Computer Anatomy - Eleanor Roosevelt High School
advertisement

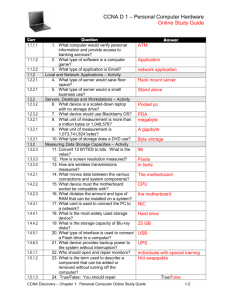
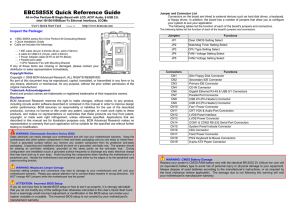
Computer Anatomy Chin-Sung Lin Eleanor Roosevelt High School The Visible Part: Computer Hardware What is a Computer? Main Memory Input Microprocessor Storage Output What is a Computer? What is a Computer? System Unit Motherboard Back Panel Interface PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connectors PS/2 Mouse PS/2 Keyboard Audio Connectors Line In Audio Out Microphone In VGA Connectors HDMI Connectors USB and Ethernet Connectors Ethernet USB Serial and Parallel Ports 25-pin Parallel Port 9-pin Serial Port ATX Connector IDE (PATA) Connector SATA Connector Advanced Graphics Port (AGP) PCI Slot Motherboard Interface Motherboard Processor Processor Central Processing Unit (CPU) Select A B Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Central Processing Unit (CPU) Select A B Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Motherboard Chipset Motherboard Chipset Cache Memory Level 2 Cache Memory Memory Hierarchy Memory Hierarchy Memory 72-pin SIMM (Single Inline Memory Module) 168-pin DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) Hard Drive Hard Drive Capacity Hard Drive Capacity Solid State Drive (SSD) Power Supply Unit Motherboard The Invisible Part: Computer Software Software Layer Structure Operating System Desktop Operating System Mobile Operating System Types of Operating Systems Single-user, single-tasking Single-user, multi-tasking Multi-user, multi-tasking Real-time operating system Single-User Single-Tasking Single user can effectively do one thing at a time. Also know as Embedded operating systems. Used in personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones. Single-User Multi-Tasking Typical desktop and laptop operating systems such as Windows and Mac OS. Single user can run several programs at the same time. Multi-User Multi-Tasking A multi-user operating system simultaneously allows many different users (hundreds or even thousands) to take advantage of the computer's resources. Unix, MVS, VMS are examples. Real-Time OS (RTOS) The fastest OS which are used in time-critical environments/applications. Control machinery, scientific instruments, industrial systems, sophisticated medical equipment, airport traffic, space flights and high speed aircraft. Operating System Operating System Functions of Operating Systems System Bootup Application Program Loading Hardware Resource Management Memory Management File System Management Security User Interface Future Technology Mobile Computing Cloud Computing Neuromorphic Chips Quantum Computer Q&A