-Rent Residential Intermediate Residential Low Rent Residential Industrial Transportation Harris and Ullman’s Multiple Nuclei Model Developed in the 1940s Recognizes that the CBD is losing its dominant position as the single nucleus of the urban area CBD Wholesale, light manufacturing Low-class residential Middle-class residential High-class residential Heavy manufacturing Outlying business district Residential Suburb Industrial suburb Periphery & Semi Periphery model Number of cities in the world can now be counted in the hundreds Difficult to model, classify, or typify urban centers Griffin Ford Sub-Saharan African City Southeast Asian City Griffin-Ford Latin American cities blend traditional elements of Latin American culture with forces of globalization to combine radial sectors and concentric zones Quality of homes drops the farther away from the CBD Periferico: similar conditions as the disamenity but characterized by drug lords fighting for dominance. Disamenity: poorest part of the city; disconnected from regular services of the city; usually controlled by gang or drug lords. Mall: Highpriced residences CBD: primary business, employment and entertainment focus. Divided into a market and a highrise sector. Spine: offices, shopping, high quality housing (upper & middle class), restaurants, theatres, and amenities. Sub-Saharan African City The world’s fastest growing cities Consists of three CBDs Ringed by satellite townships called squatter settlements The Southeast Asian City No CBD Elements of CBD present as separate clusters surrounding the old colonial port zone Model of mixed-land use How do People Make Cites? Individual roles of people, governments, corporations, developers, financial leaders, and realtors Governments can pass or deny strict laws that restrict urban development Powerful social and cultural preferences shape the character of particular parts of the city and influence who lives where New transportation enables the expansion of cities Suburbanization The process by which lands that were previously outside of the urban environment become urbanized, as people and business move to these spaces from the city. Suburbanization Cont. Transforms large areas of land from rural to urban uses Affects the large number of people who can afford to live in more expensive suburban homes Creates distinct urban regions complete with industrial, commercial, and educational components Edge Cities Often located near key freeway intersections Develop usually around shopping centers, office complexes, hotels, restaurants, and entertainment facilities Offer workplaces, shopping, and leisure activities Tyson’s Corner Virginia Cities in the Global Periphery and Semi-periphery Shantytowns-unplanned developments of crude dwellings and shelters made of mostly scrap wood, iron, and pieces of cardboard Zoning Laws-laws that ensure the use of space in ways that the society would deem culturally and environmentally acceptable Cities in the Global Core Cities can be made by remaking them, reinventing neighborhoods, or changing layouts to reflect goals and aesthetics Redlining-when financial institutions determine which neighborhoods are and refuse loans to those in the districts Blockbusting-when realtors solicit the white residents of a neighborhood to sell their homes under the guise that the neighborhood is going downhill because a black person or family has moved in More Global Core Vocab… Commercialization-process of transforming the central city into an area attractive to residents and tourists Gentrification-when individuals buy up and rehabilitate houses, raising the housing value in the neighborhood and changing the neighborhood itself More Global Core Vocab… McMansions-new houses that were made when owners bought a new home and tore it down to build a much larger home Called McMansions because of their super size and similar look Urban Sprawl & New Urbanism Urban Sprawl-when urban areas experience unrestricted growth of housing, commercial developments, and roads over large expanses of land with little concern for urban planning New Urbanismdevelopment, urban revitalization, and suburban reforms that create walk able neighborhoods with a diversity of housing and jobs Urban Sprawl Cities Gated Communities Gated Communities- fenced-in neighborhoods with controlled access gates for people and automobiles Usually have security cameras and security forces that patrol the community with the objective of creating a space of safety in an uncertain urban world. What Role do Cities Play in Globalization? World Cities-cities that function at the global scale, beyond the reach of the state borders, functioning as the service centers of the world economy. Primate City-the largest and most economically influential city within the state, with the next largest city in the state being much smaller and less influential World Cities New York City, New York London, England World Cities Cont… Tokyo, Japan Sydney, Australia World Cities Cont… Milan, Italy Singapore, Indonesia Spaces of Consumption Areas of the city whose main purpose is to encourage people to consume goods and services; driven primarily by the global media industry. Team Listings for Review Game (Urban Sprawlers) Nya Mike Marissa Kelsey Gabe* (New Urbanizers) Scott Sierra* Greg Rimma Alex *=team leader Josh