What about the whole country?
advertisement

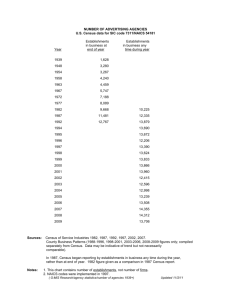
What about the whole country? Extending the Activity-Based Person-Trip Synthesizer to all 330 million Americans Judy Sun ‘14 & Luke Cheng ’14 ORF467 F13 The Process Generate Schools Generate Employee Patronage File Assign Patronage Generate Patronage-Employee Ratios A Look at the Data Generate Census File (with Microsoft Access) NN Files through 7 NJ Modules by Jake and Talal Trip File Generator: Out-of-State commuters, students, workplace assignment, 18 Tour Type (Activity Patterns) assignment, Temporal Dimension Roadmap Schools Data Employee-Patronage Data A Look at the Data Census Data Further Steps Schools Data Public Schools in the US Quick stats on Public Schools (2011) 60,000 Number of Schools in US 50,000 40,000 PUBLIC 30,000 CHARTER 20,000 10,000 Primary School Type Primary Middle High Other No Answer Total Middle # of CHARTER 2,584 615 1,316 1,145 564 6,224 High Other # of PUBLIC 51,793 16,332 19,762 5,847 3,525 97,259 No Answer Total 54,377 16,947 21,078 6,992 4,089 103,483 Public Schools: Enrollment 30,000,000 25,000,000 20,000,000 PUBLIC 15,000,000 CHARTER 10,000,000 5,000,000 - Primary School Type Primary Middle High Other No Answer Total Middle CHARTER High Other PUBLIC 896,544 166,519 368,109 626,562 (1,128) 2,056,606 No Answer Total 23,226,606 9,425,155 13,767,489 1,289,050 (7,016) 47,701,284 24,123,150 9,591,674 14,135,598 1,915,612 (8,144) 49,757,890 Private Schools in the US 20,000 18,000 Number of Schools in US 16,000 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 Primary Type Primary Secondary Combined Total Secondary Number of Schools 18,400 2,517 7,300 28,217 Combined Private Schools: Enrollment # students 2,500,000 2,000,000 1,500,000 1,000,000 500,000 Primary Secondary Type Primary Secondary Combined Total Combined # students 2,134,007 738,600 1,431,252 4,303,859 Private Schools: School Size 600 Numer of Schools 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 School Size (number of students) 1400 1600 1800 2000 Post-secondary schools (2009) Number of Schools 3,000 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 500 - Graduate Primarily Baccalaureate Primarily Non-Bacc Associate's Nondegree-granting postbac Nondegree-granting pre-bac Institution type # of Students Enrolled # of students as percent total Number of Schools Graduate 291 0% Primarily Baccalaureate 1,483,018 93% Primarily Non-Bacc 53,903 3% Associate's 49,263 3% Nondegree-granting postbac 17 0% Nondegree-granting pre-bac 10,960 1% Total 1,597,452 100% 350 2,169 623 1,745 14 2,698 7,735 Employee-Patronage Data The Process 2012 InfoGroup US Businesses File (5.80 GB) 30 CSV files with 500,000 entries (~200MB) – Shell Script 30 CSV files with patronage generation and data cleaning and mapping (~115MB) – R Script 1570 Segmented State Files (1KB to 20MB) – R Script 51 Merged State Files (8MB to 390MB) – Python Script Patronage Generation Previous Process – Manual Fine-Tuning Inconsistent: Same NAICS Code, Different Patronage/Employee Ratio Current Process – Employee Size Range, Sales Volume Range Not Perfect Data Matching businesses (Zip, County, NAICS, Latt/Long) Same Employee Size Range Assumption: Sales Volume same across time Trying to acquire the 2005 Data for better correlations Ratios from Averaging Previous EP file Comparison: Distributions Conclusion: Need to use NAICS Codes, in addition A large number of 0-1 ratio values are offset by the 7-20. Therefore, we get a surge averages of around 4-5. Difficult to capture nuances with just employee size and sales volume. Next Steps: Man-Power needed to assign ratio for each NAICS Code, Sales Volume, Employee Size combination A Look at the Data NJ Counties (Change in NJ EP File) Uncensored Un-Named Removed NJ Wide Uncensored Un-named Removed No Businesses +73,500 No Businesses +39,350 Tot Emp +4.8M Tot Emp +4.8M Emp Size +7.85 Emp Size +9.09 Tot Patrons -4.9M Tot Patrons -5.3M Avg Patrons -17.17 Avg Patrons -16.29 Nation-Wide Sales Volume No. Businesses Total Employees Avg