Strategy Implementation: Internal Control and Performance
advertisement

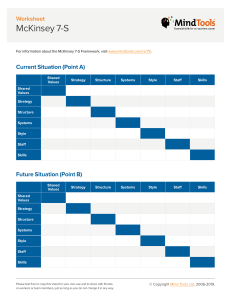
Strategy Implementation: Internal Control and Performance Chapter 12 Strategic Management:Value Creation, Sustainability, and Performance, 3e, 2014 Learning Objectives 1. Translate strategy into functional goals and activities. 2. Develop effective metrics for control and growth. 3. Different models for implementation and control. 4. Strategic leadership core responsibilities. 5 Keys to Implementation & Control Fit Strategy, structure, value chain, resources Clear and compelling objectives Relevance to employees at their levels Single currency Uniform incentive system applied to all Top management involvement Demonstrates importance & commitment Resource allocation Matched to goals & supports incentives Strategic Metrics Tied to vision, mission, overall corporate objectives Translated down to all levels and value chain activities All departments / functions included Appropriate for the level within the function Include quantitative & qualitative measures Can be used as part of a uniform incentive system Metrics Provide Feedback, Create Learning Expected Effect A Activities Actual Effect B A is expected, but B occurs Next steps Diagnose if more of activities is needed, or Change activities Three Implementation Models Balanced Scorecard Model Value-Driver-Action Model McKinsey 7-S Framework Balanced Scorecard Driven by strategy All activities and metrics consistent with strategic approach Develops "cause-and-effect logic" across four levels of the organization Requires developing "lead" and "lag" performance metrics for each level Consistent with Value Chain focus on activities Cause and Effect Logic Actions and performance in each level contribute to and enable the next level Develop Lead and Lag Metrics Lead – measure activities performed Lag – measure results of activities Discount Airline Example • Work from the bottom up • Success in each level enables the next level of performance Value-Action-Driver Model Focuses on value creation efforts Easier to implement vs. Balanced Scorecard Draws upon Key Success Factors (industry analysis) Extraordinary Resource positions Vision and mission Value-Action-Driver Model Steps 1. Identify key value drivers. 2. Outline desired stakeholder experience for each value driver dimension. 3. Translate stakeholder experience to business / market position. 4. Identify actions to take to achieve position. 5. Develop metrics to assess progress toward position. Ford Inc. Example Value Driver Consumer Economic Value Desired Stakeholder Experience Translation to Position 1. Getting most "bang for the buck." • Develop classic, popular designs to ensure high retained value. 2. "Buying is no haggling, straightforward." • List price = sales price. • No haggle sales process. 3. "Get a great price when I sell my Ford." • Reduce cost structure to best in class. Ford Inc. Example Translation to Position Actions to Take Metrics • Develop classic, popular designs to ensure high retained value. • Revamp designs where needed. • Consumer choice awards for design, performance, and value. • List price = sales price. • No haggle sales process. • Change sales process and sales incentive structure. • Cash rebates usage lowest in industry. • Average list price discounts lowest in industry. • Reduce cost structure to • Reduce excessive best in class. overhead costs in management and production. • Production unit cost/model lowest compared to peer group. McKinsey 7-S Framework Popular model dating from 1970s. Focuses on alignment and fit across the organization. Seven S's "Hard" 3 – easier to identify "Soft" 3 – more difficult to pin down exactly Centered around "Shared Values & Goals" McKinsey 7-S Framework McKinsey 7-S Framework Shared Values & Goals Embodied in Vision, Mission, Principles Strategy Value chain, resources, type of strategic approach Structure Core capabilities & related training / learning How structures help coordinate & organize Systems Alignment of systems to support strategy & structure Skills Style Culture & how it supports the type of work done Staff Onboarding process & continuity of support Strategic Leadership Establish and extol vision, mission, principles, goals Establish code of ethics Build senior management team Establish structure for communication, coordination, control Establish culture and match leadership style Ensure process exists to recognize new opportunities Rational decision making Motivation through style, and incentives