3.1 Checking Accounts
advertisement

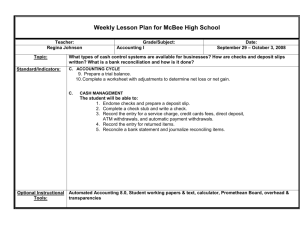
3.1 Checking Accounts Prepare a deposit slip Record entries in a check register Checking Account Many people deposit their cash receipts in a checking account at a bank and make their payments by check. A checking account is safe and easy to use. The canceled checks returned to you by the bank provide you with a record of your payments. Deposit Slip A deposit slip is used to deposit paychecks and other monies. Prepare a Deposit Slip 1153 2053 List cash deposits of bills and coins on the line labeled CASH. List each check on a separate line. List additional checks on the back. Enter total of additional checks on the Total from Other Side line. Add all the amounts and write the sum on the Subtotal line. To receive cash back from the bank, write the amount wanted on the Less Cash Received line. Subtract the cash received from the subtotal to find the Total Deposit. Sign on the signature line for cash back Deposit Slip Example Sherry has check number 825 for $800, she wants to deposit $700 of it and keep $100 in cash. Sherry Taylor Add signature if getting cash back 825 800.00 100.00 700.00 June 30 2008 Sheryl Smock 280 00 5 85 322 94 1 45 ---- --610 24 <-Gross Deposit 100 00 510 24 <-Net Deposit Textbook Pg. 85 Example A Deposit-> 14 twenties, 21 quarters, 6 dimes, checks: $322.94 & $1.45. Cash Received -> $100 June 30 2008 602 00 13 45 39 86 3 83 ---- --659 14 <-Gross Deposit ---- --659 14 <-Net Deposit Textbook Pg. 85 Example B Deposit-> 17 twenties, 18 tens, 9 fives, 37 ones, 49 quarters, 12 dimes,checks: $39.86 & $3.83. Cash Received -> $0 Checks When you write a check you direct the bank to make a payment from your checking account. Checks are numbered to make it easy to keep track of checks. Check Register The check register is part of the checkbook in which deposits and checks are recorded. A new balance, called a running balance, is calculated after each entry. – Each deposit is added to the previous balance. – Each check is subtracted from the previous balance. The balance is the amount of money in the account. Sample Check Register Payment/Debit Money going out Deposit/Credit Money coming in SEC 3-1 CHECK REGISTER #### #### 08/11 Deposit 08/13 Check Desc. 08/13 Check Desc. 825 00 96 40 2583 45 1220 00 3803 45 2978 45 2882 05 #### 08/13 Check Desc. 12 78 2869 27 Final Balance Pg. 87 C – Prev Bal $2,583.45, deposit $1,220, checks: $825, 96.40, $12.78 What’s the final balance? SEC 3-1 CHECK REGISTER #### #### #### 08/11 08/11 08/13 08/13 08/13 Deposit Deposit Check Desc. Check Desc. Check Desc. 196 00 950 00 87 83 129 500 00 629 1236 00 1865 1669 719 631 New Balance Pg. 87 D – Prev Bal $129.74, deposits: $500 & $1,236, checks: $196, $950, $87.83 What’s the new balance? 74 74 74 74 74 91 SECTION 3-1 Rev. Questions TEXTBOOK PAGE 88 #7-13, 16, 17-19, 27-32 – (17 pts.) SECTION 3-1 QUIZ WORKBOOK PAGE 29-30 – I have copies of this to give you • ( 92 pts.) Internet Extra Credit Quizzes 3.2 Electronic Banking Record electronic banking transactions Find account balance when banking electronically Electronic Banking All banks use computers to process transactions electronically. Electronic banking allows bank customers to use telephones, computers, and other technologies in place of paper transactions such as writing checks and making loan payments. Electronic Funds Transfer Banks use computers to transfer deposits and checks, or “funds,” from person to person and bank to bank. This process is called Electronic Funds Transfer, or EFT. Customer Account Numbers & Bank Identification Number Banks print the account numbers of customers and the bank identification number in Magnetic Ink Character Recognition, or MICR, form at the bottom of deposit slips and checks. ROUTING NUMBER ACCOUNT NUMBER Automatic Teller Machine Individuals can also transfer funds electronically when they use an Automatic Teller Machine, or ATM. By using an ATM card issued by your bank, you can withdraw or deposit money, see account balances, or make transfers between your accounts. Personal Identification Number A Personal Identification Number, or PIN, that is known only to you is entered into the ATM before your transaction is processed. The PIN provides protection against unauthorized use of