Cell Structure & Function
advertisement

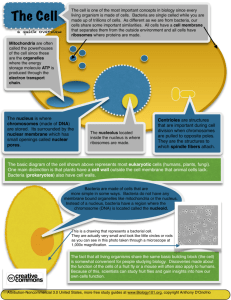
Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory • 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. (Schleiden & Schwann)(183839) • 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. (Schleiden & Schwann)(1838-39) • 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. (Virchow)(1858) Modern Cell Theory • Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: • The cell contains hereditary information(DNA) which is passed on from cell to cell during cell division. • All cells are basically the same in chemical composition and metabolic activities. • All basic chemical & physiological functions are carried out inside the cells.(movement, digestion, etc.) • Cell activity depends on the activities of subcellular structures within the cell(organelles, nucleus, plasma membrane) What is a Cell? • A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. • Cells are the basic unit of life. • Cytology can be considered the most important area of biology • Cloning, embryology, cancer research • 3 centuries of research Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Two Types of Cells •Prokaryote •Eukaryote •Pull out worksheet on Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Prokaryotes • Do not have a nucleus • Do not have membrane bound organelles (eg. NO mitochondria, NO chloroplasts) Eukaryotes • Contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Prokaryotes are cells that do not have a nucleus and do not have membrane bound organelles. These cells are smaller than eukaryotes and are believed to have existed over 2.5 billion years ago as the first cells on earth. Examples: bacteria, blue-green bacteria (cyanobacteria) and archeabacteria are prokaryotes. Archeabacteria are the bacteria that are found in very harsh conditions such as thermal vents and hot springs. Eukaryotes are cells that contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria. The nucleus is the control center for all cell activity. The mitochondria is where cell respiration takes place. In the mitochondria energy is released to support cell activities. Examples: all plant, protist, fungi and animal cells are eukaryotes. • Video Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Cell Parts Organelles Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane • Outer membrane of cell that controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell • Double layer Cell Wall • Most commonly found in plant cells, bacteria and fungi (NOT FOUND IN ANIMAL CELLS) • Supports & protects cells Inside the Cell Cytoplasm • Gel-like fluid • Contains the organelles except for the nucleus Nucleus • Directs cell activities • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane • Contains genetic material - DNA NUCLEUS Nuclear Membrane • Surrounds nucleus • Made of two layers • Nuclear pores allow material to enter and leave the nucleus NUCLEAR MEMBRANE The nuclear membrane is also called the nuclear envelope Nucleolus • The dense area inside the nucleus • Contains RNA to build proteins NUCLEOLUS RiboNucleic Acid: The nucleic acid that is used in key metabolic processes for all steps of protein synthesis in all living cells and carries the genetic information of many viruses. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, Chloroplast • Found in plant cells • Contains the green pigment chlorophyll • Where photosynthesis takes place Mitochondria • Releases energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates Endosymbiosis • How was shift made from small prokaryotic to large eukaryotic cells? • Endo (within) symbiosis (together) bio (living) • Aerobic bacterium – respiration/breaking down food (oxygen) • Cyanobaterium – photosynthesis • Came together to become the mitochondria and chloroplast we have today • Endosymbiosis Video Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape Animal cells have one or more small vacuoles (much smaller than plant cells).Plant cells have one, large central vacuole taking up 90% of cell volume. Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins • Found on rough endoplasmic reticulum & freely floating throughout the cell in the cytoplasm Golgi Bodies/Apparatus • Protein 'packaging plant' • Move materials within the cell • Move materials out of the cell • Also called the Golgi apparatus Lysosome • Vesicles that bud from the Golgi apparatus • Contain digestive enzymes • Within a cell, lysosomes digest worn-out organelles and destroy cells that are no longer functioning properly Endoplasmic Reticulum • Moves materials around in the cell • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type: ribosomes embedded in surface • Tour of a cell • Animation showing structure and function of a plant and animal cells Video