The Eukaryotic cell * Parts and their functions.
advertisement

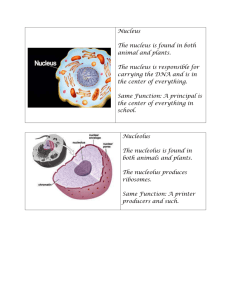
The Eukaryotic cell – Parts and their functions. Use this PowerPoint to study the parts and functions of the cell Cell Wall (Plant Cell Only) • Outermost part of plant cell. Rigid structure. Protects the cell, helps it maintain shape and gives structural support. Cell Wall (plant cell only) Cell Membrane (Animal and Plant) • Flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside the cell. • Controls what enters and leaves the cell. Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Cytoplasm (Animal and Plant) • Fluid/gel-like material inside a cell that contains salts and other molecules. Holds the cell’s organelles. Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton (Animal and Plant) • A network of threadlike proteins throughout the cytoplasm. • Gives the cell structure and helps it move. Cytoskeleton Nucleus (Animal and Plant) • Part of a eukaryotic cell that directs cell activities and contains genetic information stored in DNA. Nucleus Nucleolus (Animal and Plant) • Produces ribosomes. Located inside of the nucleus. Nucleolus Nuclear Membrane (Animal and Plant) • Surrounds the nucleus. Contains many pores (small openings). Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus. Nuclear Membrane (envelope) pores Chromatin (Animal and Plant) • Strands of genetic material in the nucleus. Contains the instructions that direct the cell’s activities. Chromatin Rough ER (Animal and Plant) • Maze like organelle that spreads throughout most of the cytoplasm. • Forms passageways that move material throughout the cell. • Contains ribosomes on the surface. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes (Animal and Plant) • Site of protein production. • Located on the surface of the rough ER as well as in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes Ribosomes Smooth ER (Animal and Plant) • Maze like organelle that spreads throughout most of the cytoplasm. • Does not contain ribosomes on the surface. • Produces lipids and removes harmful substances from the body Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER Smooth ER Mitochondria (Animal and Plant) • Produces useable energy for the cell. “Powerhouse” of the cell. • Energy produced by the mitochondria is stored as ATP. Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus (Animal and Plant) • Prepares proteins for specific jobs. Packages the proteins into vesicles that transport the proteins throughout the cell. • Also called the Golgi Body or Golgi Complex Centriole (Animal Cell Only) • Important in cell division in animal cells. • Occur in pairs and are usually found near the nucleus. Centriole Lysosome (Animal Cell Only) • Contain substances that help break down and recycle cellular components. Vacuole (Animal and Plant but different) • Sac like structure that stores food, water, and waste material. • Plant cells have one large (central) vacuole while the animal cells have many small vacuoles. Vacuole (smaller in an animal cell) Vacuole (Larger in a Plant Cell) Chloroplast (Plant Cell Only) • Membrane bound organelle that uses light energy to make food (glucose) through the process of photosynthesis. Chloroplast