your ATM card. Paying Bills with EFT EFTs may also be used to pay your monthly bills, such as utility bills. You can instruct your bank to transfer funds automatically each month from your bank account to the account of your utility provider. No checks are written or mailed. Direct Deposit Some companies use EFT to pay their employees by transferring funds directly into their employees’ bank accounts without writing any checks to the employees. This is called direct deposit. Debit Card Many people use a special form of EFT called a debit card. Debit cards allow you to pay for your purchases without using cash. Using a Debit Card You insert your debit card into a special computer terminal at stores. The computer system subtracts the amount of each purchase automatically from your checking account and adds the same amount to the store’s bank account. You may also use your debit card to withdraw cash from your account. Fees may be charged for using this card. Recording Electronic Transactions When you use a debit card you get a receipt of the transaction. Save the receipt and immediately record the payment or cash withdrawal in your check register. – Record the payment by writing the word “Debit” and adding a short description as well. – Record an ATM withdrawal by writing ATM-WD. – Record an ATM deposit by writing ATM-DEP. SEC 3-1 CHECK REGISTER DB DB Atm 08/13 Car Repairs. 08/13 Clothing Purch 08/13 Withdrawal 782 697 611 561 85 00 86 54 50 00 New Balance Pg. 92 A – Prev Bal $782.88, Debit Card: Car Repairs $85, Clothing Purchase $86.54, ATM Withdrawal $50, What’s the new balance? 88 88 34 34 SEC 3-1 CHECK REGISTER DB DB Atm 08/13 08/13 08/13 08/13 Deposit XXXXX . XXXXX Withdrawal 12 87 118 94 200 00 1248 890 50 2138 2126 2007 1807 New Balance Pg. 92 B – Prev Bal $1,248.40, Deposit $890.50, Debit Card: $12.87, $118.94, ATM Withdrawal $200, What’s the new balance? 40 90 03 09 09 SEC. 3-2 ELECTRONIC BANKING - Review Txtbk PAGE 93 # 5-8, 10-15 (16 pts.) SEC. 3-2 ELECTRONIC BANKING - Quiz Wkbk PAGE 31 # 1-5 (10 pts.) 3.3 Online Banking Calculate account balance needed to make online payments 3.3 Online-Account Access Online banking allows you to do your banking by using your personal computer and the Internet. Each bank designs its own Internet website. What you see on your screen and how you use an online banking system differs among banks. 3.3 Examples of Online Banking Services Access accounts 24 hours day, 7 days a week Transfer money between accounts Receive bills electronically Make payments Reorder checks Communicate with bank staff View account history 3.3 Sample Online Banking Screen 3.3 Making Decisions About Online Accounts When selecting a bank at which to do online banking, the most convenient choice is the bank you now use. You should also evaluate the systems at other banks. Select the system that best meets your needs, is easiest to use, and does so at the least cost. 3.3 Using Online Accounts You must identify sources of deposits to the account and decide who will be paid online. You will also have to determine the dates on which bills are due and the usual amount of the bill if it changes from month to month. Online banking simplifies the banking process, yet is very similar to using a regular checking account. SEC. 3-3 ONLINE BANKING Textbook pg. 97 Ex B B.) + - $67.00 728.00 36.90 112.85 270.00 15.00 128.00 89.23 45.50 $97.52 Balance Deposit Debit Card Purchase Debit Card Purchase Check Check Boat Insurance Charge Card Medical Bill . SEC. 3-3 ONLINE BANKING Review •Textbook PAGE 98 # 6-8, 11-13 Quiz at 10:30 SEC. 3-3 ONLINE BANKING Quiz WKBK PAGE 32 # 1-4 PRACTICE 3.4 Check Register Reconciliation Reconcile a bank statement Reconcile and correct a check register 3.4 Reconcile the Bank Statement Banks keep track of checking account transactions and send a monthly report, called a bank statement, to depositors. 3.4 Sample Bank Statement 3.4 Bank Statement Typical items on a bank statement – Checks paid by the bank – Deposits, including interest earned – ATM withdrawals – Service charges Interest earned is money paid to customers for the use of their money. A service charge is a deduction made by the bank for handling the checking account. 3.4 Canceled Check A canceled check is a check that the bank has paid and then marked so it can’t be used again. 