Firewalls and Info Services
advertisement
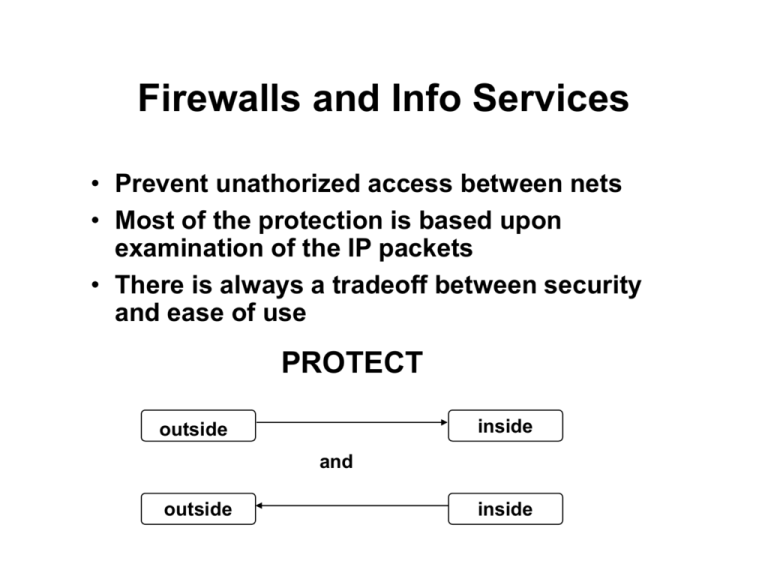
Firewalls and Info Services • Prevent unathorized access between nets • Most of the protection is based upon examination of the IP packets • There is always a tradeoff between security and ease of use PROTECT inside outside and outside inside Primary Types of Firewalls Dual-Homed Gateway Internet bastion host Inner Network Screened Host Gateway Internet Inner Network router screened host Dual-Homed Gateway Internet Inner Network bastion host passes through no agent ftp proxy X ftp request telnet request • Any data wanting to pass through to/from the bastion host should be required to pass through a PROXY agent. • Proxy software can be configured to use encryption. • Clients may need to be replaced with proxy clients Screened Host Gateway Internet router Inner Network screened host Router for other nodes X not allowed for bastion host passes through Inner Network Screened Host • Only data allowed through is data for the screened host • Router can allow holes to certain hosts on inner net. • Router uses IP addresses and port numbers to control the flow of data Some Risks • Once you allow holes in the router, the nodes to which you allow “extra” access increase your ZONE OF RISK. • Those machines need to be as secure as your screened/bastion host or represent your weak link. • The larger the program, the more susceptible to errors and security leaks. – Browsers are good examples of large programs Two Other Types of Firewalls Screening Router Internet router router Inner Network bastion host Router-only Gateway Internet router Inner Network Planning Steps • Know the details of how client-server connections are made • Determine physical location of equipment • Decide who gets access in either direction – Screening router is on basis of IP/port not user • Determine a strategy for logging activity – What to write – How to monitor – Under what conditions do you take specific actions • Must develop a failure plan if firewall breaks • Develop a thorough testing procedure Software for Firewall Support Cern WEB server • Proxy mode to handle requests for internal clients • Handles http AND OTHER PROTOCOLS – browser clients usually handle other protocols NOT SERVERS • Requires the client to be configurable to use proxy mode. Not sure how common the is in the client p.504 of text setenv http_proxy “http://web.bastion.host:80/” setenv ftp_proxy “http://web.bastion.host:80/” • What if the client doesn’t go through the WEB server? – bastion serves as a router of sorts and doesn’t let any other data through – router will deny passge if not through the screened host • Has caching features so only one copy needed for entire inner net Software for Firewall Support SOCKS • Freeware running on bastion host • Presumably configures the bastion to do filtering of data passing through • SOCKS is a proxy server dealing with TCP streams, not client dependent • The specific client must be written to be SOCKsified • SOCKsified versions are available for PCs and unix environments • Check it out at ftp.nec.com Software for Firewall Support Firewall Toolkit • tn-gw, ftp-gw, plug-gw(socket to socket) • Does NOT requires a special client • Client must RUN the program differently instead of: you must: telnet remotehost tn-gw tn-gw>connect remotehost OTHER FEATURES • “netacl” can be used with inetd.conf to check server requests against an access list first • A scaled down ftp to allow anonymous ftp to the bastion and to proxy other requests Where does the server go? WWW • Dual homed gateway – Outside the firewall » may be difficult to connect at service entry » sacrificial lamb – On bastion host » software is avialable » if server cracked, the whole inner net is vulnerable – Behind the firewall » internal access is easy / external access is difficult » needs a socksified browser – One inside and one outside » inside company confidential » outside for public info Where does the server go? WWW • Screened host – Outside firewall (as before) – On screened host segment » router only sends outside requests to a SPECIFIC port on the server – On the Screened Host itself » It controls too much access in and out Preferred • With a screened subnet – On the screened subnet » SECOND ROUTER ONLY ALLOWS ACCESS FROM THE server/port TO THE INSIDE » if server cracked, can’t get inside Where does the server go? FTP • Connections are initiated from both directions SERVER CLIENT connects to port 21 (command channel) time NET connects from port 20 (data channel) get “file” Where does the server go? FTP • Dual Homed Gateway – Possible to have your service provider handle it » the ftp clients would require the provider agent to proxy ftp – Suggest putting it on the bastion host » ftp to chroot() ed area of the disk » run daemon as a non-priviledged user • Screened host – Preferred to be inside... preferred with screened subnet – run ftp server in proxy mode – if possible, run clients in proxy (PASV) mode so client creates both end of the connection – router allows IN->OUT not OUT->IN, no inward server connections – router allows incoming on 21 and outgoing on 20 Safeguards for internal servers • Strip inner network priviledges – hostp.equiv and .rhosts • Internal machines should NOT trust server • Strip the server of networking clients – telnet, ftp, rlogin, rsh, etc. • NFS & NIS should be disabled • Kernel should not route IP packets • Disable all services in inetd.conf which do not support the service • USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH SCREENED SUBNET, THESE DO THE BEST JOB Other things to do for Protection • Leave traps for attackers – If hackers gain access to your server, they will try to access other machines by clients like telnet, rsh, etc – Change the client to look like it has errors and use it to mail the sys admin that a problem exists » error messages and delays to occupy attacker • Periodically run software to verify the integrity of your system. – Store files with encryption signatures – Files which are public relations (or more) for your business should be protected. – This way you verify no one has misrepresented you • Run servers in a chroot()ed area – Should do this anyway Helping clients access through the firewall TELNET • Always on port 23 • Screened host – an access list in the router can typically be configured to allow outgoing on port 23 • Dual Homed – use a proxy – use socks – use firewall toolkit Helping clients access through the firewall ARCHIE • Interesting because it uses UDP not TCP – The routers look at acceptable connections by looking at the CONNECT sequence – UDP does not do connections to consider acceptable data (don’t know who started it) • So how do you know whether your archie server is ok? • Special solution: only a limited (about 20) Archie servers on the net. Set router to accept from any of them • DH Gateway use a proxy – must also proxy ftp since archie uses ftp Helping clients access through the firewall Web clients • Web clients must access lots of types of servers • Easiest solution is to use cern web server and let it proxy for you • Otherwise must provide individual proxies • Routers allowing messages from inside to out solves the problem for most... not for ftp. PCs • Screened hosts can use holes in router ... • Some ftps support PASV mode so that it can be used with a screened host • For Dual Homed Gateway, use SOCKS • SOCKS is available for pc software • DLLs are (being made) available for a SOCKsified version of winsock.dll






