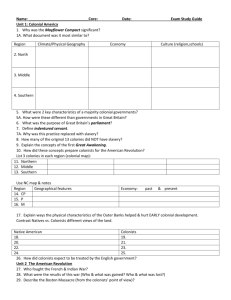
Birth of the American Republic

Birth of the American Republic
Britain Becomes a Global Power
• Geographic location allowed England to control trade
• Favorable business climate with fewer restrictions on trade
• Britain won many European battles in 1700s
• England and Wales united with Scotland to form the
United Kingdom
Map of Europe and United Kingdom
World Map
George III
• Wanted to reassert royal power as king
• Chose his own cabinet ministers and forced
Parliament to follow his will
• Asserted his brand of leadership
13 Colonies
• 13 colonies part of British empire
• Colonies were commercial centers for trade with other global areas
• Britain tried to export more than it imported
• Parliament passed laws to regulate colonial trade and manufacturing
• Many British laws were unenforceable
Map of British Empire
“ The Sun Never Set on the British Empire”
This phrase meant that the sun was always shining on the some part of the British empire around the world.
Original Thirteen Colonies
Colonial Discontent
• England fought French-Indian war
• England felt colonists should pay for colonial defense
• Parliament passed revenue laws (Stamp Act, Sugar
Act) to raise money
• Colonists balked because of “taxation without representation”
Colonial Response
• Boston Tea Party-protest tax on tea
• Colonies supported each other as Parliament tried to retaliate
• Boston Massacre – 5 protestors killed
American Revolution
• War began when British soldiers exchanged gunfire with
American minutemen at Lexington and Concord
• Continental army led by George Washington
• Declaration of Independence-written by Thomas Jefferson
•
People have right to overthrow a government that fails to protect the natural rights of citizens (life, liberty, and property-ideas of
John Locke)
• People have right to abolish unjust governments
End of War
• British had huge resources (soldiers, ships, and supplies)
• Colonists knew the terrain better
• France, enemy of Britain, offered military support
End of War (continued)
• Washington held troops together during despite low supplies, lack of food, and ammunition
• Continental Army with aid of France crushed the
British at Yorktown, Virginia
• Treaty of Paris ended the war and recognized the independence of the USA
New Government
• Articles of Confederation proved weak and ineffective
• Revolutionary leaders (Washington, Madison, Franklin,etc.) met to plan a new government with an improved constitution
• Framers of Constitution studied ideas of Enlightenment philosophers
• New Constitution divided powers between federal and state governments = federal republic
• Central feature of Separation of Powers is three branches of government – executive, legislative, and judicial (Montesquieu)
New Government
• Bill of Rights included in Constitution = people have basic rights that the government must protect
• Freedom of speech, religion, and the press
• The philosophe’s Enlightenment ideas were finally put into practice
• Constitution has been in place for more than 200 years and adopted by other democratic countries worldwide
• American Revolution inspired French to revolt against their monarchy in 1789
Video – American Revolution
Click on the following link or copy into your Internet browser: http://www.virtualprofessors.com/14-lecture-courseworld-history
Scroll down the page until you arrive at the following video title.
Please watch the video:
Tea, Taxes, and The American Revolution: Crash Course
World History #28
Homework
• Answer the following questions on a sheet of paper.
• Bring to class tomorrow to correct for points.
Powerpoint Questions
• Who was the British monarch during the American
Revolution?
• Why did Britain rise to become a global power?
(four points)
• Why did the British parliament pass the Sugar and
Stamp Acts?
• What four words did the colonists shout in protest against the Stamp and Sugar Acts?
Powerpoint Questions
• Which European country helped the colonists defeat
Britain?
• Who wrote the Declaration of Independence?
• What is a federal republic?
• What was the central feature of this federal republic?
• What did the Bill of Rights recognize?
• What is the relationship between the Bill of Rights and the Enlightenment?
• Who did the American Revolution inspire to also revolt?