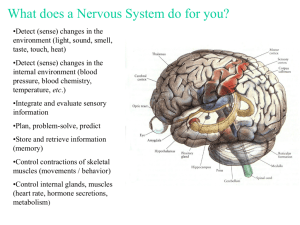
The Nervous System
advertisement

Psychology • Individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. • The adult human brain weighs about 3 pounds (1,300-1,400 g). • The human brain has about 100 billion neurons. • Neurons multiply at a rate 250,000 neurons/minute during early pregnancy. • Day 40 Brain waves are recordable! • Dendrites= the branching extensions of a neuron that receives info. and conduct impulses toward the cell body (into the neuron). • Nucleus: part of the neuron that contains chromosomes (genetic material). • Cell body a.k.a Soma= part of a cell which contains the nucleus and other parts that keep the cell healthy. • Myelin Sheath= Fatty substance that surrounds MOST axons. Speeds up conduction velocity of action potentials. • Loss of myelin is one of the main causes of Multiple Sclerosis. • Node of Ranvier: Gaps in the myelination of axons. • Axon= a neuron’s extending fiber, which conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other neurons, muscle or gland cells. • Axon terminals (a.k.a Synaptic terminal, and terminal buttons)= endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters (discussed soon) are stored. Neurons have the ability to change---to make new connections or to strengthen old ones. Examples: learning Violin player gains expertise, the motor area linked to the fingers of the left hand becomes larger (Juliano, 1998). • The network of nerve cells for communicating and processing information from within and outside the body • Consists of the brain and spinal cord. • Can be compared to a computer…processing center • Regulates EVERYTHING in your body. • Enables you to think, plan, and create. Regulate life processes. • A series of 22 fused bones protect the brain. • The adult human brain weighs about 3 pounds. • The brain devotes huge amounts of neural circuitry to the hands, lips, feet and tongue. • Your brain uses about 12 watts of power—a fraction of the energy of a household lightbulb. • A column of nerves nearly as thick as your thumb. • Extension of the brain. • Cord is a neural pathway that transmits info. b/w the brain and the peripheral nervous system. • Receives incoming info. From your sense organs. • Carries outgoing commands from the brain to muscles, glands, and organs. • There are about 13,500,000 neurons in the human spinal cord. • A reflex controlled at the level of the spinal cord, a reflex that bypasses the brain. • Examples: jerk your knee when it is tapped, pull your hand away from a burning surface, or blink when a gust of wind sent particles of debris hurtling toward your eyeballs. • The nervous system that connects the spinal cord and brain with the sensory organs, muscles, and glands. • Transmits messages b/w your central nervous system and your sensory organs and muscles. • It helps your muscles to contract in response to an INTENTIONAL command. • A.K.A. Skeletal nervous system • Controls internal bodily processes as heartbeat, respiration, digestion, blood vessels and glands. • Automatically • You can control SOME of these functions, ex. Intentionally breathing more rapidly or slowly. • Divided into two divisions: Sympathetic Nervous System and the Parasympathetic Nervous System • Speeds up bodily processes and draws energy from stored reserves. • Accelerates your heart rate and breathing • Provides more fuel/energy for the body by releasing glucose • Strong emotions, such as anxiety, fear, or anger. • +Accelerator in a car • Regulates bodily processes, such as digestion. • Converts food into glucose • Conserve energy by SLOWING DOWN bodily processes such as heart rate, breathing, etc. • Engaged when you are relaxing or digesting a meal. • +breaks in a car