3.4 Transactions Outstanding Checks that are not returned by the bank are called outstanding checks. – This means that the checks have not yet been received or paid by the bank. An outstanding deposit occurs when a deposit is made after the closing date of the bank statement and the deposit is recorded in the check register. 3.4 Reconciliation The difference (their balances do not match) in the checkbook balance and the bank statement balance is the result of the outstanding transactions, interest earned, and the service charge. To bring both balances into agreement (or match) and to make sure the bank’s records are correct, both records must be reconciled. Ms. Smock will hand out the reconciliation forms 3.4 Reconcile the Bank Statement Follow the steps on the reconciliation form on the back of the bank statement. – – – – – Enter Closing Balance from Statement Add any deposits outstanding Add lines 1 and 2 Enter total of Checks Outstanding Subtract line 4 from line 3. This amount should equal your check register balance. • If not then you need to do more steps 3.4 Sample Bank Reconciliation Form 3.4 BUSINESS TIP Outstanding items (checks and deposits) are items that you have recorded in your check register but the bank has not yet received. – That means they have not subtracted outstanding checks from the bank balance nor added outstanding deposits to the bank balance. These are two reasons most likely reasons why your balance doesn’t match the bank’s balance. 3.4 Reconcile the Check Register Add interest to the balance in the check register. Deduct service charges from the check register. The Balance from the check register should now equal the balance on the reconciliation sheet SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION PG 101 A 1,383.53 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL ------------2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 1,383.53 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 216.84 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = 1,166.69 OUTSTANDING CHECKS 129.45 87.39 Continue on the next slide - TOTAL 216.84 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE NO 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? YES 1166 69 SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION PG 101 B 793.57 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 312.09 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 1,105.66 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 207.63 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = 898.03 OUTSTANDING CHECKS 278 174.85 280 32.78 Continue on the next slide - TOTAL 207.63 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE NO 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? YES 898 03 SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION PG 102 C 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = OUTSTANDING CHECKS 727.92 Continue on the next slide - TOTAL 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? PG 102 C xx/xx Service Charge xx/xx Interest Earned YES 18 90 1 60 727 92 709 02 710 62 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? PG 102 D xx/xx Service Charge YES 7 68 457 38 449 70 SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION Closing Balance on Bank statement is 300.00. Your balance in your checkbook is 100.00. There are outstanding checks of $45 and $200. There is an outstanding deposit of $50. The bank charges $5 service charge. Interest earned is $10. Reconcile the bank statement with your checkbook. SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION x 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = 300.00 OUTSTANDING CHECKS 50.00 350.00 ---- 45.00 ---- 200.00 245.00 105.00 Continue on the next slide - TOTAL 245.00 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? YES xx/xx Service Charge xx/xx Interest Earned 5 00 10 00 100 00 95 00 105 00 SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION Closing Balance on Bank statement is 20.00. Your balance in your checkbook is 25.00. There are outstanding checks of $5 and $10. The bank charges $10 service charge. The bank made a $10 error not in your favor. Reconcile the bank statement with your checkbook. SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION x 