road_scholar_clinic_2007
advertisement

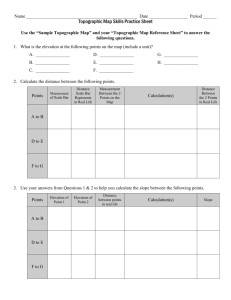
Road Scholar Event Jane Domier Illinois State Geological Survey Champaign, IL Illinois Science Olympiad Coaches Clinic October 27, 2007 Carol Stream, IL Road Scholar • The Road Scholar exam tests the students’ ability to read highway maps, internet-generated maps, or a road atlas, and to read and interpret USGS topographic maps • Storyline format • Team of 1 or 2 people • 50 minutes Tools and Rules • Provided at test: highway map, topographic quadrangle maps, USGS Map Symbol Sheet, test, and answer sheets • Students bring: protractor, ruler, symbol sheet, pencils • Optional: calculator, notes, reference materials, measuring devices • Computers are not permitted • May not write on maps or symbol sheet • Discussion with teammate encouraged Exam Format Welcome to the State Competition of the Road Scholar in Champaign, Illinois. You and your partner are being sent on a field trip to collect data for hydrology or water analysis in southern Illinois. You will be visiting areas near Charleston, Illinois, and Rend Lake State Wildlife Refuge. You are prepared for the trip, with a state highway map [HM] and two topographic maps, Charleston South [CS] and Rend Lake Dam [RLD]. You are currently located in Urbana, Illinois. Consulting your Illinois highway map, you find that the index coordinates for Urbana are _____ [1-HM]. The precise population of Urbana at the date of this map is ____ [2-HM]. Urbana is located in ____ county [3-HM], and the symbol used for Urbana tells you that it is the _____ [4-HM] of this county. This square represents section 24, Public Land Survey System. Draw a school house in the NE ¼ SW ¼ 24. Draw a large cemetery in the SE ¼ NE ¼ 24. Scoring • 1 point for each question • Teams are ranked according to total points • Several more difficult questions indicated as tiebreakers Regional / State Competitions • Same format • Some questions more involved at State level – Stream gradient (feet per 1000 feet) – Slope (feet per 100 feet) – Profiles – Interpretation of contours/landforms Highway Maps • General reference • Planimetric – shows horizontal position of physical and human features Legend, symbols, index Distances between features Distance table City and regional inserts Topographic Maps • Show elevation and landforms • Natural and human features • Larger scale than highway map; smaller area with more detail • Also called ‘topo’ maps, or quadrangle maps Map location, series, scale Road legend, title, date Marginal information Parallel to each other 1° latitude ~70 miles Carol Stream: 41° 55’ 50” N 88° 8’ 25” W Meridians converge at poles 1° longitude = 0 to ~70 miles 0° Greenwich, England 180° International Date Line Geographic Coordinate System Latitude and Longitude 7.5’ series 1:24,000 Illinois quadrangles: 8.5 miles N-S 6.5 to 7 miles E-W 30” divisions Latitude/longitude, mental sectors Projection Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) Coordinate System Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid (blue tics, 1000 meter intervals) North Zone 0,0 Central Zone 0,0 South Zone 0,0 State Plane Coordinate System State Plane Coordinate System (black tics, 10,000 foot intervals) Magnetic declination: Angular difference between magnetic north and geographic north (N. Pole) - varies with position and time Magnetic declination US Public Land Survey System (USPLS) SW¼ SW¼ Sec. 14, T2S,R3W Public Land Survey System This square represents section 24, Public Land Survey System. Write the section number on your map. Draw a race track in the NE¼ SW¼ 24. Draw a large cemetery in the SE¼ NE¼ 24. Map symbols Black: cultural features - roads, buildings, political boundaries, RR, place names Blue: hydrographic features - lakes, rivers, isobaths Brown: topography, land surfaces (sand dunes, other rough surfaces), contour lines, elevation numbers Green: vegetation, scrub, orchards, vineyards Red: important roads and public land survey system pink - urban areas – (now gray) Purple: features added from aerial photo revision (not field checked) Colors on topographic maps Elevation of features Index Intermediate Supplementary Depression Contours – lines of same elevation Constant interval Contours never cross Direction of stream flow – contours point upstream Profiles Bearings Azimuths Edge of paper or string to measure distance Subdivisions on left end for finer measurements Distance between features Length of river is 6000 feet. 60 feet rise in elevation Stream gradient = 10 feet/1000 feet Stream gradient 6000’ / 1000’ = 6 60’ / 6 = 10’ Recommended web sites and materials National Science Olympiad Road Scholar web page: http://www.soinc.org/events/roadscholar/index.htm Road Scholar Preparation - Terry Trippe: Course outline: http://www.soinc.org/events/roadscholar/Road_Scholar_Course_Outline.pdf Contest Preparation: http://www.soinc.org/events/roadscholar/Road_Scholar_Contest_Prep_Info.pdf Competition Study Guide: http://www.soinc.org/events/roadscholar/Road_Scholar_Comp_Study_Guide.pdf Competition Study Guide Answers: http://www.soinc.org/events/roadscholar/Road_Scholar_Study_Guide_Answers.pdf Exams from previous competitions: http://www.tufts.edu/as/wright_center/products/sci_olympiad/sci_olympiad_road_sc holar.html Map Reading; Reading Topographic Maps - Mark Van Hecke http://www.tufts.edu/as/wright_center/products/sci_olympiad/upload_1_15_05/pdf/r oad_scholars_2005.pdf USGS Interactive Lessons – What Do Maps Show? http://interactive2.usgs.gov/learningweb/teachers/mapsshow.htm