Types of Cells PP
advertisement

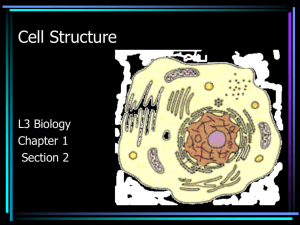
Types of Cells Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells. Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryotic means “before the nucleus.” Eukaryotic means “true nucleus” Organisms: Bacteria & Archaea Organisms: Plants, Fungi, Protists, Animals Divides by: Binary fission Divides by: Mitosis Prokaryotic Do not have structures surrounded by membranes Few internal structures One-celled organisms: Bacteria and Archaea Prokaryotic Cells three shapes Eukaryotic Contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms Plant Animal http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif Another look at the Animal Cell Cell Parts Organelles Organelles Cell membrane Cell Wall Endoplasmic reticulum(ER) Nucleus Ribosomes Nuclear Membrane Mitochondria Nucleolus Golgi Apparatus Centrosomes/Centrioles Lysosomes Chromosomes Vacuole Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cell Membrane the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. How does the cell membrane work? Has 2 layers of MOLECULES = BILAYER Bi means two The layers are made up of molecules called phospholipids Cell Membrane: PHOSPHOLIPIDS Each phospholipids has a HYDROPHOBIC and HYDROPHILIC end •HYDRO = means water •PHOBIC = means afraid •PHILIC = means loving Cell Membrane: PHOSPHOLIPIDS One end of the molecule is “afraid” of the water and one end “loves” being in the water. Proteins are stuck inside the membrane Proteins are across the bi-layer and make the holes that let ions and molecules in and out of the cell Cell Wall Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria Supports & protects cells Nucleus Directs cell activities Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Contains genetic material - DNA Nuclear Membrane Surrounds nucleus Made of two layers Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus Nucleolus Inside nucleus Contains RNA to build proteins Centrosome a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules where microtubules are made During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell The centriole is the dense center of the centrosome. Chromosomes In nucleus Made of DNA Contain instructions for traits & characteristics Cytoplasm Gel-like material outside the cell nucleus Where the organelles are located Surrounded by cell membrane Contains hereditary material Endoplasmic Reticulum Moves materials around in cell Smooth type: lacks ribosomes Main function is to collect, maintain & transport things Creates steroids Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface Ribosomes Made in nucleus Each cell contains thousands, small dot like, floating around the cell Make proteins There are two kinds of ribosomes Attached to the rough ER floating in the cell cytoplasm Mitochondria The “Power House “ of the Cell Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates Controls level of water and other materials in cell Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane Golgi Bodies also called the Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Complex Flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus packages proteins and carbohydrates into membranebound vesicles for "export" It produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes Lysosome A type of cell vesicles round organelles surrounded by a membrane Digestive “plant” for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates The enzymes bond to food & digest it (acidic interior), releasing smaller molecules absorbed by the mitochondria Vacuoles Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal In a plant the Large Vacuole contains water solution and helps maintain shape Plant Cell Animal Cell Chloroplast Usually found in plant cells Contains green chlorophyll Where photosynthesis takes place Photosynthesis : the process in which plant use water, carbon dioxide, and energy form the sun to make food (glucose) Plant vs. Animal Cells PLANT CELLS 1. Cell wall 2. One large vacuole 3. Chloroplasts 4. No lysosomes 5. Rectangular 6. Photosynthesis ANIMAL CELLS No cell wall 2. A few small vacuoles 3. No chloroplasts 4. Lysosomes 5. Roundish 6. Respiration 1. REVIEW Two Types of Cells: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Animal cells and plant cells are Eukaryotic, but have some differences Cells are made up of many organelles, each having a specific function