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = 20.00 OUTSTANDING CHECKS --------20.00 ---- 5.00 ---- 10.00 15.00 5.00 Continue on the next slide - TOTAL 15.00 6.) ADD ANY SERVICE CHARGES OR INTEREST EARNED TO THE CHECK REGISTER & UPDATE BALANCE 7.) DOES THE BALANCE EQUAL THE AMOUNT IN NUMBER 5 ON THE WORKSHEET? YES xx/xx Service Charge xx/xx Bank Error 10 00 10 00 25 00 15 00 5 00 SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION Review Textbook (16 pts.) Page 103 5-7 do on paper, 8 & 10 use reconciliation forms I will have the reconciliation forms for you #19-23 do on paper SEC. 3-4 CHECK REGISTER RECONCILIATION Quiz - Workbook page 34 # 1-4 (61 pts.) •Use the worksheet Mrs. Smock gives you. Reconciliation Form 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = OUTSTANDING CHECKS TOTAL 3.5 Other Reconciliation Problems Reconcile a checking account with outstanding transactions and other errors Reconcile the Checking Account Sometimes you must reconcile a bank statement and check register balances when deposits, checks, and EFT transactions are not recorded and when other errors are made. SEC. 3-5 OTHER RECONCILIATION PROBLEMS STEPS TO FIND PROBLEMS 1.) Check to see if balance of check register and bank statement are the same. If they don’t agree you have to reconcile the account. SEC. 3-5 OTHER RECONCILIATION PROBLEMS STEPS TO FIND PROBLEMS 2.) Compare to see if each item of on the register is also on the bank statement. If an item is on both put a checkmark on the item in the bank statement. Place an “X” on the items that need to be looked into. SEC. 3-5 OTHER RECONCILIATION PROBLEMS STEPS TO FIND PROBLEMS 3.) Prepare a reconciliation form to reconcile the bank statement. 4.) Reconcile the check register. Go over together Pg 106-107 SEC. 3-5 Pg. 106-107 632.31 OUTSTANDING CHECKS 85.00 717.31 850 8.12 852 34.28 TOTAL 42.40 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = Ch851 7/19 ck853 wrong ck853 correct atm dep 7/28 Int. earned ATM with 7/12 ATM fee 7/12 EFT truck loan Debit card fee 42.40 674.91 37 16 72 05 120 1 416 6 00 50 18 40 1181 39 1144 23 27 05 1171 28 1099 23 118 20 1217 43 1 56 1218 99 1098 99 1097 49 681 31 674 91 SEC. 3-5 Pg. 108 A 161.96 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = TOTAL 161.96 Int. earned atm dep ck307 wrong ck307 correct OUTSTANDING CHECKS 43 56 00 32 95 35 29 107 87 108 30 164 30 197 25 161 96 SEC. 3-5 Pg. 108 B 624.77 OUTSTANDING CHECKS --------624.77 201 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = ATM with Ch202 92.49 TOTAL 92.49 92.49 532.28 200 00 812 45 612 45 80 17 532 28 SEC. 3-5 REVIEW •TEXTBOOK PG 109 #7-10 •USE THE PAPER I GIVE YOU AND LABEL THE PROBLEM NUMBERS •TEXTBOOK PG 110 #18-21 •DO ON PAPER 30 POINTS SEC. 3-5 QUIZ •WKBK PG 35-36 #1-2 •I have copies for you 57 Points SEC. 3-5 Banking Simulation Banking Is Check set Integra Bank 100 Points 3.6 Savings Accounts Calculate simple interest on savings deposits Calculate compound interest on savings deposits Calculate interest using a compound interest table Interest One reason people open savings accounts is to keep their money safe. Another reason is that they earn interest on their money. Interest is money paid to an individual or institution for the privilege of using their money. Lesson 3.6 78 Transaction As with a checking account, you may deposit money into or withdraw money from your savings account. The bank teller may give you a receipt, which is an official record of the transaction. A transaction is something that happens that has to be recorded, such as a deposit or withdrawal. Simple Interest Simple interest is often figured quarterly, or four times a year, on the balance of the account at the end of each quarter. The interest is paid on the first day of the next quarter, or on January 1, April 1, July 1, and October 1. Sometimes interest is paid twice a year, or in semiannual periods (six months, or one-half year). Calculate Simple Interest To find the simple interest for any period, first find the interest on the deposit for a full year. – Then multiply that amount by the fraction of a year, such as ¼ or ½ for which you want to find interest. Interest = Principal × Rate × Time (I=PRT) SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS SIMPLE INTEREST – PD QRTLY OR SEMI-ANNUAL