Employee Size Total Patrons Average Patrons Rank State 1 California $1,889 1,579,342 23,518,022 14.89 36,820,129 23.31 2 Texas $2,115 999,331 17,624,235 17.64 24,846,695 24.86 3 Florida $1,702 895,586 12,331,524 13.77 21,231,864 23.71 4 New York $1,822 837,773 18,327,933 21.88 19,610,813 23.41 5 Pennsylvania $2,134 550,678 10,498,442 19.06 13,704,903 24.89 9 New Jersey $1,919 428,596 8,833,890 20.61 9,986,529 23.30 45 Washington DC $1,317 49,488 5,702,617 115.23 1,067,938 21.58 47 Rhode Island $1,814 46,503 1,117,140 24.02 1,201,124 25.83 48 North Dakota $1,978 44,518 492,547 11.06 1,021,077 22.94 49 Delaware $2,108 41,296 670,622 16.24 1,011,400 24.49 50 Vermont $1,554 39,230 379,291 9.67 821,193 20.93 51 Wyoming $1,679 35,881 340,342 9.49 772,090 21.52 Census Data Inputs 2010 Census Summary File 1 http://www2.census.gov/census_2010/04-Summary_File_1/ Does not convert to CSV/TXT; Files made for MS Access Process Tables (P12, P16, P29, H13, P43) with Talal’s VBA macro in MS Access (p.78) VBA Code – whereabouts unknown, perhaps with Prof K 2012 5-Year Census American Community Survey http://www2.census.gov/acs2012_5yr/summaryfile/ Income Data to assign incomes to households and residents Generation Module 1 – Outputs resident file for each county in state Rows: Individual People Attributes/Columns: County Number (replace with State Number_County Number for national file), Household ID, Household Type, Latt/Long, ID Number, Age, Sex, Traveler Type, Income Bracket Module 2 – Out of state/region/nation nodes For commenting on code, go to p.17-19 http://www.princeton.edu/~alaink/Orf467F12/MuftiTripSynth esizer_v.1.pdf Further Steps What To Do Next? Patronage Generation with NAICS, Sales Volume, Employee Size and Research – Low Difficulty I already generated a file mapping all NAICS and employment counts along with payrolls for patronage assignment using 2010 Census Data (200K entries) Census Data Generation and Rework NN Generation Modules – High Difficulty Optional: Data Verification for Employee-Patronage Files Modules Very hard-coded for NJ; not very well-commented Initial National Implementation Ideas: Treat US as one entity with external nodes at airports to represent foreigners Problem: Computationally intensive for 330M people Solution: Do a semi-randomized sample Regionalize the US and use out-of-region external nodes Less labor-intensive and parallel processing Doing each state Problem: Hard to generalize code, out-of-state nodes Extremely labor-intensive The Code: Thought Process Trips generated state-by-state Use state-level demographic information on residents Ignore state-level boundaries since we have employer and attraction information for the nation. Example: John Smith lives in NYC and works in CT. We will get his household from NYC Census file and the probability distribution of workplace in CT E-P file. When we map NYC Trips, we will see John Smith going to CT for work. When we map CT Trips, we will see John Smith returning from work. Trip destinations can be approximated using destination county centroids Requires assigning centroid to each county The Code: Thought Process Workplace assignment (without replacement): Census maps individuals to workplace John Smith lives in NYC and works in CT Use distribution to match workplace to E-P file (keep a count of employees to match the number given) John Smith mapped to an employer in CT If more than x (e.g. 250) miles, assume arrival at airport School Assignment (without replacement): Use bounds and distribution to match students with schools (assume same county) Jane (8) is mapped to elementary school in her county The Code: Thought Process Tour Type assignment and Temporal Dimension Can try to repurpose Talal’s code Add in Time Zones in Temporal Dimension Can do this with replacement (patrons) Assumptions: Same behavior across states in terms of work time and leisure time and activity patterns Out-of-Country Commuters / Non-Resident Workers International nodes for the states along the Canadian and Mexican borders Trip to the nearest border crossing