eukaryotes
advertisement

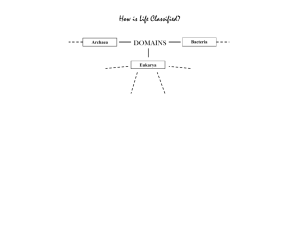
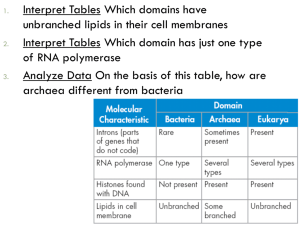
Biology Homework Police • Hand out Pamishan creatures Dichotomous Key Finishing 1.3 Main characteristics of Kingdoms • Autotrouph: an organism that obtains energy by making its own food, usually using sunlight What is an example of an autotrouph? • Heterotroph: an organism that consumes other oganisms to obtain energy. What is an example of a heterotrough? Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Cell Type Eukarya Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Prokaryote Prokaryote Cell Type Eukarya Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell Type Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell Type # of cells Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea Eukarya 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Example Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Example Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Example Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Example Nutrition Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Example Nutrition Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Example Nutrition Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs Hetertroughs Hetertroughs Example Nutrition Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs Hetertroughs Hetertroughs Example Nutrition Reproducing method Eukarya Domains & Kingdoms – the must know table 3 Domains Bacteria Archaea 6 Kingdoms Bacteria Archaea Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia Cell Type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote # of cells Unicellular Unicellular Unicellular & Multicellular Multicellular Mostly Multicellular Multicellular Example Staphylococcus Sulfolobus archaea Amoeba Maple Tree Mushroom Rabbit Nutrition Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs & Hetertroughs Autotroughs Hetertroughs Hetertroughs Asexual Asexual Asexual & sexual Sexual Sexual Sexual Reproducing method Eukarya Clarifying Domains & Kingdoms Domain Bacteria Archaea Kingdom bacteria Archaea Eukarya Protista Plantae Fungi Animalia How are the three domains different from each other? Bacteria and Archaebacteria are both prokaryotic but archaebacteria are often considered extremophiles (they can live in extremely harsh environments) Section 1.4: Classifying Types of Biodiversity • Species diversity: the variety and abundance of species in an area • Ecosystem diversity: the variety of ecosystems in the biosphere • Genetic diversity: variety of heritable characteristics (genes) in a population of interbreeding individuals • Gene Pool: genetic diversity within a population • Population: a group of individuals of the same species in a particular area and time Genetic Diversity • Does genetic diversity provide resistance to disease? • Does genetic diversity support conservation biology? Section 2.1: Classifying Types of Biodiversity Activity 1.3 Sustainability and Diversity – Find a Balance? • Complete Activity 1.3, page 33 – Procedure 1, 3. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes • The study of cells is an important step in understanding the diversity of life • Eubacteria and archaea are prokaryotes • Protists, plants, fungi and animals are eukaryotes Interactive cell models http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm 1. Examine the eukaryotic (animal and plant cell) and prokaryotic cell (bacteria cell) 2. What are some of the differences between the two types of cells? Viruses – 4 facts about them • Viruses differ from both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells • Viruses must invade cells and become functionally dependent on the workings of the host cell (what type of cells could the host be?) • Viruses are not capable of living independently outside cells • Viruses are not cellular – they have no cytoplasm, membrane-bound organelles, or cell membranes Question: do scientists consider viruses to be cells? Viruses • Virus a structure containing DNA or RNA strands surrounded by a protective protein coat; can’t live independently of cells Consequences: • Viruses can cause disease in plants and _________, which can affect ____________, species and ecosystems. Well known viruses: • ? • Did you see viruses in the classification of life? If not, is it an organism? In-class/Homework • Read page 57 • Complete Activity 2.1: Comparing Prion Diseases