Great Wall of China
advertisement

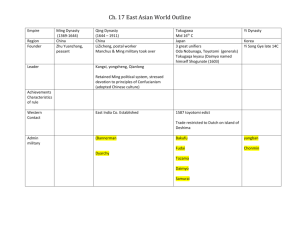
The Great Wall of China What is the Great Wall? The Great Wall of China is the world’s largest military structure. It was built as a defense to stop invaders from northern areas. The Great Wall is actually a series of walls built and rebuilt by different dynasties over 1,000 years. It has a total length of over 6,000 kilometers. The Chinese measured the wall in “li”. A single li is equivalent to half a kilometer. In Chinese the wall is called “Wan-Li Ch’ang-Ch’eng” which means 10,000-Li Long Wall. The Great Wall runs from Jiayu Pass of Gansu Province in the west to the mouth of the Yalu river in Liaonling Province in the east. Who Built The Great Wall? Zhou Dynasty (1045 b.c. – 246 b.c.) During the Zhou Dynasty, Xiongnu tribes frequently attacked northern border states. In the 7th century B.C., the northern states built their own walls for defense purposes. Qin Dynasty (221 b.c. – 207 b.c.) Qin Shi Huang was the first emperor of China and is considered the first Great Wall builder. He was a relentless tyrant who’s dynasty eventually fell to peasant uprising. The oldest section of the Great Wall was begun in 221 b.c. The construction linked together the restored ruins of older walls created in the Zhou Dynasty to create a 5000 kilometer (10,000 li) section. This is the origin of the 10,000-li wall name. First Emperor Qin Shi Huang Who Built The Great Wall? Qin Dynasty (221 b.c. – 207 b.c.) cont. It is estimated that over 3 million people (70% of China’s population at the time) were involved in the construction of the wall. The Qin Great Wall is constructed out of local materials. The builders used dry-laid stone or used layers of compacted earth. To build with compacted earth the workers first built a 4 inch high frame, then filled it with loose earth, and packed it. Thus, the wall was built one 4-inch layer at a time. A section of the Qin Wall built using the tamped-earth process. According to historical records, the Qin Great Wall was built in 10 years or about 25 miles a month. In modern dollars, the estimated cost to build the Qin Great Wall would be $260 billion. Who Built The Great Wall? Han Dynasty (206 b.c. – 220 a.d.) Han Wu-Di expanded the China empire westward into the wilderness of Central Asia. He is considered the second Great Wall builder. During the Han Dynasty the crumbling Qin wall was rebuilt and extended over 480 kilometers through the Gobi desert. Since local materials were always used for the construction, the Han Great Wall A section of the Han Wall built using water, gravel, and willow reeds. is created from a mixture of water and fine gravel, reinforced with willow reeds. These layers were compacted upon each other in much the same manor as the Qin Dynasty compacted earth. The major contribution of the Han Dynasty to the Great Wall was the watchtowers. Who Built The Great Wall? Han Dynasty (206 b.c. – 220 a.d.) cont. The watchtowers were typically spaced 15 to 30 miles apart and were used to alert other sentries to attacks and defend the wall. In the event of an attack, the guards would set fire to a mixture of wolf dung, sulfur, and saltpeter. This would create a column of smoke to alert the other watchtowers. The number of columns of smoke related to the attacking force. One column meant an outpost was under attack by a force of fewer than 500 troops. Two columns would represent a force fewer than 2500, etc. The Chinese realized the smoke beacons carried alerts faster than a rider on a horse. A watchtower signaling an attack Who Built The Great Wall? Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644) The Ming Dynasty is considered the greatest of all Great Wall builders. The walls built by the Ming Dynasty were larger, longer, and more ornate than the walls from previous dynasties. The Ming Dynasty rebuilt crumbling sections of the Han Great Wall and lengthened it to 6,400 kilometers. Kiln-fired bricks used during the Ming Dynasty The major advancement in the Ming Great Wall was the use of kiln-fired brick rather than cutting individual stones. The new wall sections were built with a tamped earth interior and encased in this brick. If you took all of the bricks from the Ming portion of the Wall alone, they could circle the Earth at the equator in a wall five feet high and three feet thick. Who Built The Great Wall? Ming Dynasty (1368 – 1644) cont. The Ming Wall crosses some of the most forbidding terrain in all of China. In some places, the Wall rises at a 70 degree angle. The Ming Dynasty also purchased cannons from Portuguese traders and mounted them in strategic watchtower locations. Section of BaDaLing wall built