Types of Business Competition
advertisement

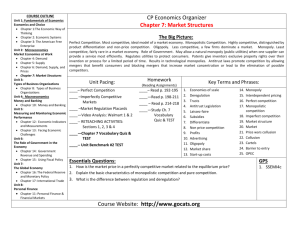
Unit 2 Economics (w/ Supply & Demand) TYPES OF BUSINESS COMPETITION PERFECT COMPETITION many sellers of identical products businesses have no control over price and it is easy for new businesses to enter the competition the only real way to attract business is friendly service and location or first come first serve examples include hay, corn, stocks PERFECT COMPETITION items sell for equilibrium price and businesses are price takers consumers control the market and demand dominates information about the products is known by all; this includes other businesses and consumers MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION many sellers of slightly different products businesses have little control over price and it is easy for new businesses to enter the competition the way to attract business is advertisement examples include jeans, tennis shoes, resturants MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION Broad price range for items in the same category selling point is dependent and focused on product differences Trying to become a monopoly OLIGOPOLY 3-5 major sellers of slightly different products businesses have some control over price and it is hard for new businesses to enter the competition the way to attract business is branding (attaching customer loyalty to your name) examples include candy, soda, cereal, cars OLIGOPOLY few sellers take in 80% of the revenue for the industry businesses will try to block out competition by offering lower prices or through legal tie ups businesses tend to copy or follow what all the others do in product and pricing; they are interdependent MONOPOLY one seller of a unique product businesses have almost total control over price; it is very hard for new businesses to enter the way to attract business is sell an item that is or seems inelastic (necessary) examples include electricity, water, diamonds MONOPOLY price can go up until people are unable to pay at all illegal in most developed countries, including the U.S. because it stops competition which causes prices to go up and quality to decrease MONOPOLY FORMATION Type 1: patent or copyright - last for the short term as you control the idea; most people sell their idea due to an inability to implement because they do not have the infrastructure Type 2: own all the resources, example is De Beers (own all the diamond mines in the world) Type 3: economy of scale – scope of business is so large that more than one business is not sustainable, example is electric plant, these are government regulated Monopoly Problems • Monopolies are bad because they cause: ▫ higher prices ▫ lower quality ▫ less variety Anti-Trust Laws • created to protect consumers by encouraging competition and choice Sherman Act (1893) • the first law against the formation of monopolies • Vague – hard to enforce • significant as the first move against the monopoly power Clayton Act (1914) • made specific practices illegal: ▫ Interlocking Directory: person cannot sit on board of directors of competing companies (Ex: Ford and GM) ▫ Price Discrimination: all people charged same price for same product ▫ Price Cutting: large corporation cannot sell at below norm prices to drive the small business out ▫ Tying Contract: to buy one product you must buy another item with it (Ex: mattress and bed frame) Mergers • 2 or more companies combine into one larger company • another way companies can become monopoly like • mergers of very large companies must be approved by the government (Federal Trade Commission) to ensure competition Types of Mergers • Horizontal Merger: 2 or more companies of the same type combine (Ex: AT&T and Cingular) • Vertical Merger: combo of companies in the same supply chain (Ex: publisher buying a paper company) • Conglomerate: combo of many different types of companies (Ex: Johnson & Johnson who own drug companies, equipment companies, baby products, food) CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING 1) 2) 3) 4) As the number of sellers drops price control increases. True or False Which two types of competition have non-price competition? What is one similarity between perfect competition and monopolistic competition? What is one difference between an oligopoly and monopolistic competition? CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING 1) 2) 3) 4) A monopoly can set any price it wants to, but at some point they will begin to lose money. True or False What is one problem consumers face when a store has a monopoly? In which type of competition do prices go to equilibrium always? In which type of competition do the sellers copy each other in style and pricing?