INTEREST = PRINCIPAL X RATE X TIME PG 112 EX: I = $400.60 X 0.055 X ½ = $11.016 OR $11.02 SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS PG 112 A & B A.) I = $860 X 0.0225 X ¼ = $4.8375 OR $4.84 B.) I = $350 X 0.031 X ½ = $5.425 OR $5.43 Compounding Interest At the end of each interest period, the interest due is calculated and added to the previous balance in the savings account. The new balance then becomes the principal on which interest is calculated for the next period, if no deposits or withdrawals are made. When you calculate interest and add it to the old principal to make a new principal on which you calculate interest for the next period, you are compounding interest. Compound Interest Regardless of how interest is earned, the total money in the savings account at the end of the last interest period is called the compound amount, assuming that no deposits or withdrawals have been made. The total interest earned, called compound interest, is the difference between the original principal and the compound amount. SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST – PAID DAILY OR QUARTERLY COMPOUND AMOUNT – TOTAL MONEY IN THE SAVINGS ACCOUNT AT THE END OF THE LAST INTEREST PERIOD COMPOUND INTEREST = =COMPOUND AMOUNT – ORIGINAL PRINCIPAL SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST – PG 113 EX: I = $800 X 0.06 X 1/4 = $12 (INTEREST FOR 1ST QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $800 + $12 = $812 (COMPOUND AMOUNT) $812 X .06 X ¼ = $12.18 (INTEREST FOR 2ND QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $812 + $12.18 = 824.18 SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST – FIND COMPOUND INTEREST FOR THE TWO INTEREST PERIODS $824.18 - $800 = $24.18 (COMPOUND INTEREST) SIMPLE INTEREST FOR SAME PROBLEM = $800 X .06 X ½ = $24 COMPOUND INTEREST FOR SAME PROBLEM = $24.18 WHICH MAKES YOU MORE INTEREST? SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST – Pg 113 C & D C) I = $700 X 0.03 X 1/4 = $5.25 (INTEREST FOR 1ST QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $700 + $5.25 = $705.25 (COMPOUND AMOUNT) $705.25 X .03 X ¼ = $5.29 (INTEREST FOR 2ND QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $705.25 + $5.29 = 710.54 SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST – Pg 113 C & D D) I = $400 X 0.05 X ½ = $10 (INTEREST FOR 1ST QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $400 + $10 = $410 (COMPOUND AMOUNT) $410 X .05 X ½ = $10.25 (INTEREST FOR 2ND QTR) FIND NEW ACCOUNT BALANCE $410 + $10.25 = $ 420.25 Interest Earned in one year $420.25 - $400 = $20.25 Compound Interest Tables When you calculate compound interest for several interest periods, you can use a compound interest table. The table shows the value of one dollar ($1) after it is compounded for various interest rates and periods. Sample Compound Interest Table Using a Compound Interest Table 1. To calculate annual interest, locate the column and row where the interest rate and the number of interest periods meet. 2. The number you find is called the multiplier. 3. Multiply the deposit amount by the multiplier to find the compound amount. 4. Subtract the original principal from the compound amount to find compound interest. SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – EX 3 PG 114 2 ½ % @ 12 yrs $400 X 1.344888 = $537.9552 -> $537.96 COMPOUND AMOUNT $537.96 - $400 = $137.96 COMPOUND INTEREST SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – PG 114 E 5% @ 3 yrs $1,100 X 1.157625 = $1273.3875 $1,273.39 COMPOUND AMOUNT $1,273.39 - $1,100 = $173.39 INTEREST COMPOUND SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – PG 114 F 6% @ 7 yrs $720 X 1.503630 = $1082.6136 $1,082.61 COMPOUND AMOUNT $1,082.61 - $720 = $362.61 INTEREST COMPOUND SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – EX 4 PG 114 1/4 X 8% = 2% QUARTERLY RATE 4 X 3 = 12 INTEREST PERIODS 2% @ 12 yrs $1,200 * 1.268242 = $1,521.89 $1,521.89 – $1,200 = $321.89 COMPOUND AMOUNT SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – PG 115 G 1/4 X 5% = 1.25% QUARTERLY RATE 4 X 2 = 8 INTEREST PERIODS 1.25% @ 8 yrs $850 * 1.104486 = $938.81 $938.81 – $850 = $88.81 COMPOUND AMOUNT INTEREST EARNED SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – PG 115 G 1/2 X 4% = 2% QUARTERLY RATE 2 X 2 = 4 INTEREST PERIODS 