during Ming Dynasty The cannons were used in defense of the Wall and as an alert (in addition to the smoke columns) to alert other sentries to an attack. It took approximately 200 years to complete the Ming Wall. In modern terms, construction of the Ming Great Wall would cost $360 billion. At its peak, the Ming Great Wall contained thousands of individual forts and towers. It was guarded by more than a million men. Sections of the Great Wall BaDaLing The BaDaLing section of the Great Wall was built at the beginning of the Ming Dynasty. It was built to safeguard the capital of Beijing and is considered an important strategic point. BaDaLing has battle forts at important locations including the corners. It is 7.8 meters in height and 5 meters wide. The top of the wall is paved with square bricks and is wide enough for six horses or ten soldiers to march side by side. The BaDaLing wall is built from local materials including green bricks from the surrounding hills and rectangular slabs of stone. Section of BaDaLing wall near Beijing Sections of the Great Wall BaDaLing cont. Near BaDaLing is the Pass of Conscripted Laborers. The important gateway northwest of Beijing is believed to be named after the workers and slaves conscripted to build the Great Wall. It is built 10 kilometers south of the BaDaLing section in an 18.5 long valley. Pass of Conscripted Laborers Passage Inscriptions The interior of the Pass contains carvings of elephants, lions, birds, flowers, and heavenly kings as well as charms in six languages. Sections of the Great Wall Mutianyu Section The Mutianyu Section of the Great Wall is located 70 kilometers northeast of Beijing. It links the Gubeikou section on the east and the BaDaLing section on the west. The Mutianyu Wall one of the best-preserved parts of the Great Wall and is older than the BaDaLing section. It is heavily fortified to stop invaders and some of the battle forts are as close as 50 meters apart. The upper protective walls are notched on both the inside and outside so that shots could be fired at enemies on either side. This feature is very rare on other parts of the Great Wall. Mutianyu Section Sections of the Great Wall JinShanLing Section The JinShanLing section contains 67 watchtowers within an 11 kilometer stretch. Each watchtower is unique and an example of different architecture. This section of the Wall is 5 to 8 meters high. Its sides taper from 6 meters wide at the bottom to 5 meters wide at the top. The JinShanLing Wall is considered to be the most spectacular section of the Wall and representative of the Ming Dynasty. JinShanLing Section with Watchtowers The battlements take advantage of mountain ridges to give guards the advantage of high terrain. And is part of the GujbeiKou defense barrier. Sections of the Great Wall Simatai Section The Simatai Section is located east of JinShanLing and is also part of the Gubeikou defense barrier. It is 5.4 kilometers long and has 35 watchtowers. This section of Great Wall is uniquely designed by incorporating the different characteristics of other sections of the Great Wall. The Simatai Wall rises and falls with the precipitous mountain ridge and the watchtowers are located high upon the hilltops. Simatai Section of Great Wall Sections of the Great Wall Lost Sections of the Great Wall Since the 1600’s, parts of the Wall in some areas have been dismantled to provide building materials. Other areas have succumb to nature and are buried by silt. Using satellite data, scientist have rediscovered more than 600 miles of buried Wall in the past decade. Scientist have discovered a deteriorated second wall running parallel to the BaDaLing section. Only a few meters separate the locations. “It was partially buried and so degraded that you’d have to know it was there to recognize it in the field.”, says Diane Evans, project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Satellite Photo of the Great Wall Note double lines in B&W radar images – remainder of previous wall. References: Books: Ann Paludan, Chronicle of the Chinese Emperors. New York: Thames & Hudson Inc., 1998 Robert E. Murowchick, Cradles of Civilization – China. Normand: University of Oklahoma Press, 1994 Magazine: The Great Wall’s Ancestor, Discover (Aug. 1996) Internet: The Great Wall, www.chinavista.com/travel/greatwall/greatwall.html (2001) Viewed: 11-05-2001 Billy Chan, The Great Wall of China, www.londonccnc.ca/chinese_school/greatwall/ (2001) Viewed: 11-05-2001 Secrets of the Great Wall, www.discovery.com/stories/history/greatwall/greatwall.html (2001) Viewed: 11-05-2001 Famous Scene of the Great Wall, www.travelchinaguide.com/china_great_wall/scene/index.htm (2001) Viewed: 11-05-2001