2% @ 4 yrs $1,600 * 1.082432 = $1,731.89 COMPOUND AMOUNT $1,731.89 – $1,600 = $131.89 INTEREST EARNED SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS COMPOUND INTEREST TABLES – Review 3-6 -> WKBK PG 37-38 ALL #1-5 Simple Interest #6-9 Calculate Compound Interest Manually #10-18 Use Compound Table I will make copies of this for you. SEC. 3-6 SAVINGS ACCOUNTS QUIZ TEXTBK PG 116 #7-18, 31-35 •For problem number 17 the money is in the bank for only 3 compounding periods. •For problem number 34 use the table on page 41 Extra Credit Pg. 116 #19 & 20 3.7 Money Market and CD Accounts Calculate interest earned on special savings accounts Calculate the penalty for early withdrawals from CD accounts Compare the interest earned on savings accounts Calculate the effective rate of interest 3.7 Special Savings Accounts In addition to regular passbook savings accounts, many banks also offer special savings accounts for long-term savers. The interest rates paid on these special savings accounts are higher than the rates paid on regular savings accounts. 3.7 CERTIFICATE OF DEPOSIT The certificate of deposit is widely referred to as a CD. The CD is also known as a time deposit or a savings certificate. Some government rules apply to certificate of deposit accounts. (continued on the next slide) 3.7 CERTIFICATE OF DEPOSIT Most banks require depositors to meet certain requirements. – Deposit a minimum amount. – Leave the money on deposit for a minimum time. The time may be specified in number of days, months, or years. The minimum time is called the term. The date that marks the end of the term is the maturity date. – Pay a penalty if money is withdrawn before the end of the term. 3.7 MONEY MARKET ACCOUNTS Money market accounts offer higher interest rates than regular accounts. Special rules apply: – A minimum balance must be kept in the account for the term specified. More money may be added to the account at any time. – The interest rate paid is fixed for short periods of time. – A small number of checks may be written against the account. 3-7 MONEY MARKETS & CD ACCOUNTS 1/12 PG. 119 A & B A.) 10,000 x .054 x 3 = $1,620 B.) 2,000 x .044 x .08333= $7.33 2,000 x .0432 x .08333 = $7.20 7.33 + 7.20 = $14.53 3.7 Penalties on CDs By law, banks must charge depositors a penalty for withdrawing money early from a certificate of deposit. Each bank sets its own penalty for early withdrawals. The penalty usually varies with the term of the certificate. 3-7 MONEY MARKETS & CD ACCOUNTS 3/12 PG 120 C & D C.) 500 x .049 x .25 = $6.13 D.) 1,000 x .067 x 1 = $67 1,000 – 67 = $933 3.7 Compare Savings Accounts Savings accounts are often compared by the interest earned in each account. To compare, calculate the interest that would be earned by each type of account for the same time period. 3-7 MONEY MARKETS & CD ACCOUNTS PAGE 121 E & F E.) .0535 x .5 x 1,400 = $37.45 37.45 – 15.13 = $22.32 F.) .0426 x .75 x 1,500 = $47.93 47.93 – 31.37 = $16.56 3.7 Effective Rate of Interest The effective rate of interest is the rate you actually earn by keeping your money on deposit for one year. The annual rate and the effective rate you earn can be different. The effective rate is sometimes referred to as the annual percentage yield. Amount of Interest Earned for One Year Amount of Money on Deposit = Effective Rate of Interest 3-7 PG 122 G & H – Use Table on Pg. 113 G.) 6% / 4 = 1.5% 1 x 4 = 4 yrs Pg. 113 1.5% at 4 yrs. 1.061364 x 2,000 = $2,122.728 2,122.728 - 2,000 = $122.728 122.73 / 2,000 = .061364 = 6.14% 3-7 PG 122 G & H – Use Table on Pg. 113 H.) 5% / 2 = 2.5% 1 x 2 = 2 yrs Pg. 113 2.5% at 2 yrs. 1.050625 x 6,000 = $6,303.75 6,303.75 - 6,000 = $303.75 303.75 / 6,000 = .050625 = 5.10% SEC. 3-7 MONEY MARKETS & CD ACCOUNTS Review 3-7 -> WKBK PG 39 - 40 ALL 40 pts 10:30 Quiz Begins SEC. 3-7 MONEY MARKETS & CD ACCOUNTS Quiz 3.7 -> TXTBK PG 123 #9-11, 13, 18-20 #9 – all simple interest no compound 30 pts CHAPTER 3 REVIEW PAGE 124 – 125 ALL 40 pts. CHAPTER 3 TEST PAGE 129 # 11-18 100 Pts. CHAPTER 3 INTEGRATED PROJECT Integrated Project 100 Pts. CHAPTER 3 GOOGLE DOCS FIND AND RATE TYPES OF SAVINGS ACCOUNTS GOOGLE DOCS PROJECT 100 Pts. Reconciliation Form 1.) ENTER CLOSING BAL 2.) ADD ANY DEPOSITS + 3.)ADD LINES 1 & 2 = 4.) TTL OF CHKS OUT 5.) LINE 3 – LINE 4 = OUTSTANDING CHECKS TOTAL